Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >How to use global variables in python
How to use global variables in python
- coldplay.xixiOriginal
- 2020-09-11 14:18:4033349browse
Use of python global variables: 1. To reference the global variable, the code is [if i in b:print("%d in list b" %i)]; 2. To modify the global variable, the code is [print "before func b:", b].

Usage of python global variables:
1. Quote
The global variable used is only a reference. If its value is not modified in the function, there is no need to add the global keyword. For example:
#! /usr/bin/python
a = 1
b = [2, 3]
def func():
if a == 1:
print("a: %d" %a)
for i in range(4):
if i in b:
print("%d in list b" %i)
else:
print("%d not in list b" %i)
if __name__ == '__main__':
func()Output result:
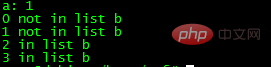
It can be seen that both lists and variables can be quoted directly.
2. Modify the global variables used in
. If they need to be modified in the function, it will involve ambiguity issues, such as:
#! /usr/bin/python
a = 1
b = [2, 3]
def func():
a = 2
print "in func a:", a
b[0] = 1
print "in func b:", b
if __name__ == '__main__':
print "before func a:", a
print "before func b:", b
func()
print "after func a:", a
print "after func b:", bOutput Result:
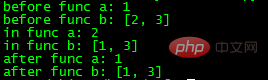
It can be seen that for variable a, "a = 2" in function func, because existence can mean referencing global variable a, or creating one The ambiguity of new local variables, so python specifies by default to create a new local variable to eliminate this ambiguity, but for list b, "b[0] = 1" does not have this ambiguity.
Therefore, the global variable is modified directly, but if it is changed to "b = [3, 4]", then b will also become a local variable. In particular, when the statement "if a == 1:" is added before a = 2 in func, the script runs incorrectly because this statement introduces a global variable, causing the statement "a = 1" to be unable to create a variable with the same name. local variables.
Therefore, you need to modify the global variable a. You can add the global a statement before "a = 2", such as:
#! /usr/bin/python
a = 1
b = [2, 3]
def func():
global a
a = 2
print "in func a:", a
b[0] = 1
print "in func b:", b
if __name__ == '__main__':
print "before func a:", a
print "before func b:", b
func()
print "after func a:", a
print "after func b:", bOutput result:
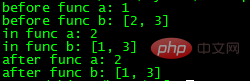
Conclusion: When referencing global variables, you do not need a global statement. To modify global variables, you need to use a global statement. In particular, if you only modify the values of elements in lists, dictionaries, etc., you can use global variables directly without the need for a global statement.
The above is the detailed content of How to use global variables in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

