
The entrance of the C program is the main function. Generally speaking, as long as the normal operation ends, it starts from the first sentence of the main function and ends with the last sentence.
For example:
int main()//程序开始
{
printf("Hello!\n");
return 0;//程序结束,返回值
}But if the program encounters return (in the main function) exit (whether in the main function or a sub-function) in the middle of the execution of the program, the program will also end.
How to write the main function in C language
The main function is the entry function of the C program, that is, the execution of the program is Starting from the main function, calls to other functions are also directly or indirectly called in the main function. So who is calling the main function? The answer is the operating system. Since the development of C language, there are many different ways of writing the main function. Let’s explore the different ways of writing . Note: The test environment is Ubuntu 17.10, and the GCC version is 7.2.0.
NO.1
main(){}
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
main(){
printf("Hello World\n");
}</stdio.h>

NO.2##
void main(){}Example:
#include <stdio.h>
void main(){
printf("Hello World\n");
}</stdio.h>

NO.3##int main(){}Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}</stdio.h>

NO.4int main(void){}Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}</stdio.h>

NO.5int main(int argc,char *argv[]){}Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}</stdio.h>

NO.6int main(int argc,char **argv){}Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc,char **argv){
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}</stdio.h>
 From the above test, writing method 1 It can be compiled normally under the C90 standard, but a warning will be thrown under the C99 and C11 standards (the return value is not written, the default return value is int, which is equivalent to writing method 1 and writing method 3). Writing methods 2-6 can be compiled normally under the C90, C99, and C11 standards. Among so many ways of writing, which one is the standard way of writing the main function? So I checked the C standard document for the standard way of writing the main function, see the picture below:
From the above test, writing method 1 It can be compiled normally under the C90 standard, but a warning will be thrown under the C99 and C11 standards (the return value is not written, the default return value is int, which is equivalent to writing method 1 and writing method 3). Writing methods 2-6 can be compiled normally under the C90, C99, and C11 standards. Among so many ways of writing, which one is the standard way of writing the main function? So I checked the C standard document for the standard way of writing the main function, see the picture below:
 ## It can be seen from the standard document that the writing methods 4, 5, and 6 are This is the standard way of writing the main function. Writing method 5 is equivalent to writing method 6. Then why are there writing methods 1, 2, and 3? That's because from the time when the C language was designed in 1972 to the release of the C90 standard, different implementations of the C language resulted in differences in the main function. Writing method 2 is strongly not recommended because the main function is called by the operating system. The operating system will judge whether the program is executed correctly based on the return value of the main function. If void is returned, what state does it represent? Moreover, some compilers support this writing method, some compilers do not support it, and all standards do not recognize this writing method. Writing methods 1 and 3 are still barely acceptable, but it is not recommended. It is best to write according to the standard writing method. Why should we write according to the standard writing method? That's because in order to make C programs more portable. Writing method 5 is equivalent to writing method 6. The first parameter represents the number of main function parameters, and the second parameter uses pointers to point to these parameters respectively. argv[0] represents the program name, argv[1] to argv[argc-1] represent program parameters. Let’s take a look at the return value of the main function, see the picture below
## It can be seen from the standard document that the writing methods 4, 5, and 6 are This is the standard way of writing the main function. Writing method 5 is equivalent to writing method 6. Then why are there writing methods 1, 2, and 3? That's because from the time when the C language was designed in 1972 to the release of the C90 standard, different implementations of the C language resulted in differences in the main function. Writing method 2 is strongly not recommended because the main function is called by the operating system. The operating system will judge whether the program is executed correctly based on the return value of the main function. If void is returned, what state does it represent? Moreover, some compilers support this writing method, some compilers do not support it, and all standards do not recognize this writing method. Writing methods 1 and 3 are still barely acceptable, but it is not recommended. It is best to write according to the standard writing method. Why should we write according to the standard writing method? That's because in order to make C programs more portable. Writing method 5 is equivalent to writing method 6. The first parameter represents the number of main function parameters, and the second parameter uses pointers to point to these parameters respectively. argv[0] represents the program name, argv[1] to argv[argc-1] represent program parameters. Let’s take a look at the return value of the main function, see the picture below
It can be seen from the figure that if the return value of the main function is a compatible type of int type, the value returned from the main function together with exit is equivalent to executing exit xxx. xxx represents the value returned from the main function. If you forget to write the return statement, when the closing brace } of the main function body is executed, the default value 0 will be returned. Returning 0 means that the program execution is successful and the program exits. If the return type of the main function is not a compatible type of int type, the status returned by the program to the operating system will be unclear.
C standard document download address:
Portal: http://download.csdn.net/download/u012219371/10184521
C standard introduction:
Portal: http://blog.csdn.net/u012219371/article/details/78951972
Related recommendations: c language tutorial video
The above is the detailed content of Where does the execution of a c program start and end?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 C程序计算3D空间中三个点之间的距离Aug 29, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
C程序计算3D空间中三个点之间的距离Aug 29, 2023 pm 12:41 PM给定一个三维平面,因此有三个坐标,任务是找到给定点之间的距离并显示结果。在三维平面上,有三个坐标轴,x轴的坐标为(x1,y1,z1),y轴的坐标为(x2,y2,z2),z轴的坐标为(x3,y3,z)。计算它们之间的距离有一个直接的公式如下所示$$\sqrt{\lgroupx2-x1\rgroup^{2}+\lgroupy2-y1\rgroup^{2}+\lgroupz2-z1\rgroup^{2}}$$下面是表示三个不同坐标轴及其坐标的图示下面使用的方法如下−输入坐标(x1,
 二项式系数表的C程序Aug 26, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
二项式系数表的C程序Aug 26, 2023 pm 12:49 PMGivenwithapositiveintegervaluelet’ssay‘val’andthetaskistoprintthevalueofbinomialcoefficientB(n,k)where,nandkbeanyvaluebetween0tovalandhencedisplaytheresult.WhatisBinomialCoefficientBinomialcoefficient(n,k)istheorderofcho
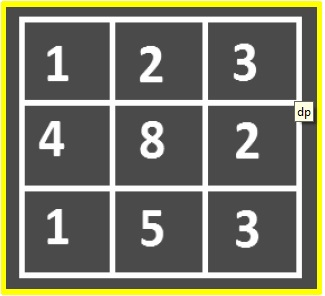 最小成本路径的C程序Aug 26, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
最小成本路径的C程序Aug 26, 2023 pm 06:17 PM在这里,我们将解决C语言中的最小成本路径问题。这意味着在2D矩阵上完成,其中每个单元格都有一个移动成本。我们必须找到一条从左上角到右下角且行程成本最小的路径。您只能从给定单元格向下和右下遍历单元格。为了解决这个特定问题,动态编程比递归更好。给定成本矩阵cost[][]和位置(m,n),我们必须编写一个函数,返回从(0,0)到达(m,n)的最小路径成本到达(m,n)的路径的总成本是该路径上所有成本的总和(包括源和目的地)。假设−所有成本是积极的。输入矩阵中不存在负成本循环示例查找到(2,2)的最小
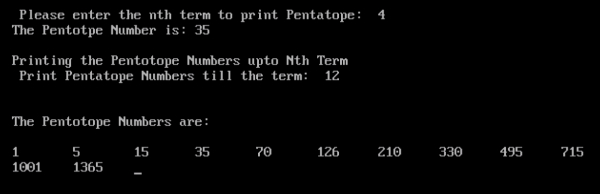 在C语言中编写一个程序,打印出N个五角数的序列Aug 25, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
在C语言中编写一个程序,打印出N个五角数的序列Aug 25, 2023 pm 02:25 PM程序说明五维体数是帕斯卡三角形的任意一行中第五个数字,从左到右或从右到左开始,起始于5项行14641。这种数字的前几个是1,5,15,35,70,126,210,330,495,715,1001,1365Pentatopenumbersbelongintheclassoffiguratenumbers,whichcanberepresentedasregular,discretegeometricpatterns.Theformulaforthenthpentatopicnumberis$$\l
 C++程序以找到给定值的反正切Aug 26, 2023 am 10:09 AM
C++程序以找到给定值的反正切Aug 26, 2023 am 10:09 AM我们在三角学中最常使用的比率包括正弦、余弦、正切等等。您可以使用角度来计算这些比率。如果我们知道比率值,我们还可以使用反三角函数计算角度。本课程将向您展示如何使用C++的反正切(arctan)函数,使用正切值(以弧度为单位)计算角度。atan()函数使用atan()技术和反三角正切函数计算角度。C++标准库包含这个函数。在使用这种方法之前,我们必须导入cmath库。此方法返回以弧度为单位的角度,并采用正切值作为参数。以下使用简单的语法-语法#include<cmath>atan(&l
 C++程序:替换特定索引处的字符Aug 25, 2023 pm 10:53 PM
C++程序:替换特定索引处的字符Aug 25, 2023 pm 10:53 PM字符串是一组字符。我们也可以将它们称为字符数组。考虑到一个由字符串组成的字符数组,这些字符串具有指定的索引和值。有时候我们可以对字符串进行一些修改,其中一种修改是替换字符通过提供一个特定的索引。在本文中,我们将看到如何替换一个字符从一个specificindexinsideastringusingC++.语法String_variable[<givenindex>]=<newcharacter>在C++中,我们可以使用索引访问字符串字符。在
 C程序输入一个由空格分隔的整数序列的数组Aug 25, 2023 am 11:33 AM
C程序输入一个由空格分隔的整数序列的数组Aug 25, 2023 am 11:33 AM问题陈述编写一个C程序,以空格分隔的整数作为数组输入。SampleExamples输入12345输出‘Arrayelementsare-’1,2,3,4,5Explanation的中文翻译为:解释输入包含5个以空格分隔的整数。输入997687542356878967343423输出‘Arrayelementsare-’99,76,87,54,23,56,878,967,34,34,23Explanation的中文翻译为:解释输入包含11个以空格分隔的整数。方法一在这种方法中,我们将把输入中的以空
 计算六边形内切圆内的正方形面积的C程序Aug 28, 2023 pm 08:41 PM
计算六边形内切圆内的正方形面积的C程序Aug 28, 2023 pm 08:41 PM给定一个正六边形内接的圆内切的正方形,我们需要找到正方形的面积,为此我们需要找到正方形边长和正六边形边长之间的关系。正六边形内接圆的半径的数学公式为,r=A√3/2由于正方形的对角线等于圆的直径,所以半径和边长之间的关系为,a=√r根据正六边形的边长,a=√3A/√2所以,正方形的面积,面积=a2=(√3A/√2)2示例#include<stdio.h>#inclu


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.





