Home >Backend Development >C#.Net Tutorial >What is the general calling form of fwrite function?
What is the general calling form of fwrite function?
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2020-08-29 16:31:447856browse
The general calling form of the fwrite function is "fwrite(buffer,size,count,fp);"; where buffer is the starting address of the data block to be output, and size is the bytes of each data block. Number, count is used to specify the data block to be written or output each time, and fp is the file pointer.

fwrite() is a file processing function in the C language standard library. Its function is to write several data blocks to the specified file. If executed successfully, Returns the number of data blocks actually written. This function operates on files in binary form and is not limited to text files.
Syntax:
fwrite(buffer,size,count,fp)
Parameters:
buffer is the data to be output The starting address of the block
size is the number of bytes of each data block
count is used to specify the data to be written or output each time Block
#fp is the file pointer.
The function returns the number of written data.
Note
(1) The stream fclose() must be closed after the write operation fwrite().
(2) Without closing the stream, every time data is read or written, the file pointer will point to the next data location to be written or read.
Common types of reading and writing
(1)Write int data to file
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main ()
{
FILE * pFile;
int buffer[] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
if((pFile = fopen ("myfile.txt", "wb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
//可以写多个连续的数据(这里一次写4个)
fwrite (buffer , sizeof(int), 4, pFile);
fclose (pFile);
return 0;
}(2)Read int data
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main () {
FILE * fp;
int buffer[4];
if((fp=fopen("myfile.txt","rb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
if(fread(buffer,sizeof(int),4,fp)!=4) //可以一次读取
{
printf("file read error\n");
exit(0);
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
printf("%d\n",buffer[i]);
return 0;
}Execution result:
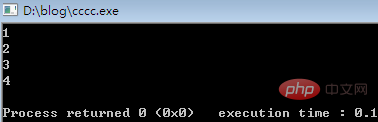
5. Read and write structure data
(1)Write structure data to file
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct{
int age;
char name[30];
}people;
int main ()
{
FILE * pFile;
int i;
people per[3];
per[0].age=20;strcpy(per[0].name,"li");
per[1].age=18;strcpy(per[1].name,"wang");
per[2].age=21;strcpy(per[2].name,"zhang");
if((pFile = fopen ("myfile.txt", "wb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
if(fwrite(&per[i],sizeof(people),1,pFile)!=1)
printf("file write error\n");
}
fclose (pFile);
return 0;
}(2) Read structure data
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct{
int age;
char name[30];
}people;
int main () {
FILE * fp;
people per;
if((fp=fopen("myfile.txt","rb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
while(fread(&per,sizeof(people),1,fp)==1) //如果读到数据,就显示;否则退出
{
printf("%d %s\n",per.age,per.name);
}
return 0;
}Execution result:
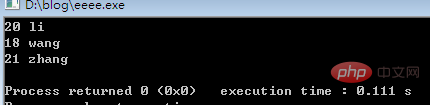
Related recommendations:c language tutorial video
The above is the detailed content of What is the general calling form of fwrite function?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

