python tutorial column introduces the operation of pandas today. 
pandas has a very powerful method, which is accessor. It can be understood as a property interface through which additional methods can be obtained. In fact, this is still very general. Let’s understand it through code and examples.
>>> pd.Series._accessors
{'cat', 'str', 'dt'}复制代码
Using the _accessors method for the Series data structure, we get 3 objects: cat, str, dt.
- .cat: is used for categorical data (Categorical data)
- .str: is used for character data (String Object data)
- .dt: Used for time data (datetime-like data)
Let’s take a look at how these three objects are used in turn.
Use of str object
Series data type: str string
# 定义一个Series序列 >>> addr = pd.Series([ ... 'Washington, D.C. 20003', ... 'Brooklyn, NY 11211-1755', ... 'Omaha, NE 68154', ... 'Pittsburgh, PA 15211' ... ]) >>> addr.str.upper() 0 WASHINGTON, D.C. 20003 1 BROOKLYN, NY 11211-1755 2 OMAHA, NE 68154 3 PITTSBURGH, PA 15211 dtype: object >>> addr.str.count(r'\d') 0 5 1 9 2 5 3 5 dtype: int64复制代码
Instructions on the two methods of the above str object:
- Series.str.upper: Change all strings in Series to uppercase;
- Series.str.count: Change all characters in Series Count the number of strings;
In fact, it is not difficult to find that the usage of this usage is very similar to the operation of strings in Python. Yes, you can do such simple operations in pandas, but the difference is that you are operating an entire column of string data. Still based on the above data set, let’s look at another operation:
>>> regex = (r'(?P<city>[A-Za-z ]+), ' # 一个或更多字母
... r'(?P<state>[A-Z]{2}) ' # 两个大写字母
... r'(?P<zip>\d{5}(?:-\d{4})?)') # 可选的4个延伸数字
...
>>> addr.str.replace('.', '').str.extract(regex)
city state zip
0 Washington DC 20003
1 Brooklyn NY 11211-1755
2 Omaha NE 68154
3 Pittsburgh PA 15211复制代码Description of the two methods of the above str object:
- Series.str.replace:Replace the specified string in the Series;
- Series.str.extract: Extract the data information in the string through regular expressions;
This The usage is a bit complicated, because it is obvious that this is a chain usage. Replace " . " with "" through replace, which is empty, then use 3 regular expressions (corresponding to city, state, zip respectively) to extract the data through extract ,And changed from the original Series data structure to the DataFrame data structure.
Of course, in addition to the above usage, commonly used attributes and methods include .rstrip, .contains, split, etc. Let’s check the str attribute through the following code Complete list:
>>> [i for i in dir(pd.Series.str) if not i.startswith('_')] ['capitalize', 'cat', 'center', 'contains', 'count', 'decode', 'encode', 'endswith', 'extract', 'extractall', 'find', 'findall', 'get', 'get_dummies', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'len', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'match', 'normalize', 'pad', 'partition', 'repeat', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'slice', 'slice_replace', 'split', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'wrap', 'zfill']复制代码
There are many attributes. For specific usage, if you are interested, you can explore and practice by yourself.
Use of dt object
Series data type: datetime
Because the data requires datetime type, the following uses pandas’ date_range() to generate a Group date datetime demonstrates how to perform dt object operations.
>>> daterng = pd.Series(pd.date_range('2017', periods=9, freq='Q')) >>> daterng 0 2017-03-31 1 2017-06-30 2 2017-09-30 3 2017-12-31 4 2018-03-31 5 2018-06-30 6 2018-09-30 7 2018-12-31 8 2019-03-31 dtype: datetime64[ns] >>> daterng.dt.day_name() 0 Friday 1 Friday 2 Saturday 3 Sunday 4 Saturday 5 Saturday 6 Sunday 7 Monday 8 Sunday dtype: object >>> # 查看下半年 >>> daterng[daterng.dt.quarter > 2] 2 2017-09-30 3 2017-12-31 6 2018-09-30 7 2018-12-31 dtype: datetime64[ns] >>> daterng[daterng.dt.is_year_end] 3 2017-12-31 7 2018-12-31 dtype: datetime64[ns]复制代码
The above three methods of dt are explained:
- Series.dt.day_name(): Judge the day of the week from the date;
- Series.dt.quarter: Determine the season from the date;
- Series.dt.is_year_end: Determine whether it is the end of the year from the date;
Other methods are also based on some transformations of datetime, and use transformations to view specific micro or macro dates.
Use of cat object
Series data type: Category
Before talking about the use of cat object, let’s talk about the Category data type. The effect is very powerful. Although we do not frequently run g data in memory, we always encounter situations where executing a few lines of code will wait for a long time. One benefit of using Category data is that can save time and space consumption. Let’s learn through several examples.
>>> colors = pd.Series([ ... 'periwinkle', ... 'mint green', ... 'burnt orange', ... 'periwinkle', ... 'burnt orange', ... 'rose', ... 'rose', ... 'mint green', ... 'rose', ... 'navy' ... ]) ... >>> import sys >>> colors.apply(sys.getsizeof) 0 59 1 59 2 61 3 59 4 61 5 53 6 53 7 59 8 53 9 53 dtype: int64复制代码
Above we used sys.getsizeof to display the memory usage. The number represents the number of bytes.
There is another way to calculate content occupancy: memory_usage(), which will be used later.
Now we map the unique values of the colors above to a set of integers, and then look at the memory occupied.
>>> mapper = {v: k for k, v in enumerate(colors.unique())}
>>> mapper
{'periwinkle': 0, 'mint green': 1, 'burnt orange': 2, 'rose': 3, 'navy': 4}
>>> as_int = colors.map(mapper)
>>> as_int
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 0
4 2
5 3
6 3
7 1
8 3
9 4
dtype: int64
>>> as_int.apply(sys.getsizeof)
0 24
1 28
2 28
3 24
4 28
5 28
6 28
7 28
8 28
9 28
dtype: int64复制代码Note: For the above integer value mapping, you can also use the simpler pd.factorize() method instead.
We found that the memory occupied above is half that of using the object type. In fact, this situation is similar to the internal principle of Category data type.
Difference in memory usage: The memory occupied by Categorical is proportional to the number of Categorical categories and the length of the data. On the contrary, the memory occupied by object is a constant multiplied by the data. length.
The following is a comparison of object memory usage and category memory usage.
>>> colors.memory_usage(index=False, deep=True) 650 >>> colors.astype('category').memory_usage(index=False, deep=True) 495复制代码
上面结果是使用object和Category两种情况下内存的占用情况。我们发现效果并没有我们想象中的那么好。但是注意Category内存是成比例的,如果数据集的数据量很大,但不重复分类(unique)值很少的情况下,那么Category的内存占用可以节省达到10倍以上,比如下面数据量增大的情况:
>>> manycolors = colors.repeat(10) >>> len(manycolors) / manycolors.nunique() 20.0 >>> manycolors.memory_usage(index=False, deep=True) 6500 >>> manycolors.astype('category').memory_usage(index=False, deep=True) 585复制代码
可以看到,在数据量增加10倍以后,使用Category所占内容节省了10倍以上。
除了占用内存节省外,另一个额外的好处是计算效率有了很大的提升。因为对于Category类型的Series,str字符的操作发生在.cat.categories的非重复值上,而并非原Series上的所有元素上。也就是说对于每个非重复值都只做一次操作,然后再向与非重复值同类的值映射过去。
对于Category的数据类型,可以使用accessor的cat对象,以及相应的属性和方法来操作Category数据。
>>> ccolors = colors.astype('category') >>> ccolors.cat.categories Index(['burnt orange', 'mint green', 'navy', 'periwinkle', 'rose'], dtype='object')复制代码
实际上,对于开始的整数类型映射,我们可以先通过reorder_categories进行重新排序,然后再使用cat.codes来实现对整数的映射,来达到同样的效果。
>>> ccolors.cat.reorder_categories(mapper).cat.codes 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 0 4 2 5 3 6 3 7 1 8 3 9 4 dtype: int8复制代码
dtype类型是Numpy的int8(-127~128)。可以看出以上只需要一个单字节就可以在内存中包含所有的值。我们开始的做法默认使用了int64类型,然而通过pandas的使用可以很智能的将Category数据类型变为最小的类型。
让我们来看一下cat还有什么其它的属性和方法可以使用。下面cat的这些属性基本都是关于查看和操作Category数据类型的。
>>> [i for i in dir(ccolors.cat) if not i.startswith('_')] ['add_categories', 'as_ordered', 'as_unordered', 'categories', 'codes', 'ordered', 'remove_categories', 'remove_unused_categories', 'rename_categories', 'reorder_categories', 'set_categories']复制代码
但是Category数据的使用不是很灵活。例如,插入一个之前没有的值,首先需要将这个值添加到.categories的容器中,然后再添加值。
>>> ccolors.iloc[5] = 'a new color' # ... ValueError: Cannot setitem on a Categorical with a new category, set the categories first >>> ccolors = ccolors.cat.add_categories(['a new color']) >>> ccolors.iloc[5] = 'a new color' 复制代码
如果你想设置值或重塑数据,而非进行新的运算操作,那么Category类型不是那么有用。
相关免费学习推荐:python教程(视频)
The above is the detailed content of Teach you the cool pandas operations that 1% of people know. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 python pandas安装方法Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:33 PM
python pandas安装方法Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:33 PMpython可以通过使用pip、使用conda、从源代码、使用IDE集成的包管理工具来安装pandas。详细介绍:1、使用pip,在终端或命令提示符中运行pip install pandas命令即可安装pandas;2、使用conda,在终端或命令提示符中运行conda install pandas命令即可安装pandas;3、从源代码安装等等。
 日常工作中,Python+Pandas是否能代替Excel+VBA?May 04, 2023 am 11:37 AM
日常工作中,Python+Pandas是否能代替Excel+VBA?May 04, 2023 am 11:37 AM知乎上有个热门提问,日常工作中Python+Pandas是否能代替Excel+VBA?我的建议是,两者是互补关系,不存在谁替代谁。复杂数据分析挖掘用Python+Pandas,日常简单数据处理用Excel+VBA。从数据处理分析能力来看,Python+Pandas肯定是能取代Excel+VBA的,而且要远远比后者强大。但从便利性、传播性、市场认可度来看,Excel+VBA在职场工作上还是无法取代的。因为Excel符合绝大多数人的使用习惯,使用成本更低。就像Photoshop能修出更专业的照片,为
 如何使用Python中的Pandas按特定列合并两个CSV文件?Sep 08, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
如何使用Python中的Pandas按特定列合并两个CSV文件?Sep 08, 2023 pm 02:01 PMCSV(逗号分隔值)文件广泛用于以简单格式存储和交换数据。在许多数据处理任务中,需要基于特定列合并两个或多个CSV文件。幸运的是,这可以使用Python中的Pandas库轻松实现。在本文中,我们将学习如何使用Python中的Pandas按特定列合并两个CSV文件。什么是Pandas库?Pandas是一个用于Python信息控制和检查的开源库。它提供了用于处理结构化数据(例如表格、时间序列和多维数据)以及高性能数据结构的工具。Pandas广泛应用于金融、数据科学、机器学习和其他需要数据操作的领域。
 时间序列特征提取的Python和Pandas代码示例Apr 12, 2023 pm 05:43 PM
时间序列特征提取的Python和Pandas代码示例Apr 12, 2023 pm 05:43 PM使用Pandas和Python从时间序列数据中提取有意义的特征,包括移动平均,自相关和傅里叶变换。前言时间序列分析是理解和预测各个行业(如金融、经济、医疗保健等)趋势的强大工具。特征提取是这一过程中的关键步骤,它涉及将原始数据转换为有意义的特征,可用于训练模型进行预测和分析。在本文中,我们将探索使用Python和Pandas的时间序列特征提取技术。在深入研究特征提取之前,让我们简要回顾一下时间序列数据。时间序列数据是按时间顺序索引的数据点序列。时间序列数据的例子包括股票价格、温度测量和交通数据。
 pandas写入excel有哪些方法Nov 22, 2023 am 11:46 AM
pandas写入excel有哪些方法Nov 22, 2023 am 11:46 AMpandas写入excel的方法有:1、安装所需的库;2、读取数据集;3、写入Excel文件;4、指定工作表名称;5、格式化输出;6、自定义样式。Pandas是一个流行的Python数据分析库,提供了许多强大的数据清洗和分析功能,要将Pandas数据写入Excel文件,可以使用Pandas提供的“to_excel()”方法。
 pandas如何读取txt文件Nov 21, 2023 pm 03:54 PM
pandas如何读取txt文件Nov 21, 2023 pm 03:54 PMpandas读取txt文件的步骤:1、安装Pandas库;2、使用“read_csv”函数读取txt文件,并指定文件路径和文件分隔符;3、Pandas将数据读取为一个名为DataFrame的对象;4、如果第一行包含列名,则可以通过将header参数设置为0来指定,如果没有,则设置为None;5、如果txt文件中包含缺失值或空值,可以使用“na_values”指定这些缺失值。
 pandas怎么读取csv文件Dec 01, 2023 pm 04:18 PM
pandas怎么读取csv文件Dec 01, 2023 pm 04:18 PM读取CSV文件的方法有使用read_csv()函数、指定分隔符、指定列名、跳过行、缺失值处理、自定义数据类型等。详细介绍:1、read_csv()函数是Pandas中最常用的读取CSV文件的方法。它可以从本地文件系统或远程URL加载CSV数据,并返回一个DataFrame对象;2、指定分隔符,默认情况下,read_csv()函数将使用逗号作为CSV文件的分隔符等等。
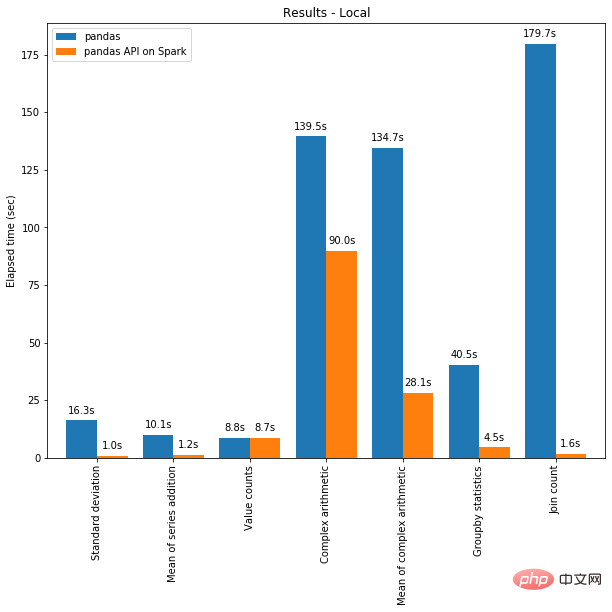 Pandas 与 PySpark 强强联手,功能与速度齐飞!May 01, 2023 pm 09:19 PM
Pandas 与 PySpark 强强联手,功能与速度齐飞!May 01, 2023 pm 09:19 PM使用Python做数据处理的数据科学家或数据从业者,对数据科学包pandas并不陌生,也不乏像云朵君一样的pandas重度使用者,项目开始写的第一行代码,大多是importpandasaspd。pandas做数据处理可以说是yyds!而他的缺点也是非常明显,pandas只能单机处理,它不能随数据量线性伸缩。例如,如果pandas试图读取的数据集大于一台机器的可用内存,则会因内存不足而失败。另外pandas在处理大型数据方面非常慢,虽然有像Dask或Vaex等其他库来优化提升数


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment







