Mysql Video Tutorial column introduces InnoDB’s insertion buffer.

The InnoDB engine has several key features that bring better performance and reliability:
- Insert Buffer )
- Double Write
- Adaptive Hash Index
- Async IO
- Refresh adjacency Page (Flush Neighbor Page)
Today our topic is Insert Buffer (Insert Buffer) , because the underlying data of the InnoDB engine is stored in a structured B-tree, and for the index we have aggregation Indexes and nonclustered indexes.
Inserting data will inevitably cause changes in the index. Needless to say, clustered indexes are generally in ascending order. Non-clustered indexes are not necessarily data, and their discrete nature leads to continuous changes in the structure during insertion, resulting in reduced insertion performance.
So in order to solve the problem of non-clustered index insertion performance, the InnoDB engine created the Insert Buffer.
Storage of Insert Buffer

#Seeing the picture above, you may think that Insert Buffer is a component of the InnoDB buffer pool.
**Key point: **In fact, it is true or false. The InnoDB buffer pool does contain the information of the Insert Buffer, but the Insert Buffer actually exists physically like the data page (a shared table exists in the form of a B-tree) in space).
The role of Insert Buffer
Let me talk about a few points first:
A table can only have one primary key index. That's because its physical storage is a B-tree. (Don’t forget the data stored in the clustered index leaf nodes, and there is only one copy of the data)
The non-clustered index leaf nodes store the primary key of the clustered index

Insertion into clustered index
First of all, we know that in the InnoDB storage engine, the primary key is the unique identifier of the row (that is, we often Clustered index). We usually insert data incrementally according to the primary key, so the clustered index is sequential and does not require random reading from the disk.
For example, table:
CREATE TABLE test( id INT AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(30), PRIMARY KEY(id) );复制代码
As above, I created a primary key id, which has the following characteristics:
- The Id column is auto-increasing
- When a NULL value is inserted into the Id column, its value will be incremented due to AUTO_INCREMENT
- At the same time, the row records in the data page are stored in order according to the id value
Generally, due to The orderliness of the clustered index does not require random reading of data in the page, because this type of sequential insertion is very fast.
But if you insert the column ID into data such as UUID, then your insertion will be as random as a non-clustered index. It will cause your B tree structure to keep changing, and the performance will inevitably be affected.
Insertion of non-clustered index
Many times our table will have many non-clustered indexes. For example, I query according to the b field, and the b field is not unique. As shown in the following table:
CREATE TABLE test( id INT AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(30), PRIMARY KEY(id), KEY(name) );复制代码
Here I created an x table, which has the following characteristics:
- There is a clustered index id
- There is a non-unique non-clustered index Index name
- When inserting data, the data pages are stored in order according to the primary key id
- The data insertion of the auxiliary index name is not sequential
The non-clustered index is also the same It is a B-tree, but the leaf nodes store the primary key and name value of the clustered index.
Because there is no guarantee that the data in the name column is sequential, the insertion of the non-clustered index tree must not be sequential.
Of course, if the name column inserts time type data, the insertion of the non-clustered index is also sequential.
The arrival of Insert Buffer
It can be seen that the discrete nature of non-clustered index insertion leads to a decrease in insertion performance, so the InnoDB engine designed the Insert Buffer to improve insertion performance. .
Let me take a look at how to insert using Insert Buffer:

Firstly, for the insert or update operation of non-clustered index, Instead of inserting directly into the index page each time, it first determines whether the inserted non-clustered index page is in the buffer pool.
If it is there, insert it directly; if it is not there, put it into an Insert Buffer object first.
It feels to the outside as if the tree has inserted the leaf nodes of the non-clustered index, but in fact they are stored in other locations
Perform Insert Buffer and auxiliary index pages with a certain frequency and situation The merge operation of child nodes usually merges multiple insertion operations together, which greatly improves the insertion performance of non-clustered indexes.
Insert Buffer的使用要求:
- 索引是非聚集索引
- 索引不是唯一(unique)的
只有满足上面两个必要条件时,InnoDB存储引擎才会使用Insert Buffer来提高插入性能。
那为什么必须满足上面两个条件呢?
第一点索引是非聚集索引就不用说了,人家聚集索引本来就是顺序的也不需要你
第二点必须不是唯一(unique)的,因为在写入Insert Buffer时,数据库并不会去判断插入记录的唯一性。如果再去查找肯定又是离散读取的情况了,这样InsertBuffer就失去了意义。
Insert Buffer信息查看
我们可以使用命令SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS来查看Insert Buffer的信息:
------------------------------------- INSERT BUFFER AND ADAPTIVE HASH INDEX ------------------------------------- Ibuf: size 7545, free list len 3790, seg size 11336, 8075308 inserts,7540969 merged sec, 2246304 merges ...复制代码
使用命令后,我们会看到很多信息,这里我们只看下INSERT BUFFER 的:
seg size 代表当前Insert Buffer的大小 11336*16KB
free listlen 代表了空闲列表的长度
size 代表了已经合并记录页的数量
Inserts 代表了插入的记录数
merged recs 代表了合并的插入记录数量
merges 代表合并的次数,也就是实际读取页的次数
merges:merged recs大约为1∶3,代表了Insert Buffer 将对于非聚集索引页的离散IO逻辑请求大约降低了2/3
Insert Buffer的问题
说了这么多针对于Insert Buffer的好处,但目前Insert Buffer也存在一个问题:
即在写密集的情况下,插入缓冲会占用过多的缓冲池内存(innodb_buffer_pool),默认最大可以占用到1/2的缓冲池内存。
占用了过大的缓冲池必然会对其他缓冲池操作带来影响
Insert Buffer的优化
MySQL5.5之前的版本中其实都叫做Insert Buffer,之后优化为 Change Buffer 可以看做是 Insert Buffer 的升级版。
插入缓冲( Insert Buffer)这个其实只针对 INSERT 操作做了缓冲,而Change Buffer 对INSERT、DELETE、UPDATE都进行了缓冲,所以可以统称为写缓冲,其可以分为:
Insert Buffer
Delete Buffer
Purgebuffer
总结:
Insert Buffer到底是个什么?
其实Insert Buffer的数据结构就是一棵B+树。
在MySQL 4.1之前的版本中每张表有一棵Insert Buffer B+树
目前版本是全局只有一棵Insert Buffer B+树,负责对所有的表的辅助索引进行Insert Buffer
这棵B+树存放在共享表空间ibdata1中
以下几种情况下 Insert Buffer会写入真正非聚集索引,也就是所说的Merge Insert Buffer
- 当辅助索引页被读取到缓冲池中时
- Insert Buffer Bitmap页追踪到该辅助索引页已无可用空间时
- Master Thread线程中每秒或每10秒会进行一次Merge Insert Buffer的操作
一句话概括下:
Insert Buffer 就是用于提升非聚集索引页的插入性能的,其数据结构类似于数据页的一个B+树,物理存储在共享表空间ibdata1中 。
相关免费学习推荐:mysql视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Introducing important knowledge points: InnoDB's insertion buffer. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 MySQL如何从二进制内容看InnoDB行格式Jun 03, 2023 am 09:55 AM
MySQL如何从二进制内容看InnoDB行格式Jun 03, 2023 am 09:55 AMInnoDB是一个将表中的数据存储到磁盘上的存储引擎,所以即使关机后重启我们的数据还是存在的。而真正处理数据的过程是发生在内存中的,所以需要把磁盘中的数据加载到内存中,如果是处理写入或修改请求的话,还需要把内存中的内容刷新到磁盘上。而我们知道读写磁盘的速度非常慢,和内存读写差了几个数量级,所以当我们想从表中获取某些记录时,InnoDB存储引擎需要一条一条的把记录从磁盘上读出来么?InnoDB采取的方式是:将数据划分为若干个页,以页作为磁盘和内存之间交互的基本单位,InnoDB中页的大小一般为16
 mysql innodb是什么Apr 14, 2023 am 10:19 AM
mysql innodb是什么Apr 14, 2023 am 10:19 AMInnoDB是MySQL的数据库引擎之一,现为MySQL的默认存储引擎,为MySQL AB发布binary的标准之一;InnoDB采用双轨制授权,一个是GPL授权,另一个是专有软件授权。InnoDB是事务型数据库的首选引擎,支持事务安全表(ACID);InnoDB支持行级锁,行级锁可以最大程度的支持并发,行级锁是由存储引擎层实现的。
 mysql innodb异常怎么处理Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
mysql innodb异常怎么处理Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:01 PM一、回退重新装mysql为避免再从其他地方导入这个数据的麻烦,先对当前库的数据库文件做了个备份(/var/lib/mysql/位置)。接下来将Perconaserver5.7包进行了卸载,重新安装原先老的5.1.71的包,启动mysql服务,提示Unknown/unsupportedtabletype:innodb,无法正常启动。11050912:04:27InnoDB:Initializingbufferpool,size=384.0M11050912:04:27InnoDB:Complete
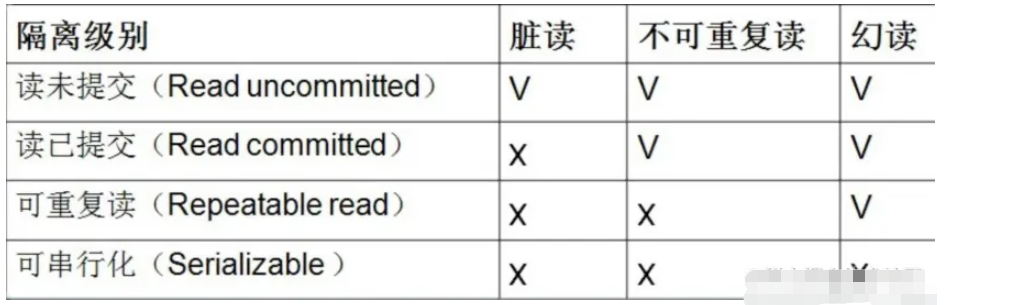 Mysql中的innoDB怎么解决幻读May 27, 2023 pm 03:34 PM
Mysql中的innoDB怎么解决幻读May 27, 2023 pm 03:34 PM1.Mysql的事务隔离级别这四种隔离级别,当存在多个事务并发冲突的时候,可能会出现脏读,不可重复读,幻读的一些问题,而innoDB在可重复读隔离级别模式下解决了幻读的一个问题,2.什么是幻读幻读是指在同一个事务中,前后两次查询相同范围的时候得到的结果不一致如图,第一个事务里面,我们执行一个范围查询,这个时候满足条件的数据只有一条,而在第二个事务里面,它插入一行数据并且进行了提交,接着第一个事务再去查询的时候,得到的结果比第一次查询的结果多出来一条数据,注意第一个事务的第一次和第二次查询,都在同
 MySQL储存引擎选型对比:InnoDB、MyISAM与Memory性能指标评估Jul 26, 2023 am 11:25 AM
MySQL储存引擎选型对比:InnoDB、MyISAM与Memory性能指标评估Jul 26, 2023 am 11:25 AMMySQL储存引擎选型对比:InnoDB、MyISAM与Memory性能指标评估引言:在MySQL数据库中,储存引擎的选择对于系统性能和数据完整性起着至关重要的作用。MySQL提供了多种储存引擎,其中最常用的引擎包括InnoDB、MyISAM和Memory。本文将就这三种储存引擎进行性能指标评估,并通过代码示例进行比较。一、InnoDB引擎InnoDB是My
 如何使用MyISAM和InnoDB存储引擎来优化MySQL性能May 11, 2023 pm 06:51 PM
如何使用MyISAM和InnoDB存储引擎来优化MySQL性能May 11, 2023 pm 06:51 PMMySQL是一款广泛使用的数据库管理系统,不同的存储引擎对数据库性能有不同的影响。MyISAM和InnoDB是MySQL中最常用的两种存储引擎,它们的特点各有不同,使用不当可能会影响数据库的性能。本文将介绍如何使用这两种存储引擎来优化MySQL性能。一、MyISAM存储引擎MyISAM是MySQL最常用的存储引擎,它的优点是速度快,存储占用空间小。MyISA
 提高MySQL存储引擎读取性能的技巧和策略:MyISAM与InnoDB对比分析Jul 26, 2023 am 10:01 AM
提高MySQL存储引擎读取性能的技巧和策略:MyISAM与InnoDB对比分析Jul 26, 2023 am 10:01 AM提高MySQL存储引擎读取性能的技巧和策略:MyISAM与InnoDB对比分析引言:MySQL是最常用的开源关系型数据库管理系统之一,主要用于存储和管理大量结构化数据。在应用中,对于数据库的读取性能往往是非常重要的,因为读取操作是大部分应用的主要操作类型。本文将重点讨论如何提高MySQL存储引擎的读取性能,重点对比分析MyISAM和InnoDB这两个常用的存
 支持GIS数据的MySQL存储引擎:InnoDB中的空间索引优化Jul 24, 2023 pm 11:07 PM
支持GIS数据的MySQL存储引擎:InnoDB中的空间索引优化Jul 24, 2023 pm 11:07 PM支持GIS数据的MySQL存储引擎:InnoDB中的空间索引优化摘要:在现代的数据库应用中,地理信息系统(GIS)数据扮演着越来越重要的角色。GIS数据处理是复杂和动态的,传统的关系型数据库并不擅长处理这种类型的数据。然而,MySQL提供了一种存储引擎,即InnoDB,可以优化GIS数据的处理。本文将介绍如何在InnoDB存储引擎上使用空间索引来优化GIS数


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),







