Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Introducing advanced MySQL database SQL statements
Introducing advanced MySQL database SQL statements
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2021-02-19 09:26:242288browse

Free learning recommendation: mysql tutorial(Video )
1. Preparation work
1. Install MySQL database
Shell script with one click Deployment - source code compilation and installation of MySQL
2. Experiment preparation, data table configuration
mysql -uroot -p
show databases;
create database train_ticket;
use train_ticket;
create table REGION(region varchar(10),site varchar(20));
create table FARE(site varchar(20),money int(10),date varchar(15));
desc REGION;
desc FARE;
insert into REGION values ('south','changsha');
insert into REGION values ('south','nanchang');
insert into REGION values ('north','beijing');
insert into REGION values ('north','tianjin');
insert into FARE values ('changsha',1000,'2021-01-30');
insert into FARE values ('nanchang',700,'2021-01-30');
insert into FARE values ('beijing',1500,'2021-01-30');
insert into FARE values ('tianjin',1200,'2021-01-30');
insert into FARE values ('beijing',2200,'2021-02-05');
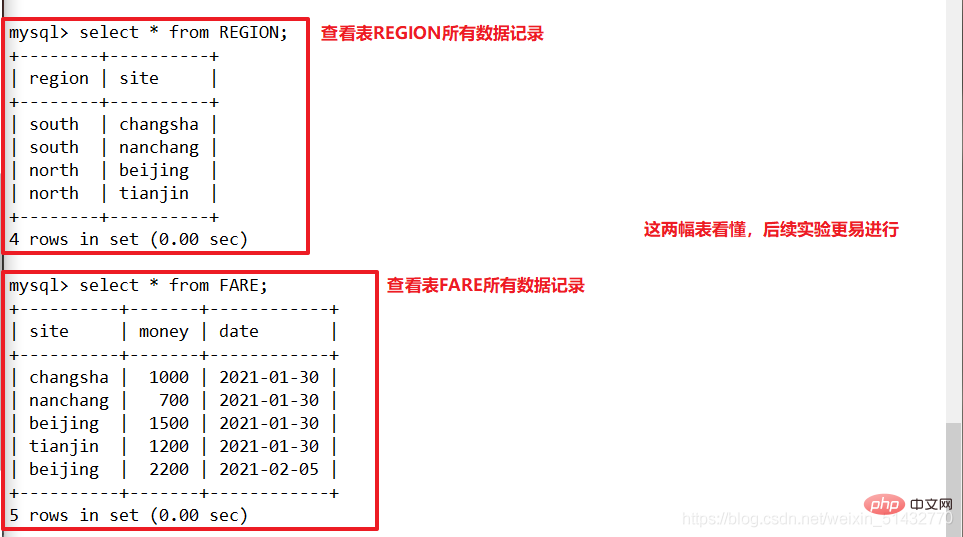
select * from REGION;
select * from FARE;

2. MySQL Advanced (Advanced) SQL Statement
1. SELECT
Displays all the data in one or several fields in the table
Syntax: SELECT field FROM table name
select region from REGION;
2, DISTINCT
Do not display duplicate data (remove duplication)
Syntax: SELECT DISTINCT field FROM table name
select distinct region from REGION;
3, WHERE
Conditional query
Syntax: SELECT field FROM Table name WHERE condition
select site from FARE where money > 1000;
select site from FARE where money <p><strong>4, AND, OR</strong></p><p><strong>and (and), or (or) </strong><br> Syntax: SELECT field FROM table name WHERE condition 1 ([AND|OR] condition 2); </p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">select site from FARE where money > 1000 and (money = 700);
select site,money,date from FARE where money >= 500 and (date <p><strong>5, IN</strong></p><p><strong>Display information of known values</strong><br> Syntax: SELECT field FROM table name WHERE field IN ('value 1', 'value 2',...); </p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">select site,money from FARE where money in (700,1000);6, BETWEEN
Display data within two value ranges
Syntax: SELECT field FROM table name WHERE field BETWEEN 'value one' and 'value two';
select * from FARE where money between 500 and 1000;
7, Wildcard, LIKE
Usually wildcard characters are used together with LIKE
%: The percent sign represents zero, one or more characters
_: Underscore represents a single character
LIKE: used to match patterns to find information
Syntax: SELECT field FROM table name WHERE field LIKE 'pattern';
select * from FARE where site like 'be%'; select site,money from FARE where site like '%jin_';
8, ORDER BY
Sort by keyword
Syntax: SELECT field FROM table name [WHERE condition] ORDER BY field [ASC,DESC];
#ASC: Sort in ascending order, the default sorting method
#DESC: Sort in descending order
select * from FARE order by money desc; select date,money from FARE order by money desc;
Function
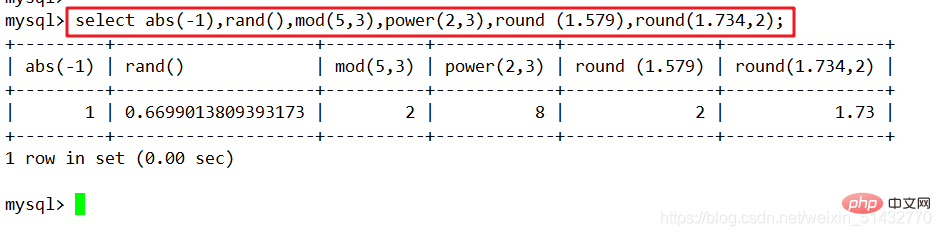
1. Mathematical function
| abs(x) | Returns the absolute value of x |
|---|---|
| rand() | Returns a random number from 0 to 1 |
| mod(x,y) | Returns the remainder after dividing x by y |
| power(x,y) | Returns x raised to the power of y |
| round(x) | Return the nearest integer to x |
| round(x,y) | Retain y decimal places of x Rounded value |
| sqrt(x) | Returns the square root of x |
| truncate(x,y) | Returns the value of the number x truncated to y decimal places |
| ceil(x) | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to x |
| floor(x) | Return the largest integer less than or equal to x |
| Return The largest value in the set | |
| Returns the smallest value in the set |
select sqrt(9),truncate(1.234,2),ceil(1.2),floor(1.9),greatest(1,2,3,4),least(1,2,3,4);

2. Aggregation function
| Return the average value of the specified column | |
|---|---|
| Return the number of non-NULL values in the specified column | |
| Returns the minimum value of the specified column | |
| Returns the minimum value of the specified column Maximum value | |
| Returns the sum of all values in the specified column |
| trim() | 返回去除指定格式的值 |
|---|---|
| concat(x,y) | 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串 |
| substr(x,y) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同 |
| substr(x,y,z) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串 |
| length(x) | 返回字符串 x 的长度 |
| replace(x,y,z) | 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y |
| upper(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母 |
| lower(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母 |
| left(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符 |
| right(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符 |
| repeat(x,y) | 将字符串 x 重复 y 次 |
| space(x) | 返回 x 个空格 |
| strcmp(x,y) | 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1 |
| reverse(x) | 将字符串 x 反转 |
SELECT TRIM ([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] FROM ] 字符串);
#[位置]:的值可以为 LEADING (起头), TRAILING (结尾), BOTH (起头及结尾)。
#[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。
select trim(leading 'na' from 'nanchang');
select trim(trailing '--' from 'nanchang--');
select trim(both '--' from '--nanchang--');
select concat(region,site) from REGION where region = 'south';
select concat(region,' ',site) from REGION where region = 'south';
select substr(money,1,2) from FARE;
select length(site) from FARE;
select replace(site,'ji','--') from FARE;
select upper(site) from FARE;
select lower('HAHAHA');
select left(site,2) from FARE;
select right(site,3) from FARE;
select repeat(site,2) from FARE;
select space(2);
select strcmp(100,200);
select reverse(site) from FARE;
4、| | 连接符
如果sql_mode开启开启了PIPES_AS_CONCAT,"||"视为字符串的连接操作符而非或运算符,和字符串的拼接函数Concat相类似,这和Oracle数据库使用方法一样的
mysql -uroot -p use train_ticket; select region || ' ' || site from REGION where region = 'north'; select site || ' ' || money || ' ' || date from FARE;
5、GROUP BY
BY后面的栏位的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的
GROUP BY 有一个原则,就是 SELECT 后面的所有列中,没有使用聚合函数的列,必须出现在GROUP BY后面。
语法:SELECT 字段1,SUM(字段2) FROM 表名 GROUP BY 字段1;
select site,sum(money) from FARE group by site; select site,sum(money),date from FARE group by site order by money desc; select site,count(money),sum(money),date from FARE group by site order by money desc;
6、HAVING
用来过滤由GROUP BY语句返回的记录集,通常与GROUP BY语句联合使用。
HAVING语句的存在弥补了WHERE关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。如果被SELECT的只有函数栏,那就不需要GROUP BY子句。
语法:SELECT 字段1,SUM(字段2) FROM 表名 GROUP BY 字段1 HAVING(函数条件);
select site,count(money),sum(money),date from FARE group by site having sum(money) >=700;
7、别名
字段别名、表格别名
语法:SELECT “表格別名”.“字段1” [AS] “字段1別名” FROM “表格名” [AS] “表格別名”;
select RE.region AS reg, count(site) from REGION AS RE group by reg; select FA.site AS si,sum(money),count(money),date AS da from FARE AS FA group by si;
8、子查询
连接表格,在WHERE 子句或HAVING 子句中插入另一个SQL 语句
语法:SELECT 字段1 FROM 表格1 WHERE 字段2 [比较运算符] (SELECT 字段1 FROM 表格2 WHERE 条件)
可以是符号的运算符
例:=、>、=、
也可以是文字的运算符
例:LIKE、IN、BETWEEN
select A.site,region from REGION AS A where A.site in(select B.site from FARE AS B where money<blockquote><p><strong>相关免费推荐:<a href="https://www.php.cn/sql/" target="_blank">SQL教程</a></strong></p></blockquote>
The above is the detailed content of Introducing advanced MySQL database SQL statements. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!