Let’s talk about Go’s goroutine and Channel
Recommended related articles: "Talk about concurrent programming in Go (1)"
1. Use channel to wait for the task to end
package mainimport ( "fmt" "time")func createWorker(id int) chan
package mainimport (
"fmt")type worker struct {
in chan int
done chan bool}func createWorker(id int) worker {
w := worker{
in: make(chan int),
done: make(chan bool),
}
go doWorker(id, w.in, w.done)
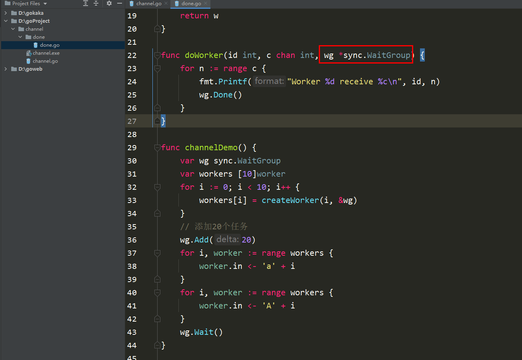
return w}func doWorker(id int, c chan int, done chan bool) {
for n := range c {
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %c\n", id, n)
done package mainimport (
"fmt")type worker struct {
in chan int
done chan bool}func createWorker(id int) worker {
w := worker{
in: make(chan int),
done: make(chan bool),
}
go doWorker(id, w.in, w.done)
return w}func doWorker(id int, c chan int, done chan bool) {
for n := range c {
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %c\n", id, n)
done package mainimport (
"fmt"
"sync")type worker struct {
in chan int
wg *sync.WaitGroup}func createWorker(id int, wg *sync.WaitGroup) worker {
w := worker{
in: make(chan int),
wg: wg,
}
go doWorker(id, w.in, wg)
return w}func doWorker(id int, c chan int, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
for n := range c {
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %c\n", id, n)
wg.Done()
}}func channelDemo() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup var workers [10]worker for i := 0; i package mainimport (
"fmt"
"sync")type worker struct {
in chan int
done func()}func createWorker(id int, wg *sync.WaitGroup) worker {
w := worker{
in: make(chan int),
done: func() {
wg.Done()
},
}
go doWorker(id, w)
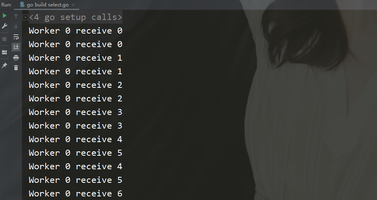
return w}func doWorker(id int, w worker) {
for n := range w.in {
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %c\n", id, n)
w.done()
}}func channelDemo() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup var workers [10]worker for i := 0; i package mainimport (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time")func generator() chan int {
out := make(chan int)
go func() {
i := 0
for {
// 随机睡眠1500毫秒以内
time.Sleep(
time.Duration(rand.Intn(1500)) *
time.Millisecond)
// 往out这个channel发送i值
out package mainimport (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time")func worker(id int, c chan int) {
for n := range c {
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %d\n", id, n)
}}func createWorker(id int) chanpackage mainimport (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time")func worker(id int, c chan int) {
for n := range c {
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %d\n", id, n)
}}func createWorker(id int) chanpackage mainimport (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time")func worker(id int, c chan int) {
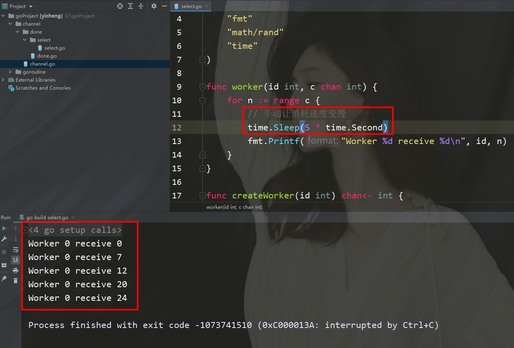
for n := range c {
// 手动让消耗速度变慢
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %d\n", id, n)
}}func createWorker(id int) chan 0 {
activeWorker = worker // 取出索引为0的值
activeValue = values[0]
}
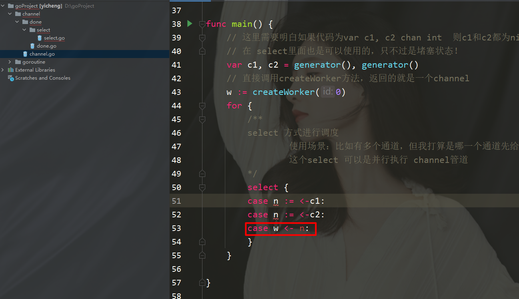
/**
select 方式进行调度
使用场景:比如有多个通道,但我打算是哪一个通道先给我数据,我就先执行谁
这个select 可以是并行执行 channel管道
*/
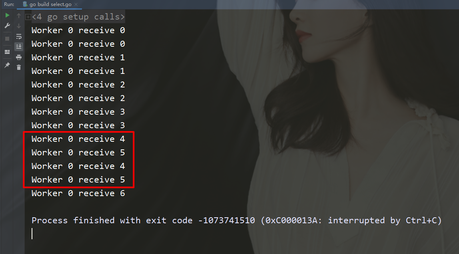
select {
case n := package mainimport (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time")func worker(id int, c chan int) {
for n := range c {
// 手动让消耗速度变慢
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %d\n", id, n)
}}func createWorker(id int) chan 0 {
activeWorker = worker // 取出索引为0的值
activeValue = values[0]
}
/**
select 方式进行调度
使用场景:比如有多个通道,但我打算是哪一个通道先给我数据,我就先执行谁
这个select 可以是并行执行 channel管道
*/
select {
case n := package mainimport (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time")func worker(id int, c chan int) {
for n := range c {
// 手动让消耗速度变慢
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Printf("Worker %d receive %d\n", id, n)
}}func createWorker(id int) chan 0 {
activeWorker = worker // 取出索引为0的值
activeValue = values[0]
}
/**
select 方式进行调度
使用场景:比如有多个通道,但我打算是哪一个通道先给我数据,我就先执行谁
这个select 可以是并行执行 channel管道
*/
select {
case n := The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about concurrent programming in Go (2). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 go语言有没有缩进Dec 01, 2022 pm 06:54 PM
go语言有没有缩进Dec 01, 2022 pm 06:54 PMgo语言有缩进。在go语言中,缩进直接使用gofmt工具格式化即可(gofmt使用tab进行缩进);gofmt工具会以标准样式的缩进和垂直对齐方式对源代码进行格式化,甚至必要情况下注释也会重新格式化。
 一文浅析Golang中的闭包Nov 21, 2022 pm 08:36 PM
一文浅析Golang中的闭包Nov 21, 2022 pm 08:36 PM闭包(closure)是一个函数以及其捆绑的周边环境状态(lexical environment,词法环境)的引用的组合。 换而言之,闭包让开发者可以从内部函数访问外部函数的作用域。 闭包会随着函数的创建而被同时创建。
 聊聊Golang中的几种常用基本数据类型Jun 30, 2022 am 11:34 AM
聊聊Golang中的几种常用基本数据类型Jun 30, 2022 am 11:34 AM本篇文章带大家了解一下golang 的几种常用的基本数据类型,如整型,浮点型,字符,字符串,布尔型等,并介绍了一些常用的类型转换操作。
 go语言为什么叫goNov 28, 2022 pm 06:19 PM
go语言为什么叫goNov 28, 2022 pm 06:19 PMgo语言叫go的原因:想表达这门语言的运行速度、开发速度、学习速度(develop)都像gopher一样快。gopher是一种生活在加拿大的小动物,go的吉祥物就是这个小动物,它的中文名叫做囊地鼠,它们最大的特点就是挖洞速度特别快,当然可能不止是挖洞啦。
 tidb是go语言么Dec 02, 2022 pm 06:24 PM
tidb是go语言么Dec 02, 2022 pm 06:24 PM是,TiDB采用go语言编写。TiDB是一个分布式NewSQL数据库;它支持水平弹性扩展、ACID事务、标准SQL、MySQL语法和MySQL协议,具有数据强一致的高可用特性。TiDB架构中的PD储存了集群的元信息,如key在哪个TiKV节点;PD还负责集群的负载均衡以及数据分片等。PD通过内嵌etcd来支持数据分布和容错;PD采用go语言编写。
 聊聊Golang自带的HttpClient超时机制Nov 18, 2022 pm 08:25 PM
聊聊Golang自带的HttpClient超时机制Nov 18, 2022 pm 08:25 PM在写 Go 的过程中经常对比这两种语言的特性,踩了不少坑,也发现了不少有意思的地方,下面本篇就来聊聊 Go 自带的 HttpClient 的超时机制,希望对大家有所帮助。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment