Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Detailed explanation of Python photo synthesis method
Detailed explanation of Python photo synthesis method
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2020-08-29 16:26:123998browse

【Related learning recommendations: python tutorial】
Article directory
- Foreword
- Github
- Effect
- Implementation process
- Overall code
Preface
When I was watching a movie, I found a photo wall function. I thought it was fun to generate photos in this way, so I started to do it with Python and thought it would be useful. It might be a good idea to take a photo as a souvenir.
P: Later I learned that the function I want to do is called montage puzzle, so I will keep this blog record for now. I will take a look at the algorithm of montage puzzle when I have time
Github
https://github.com/jiandi1027/photo.git
Effect
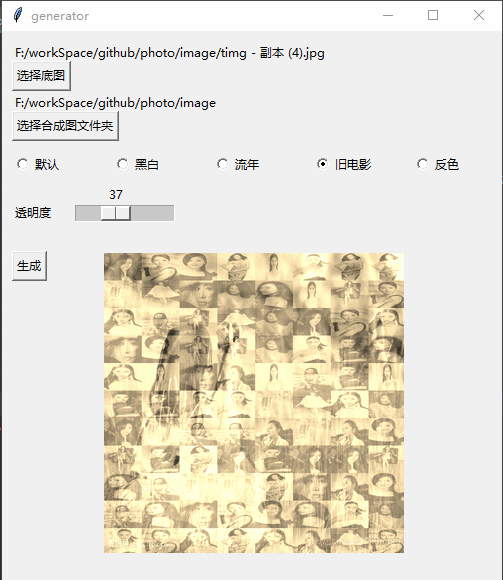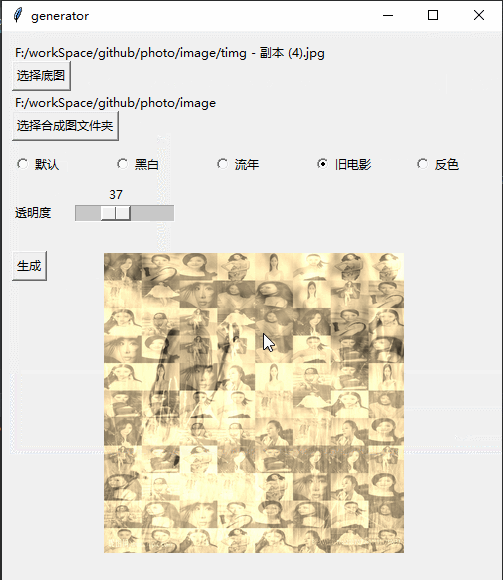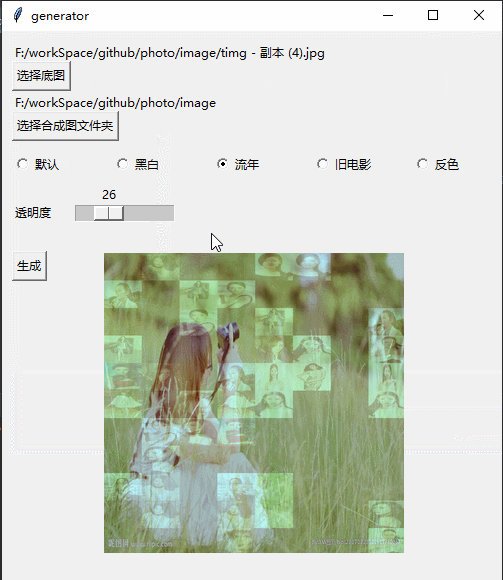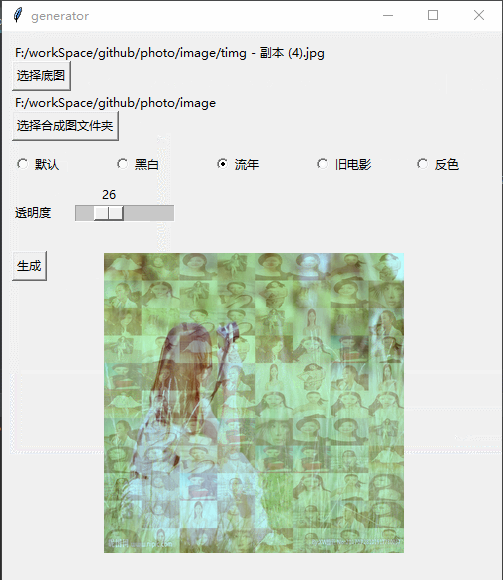
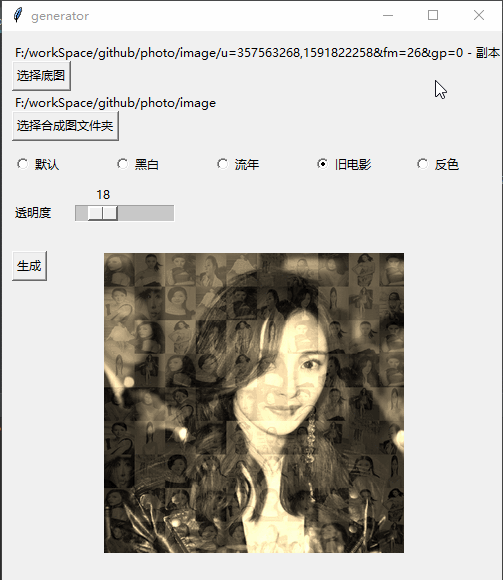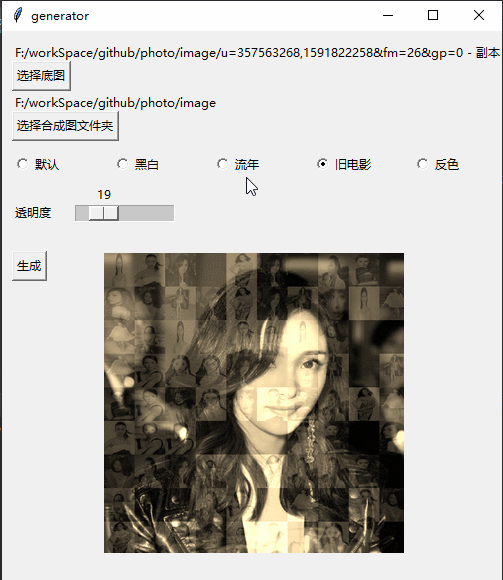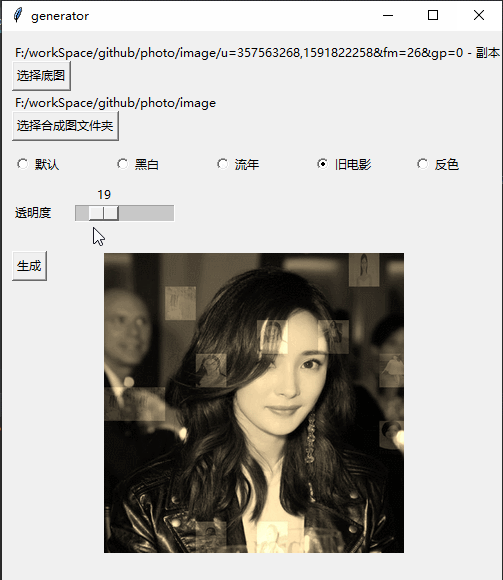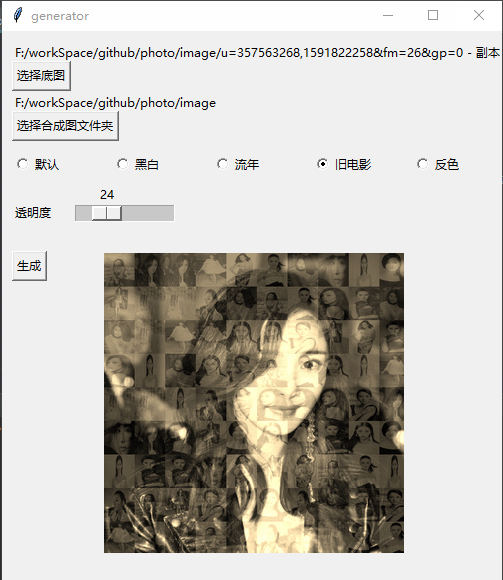
Implementation process
1. Get the number N of pictures in the picture folder, split the base image into XY blocks, and make X * Y
# 打开图片
base = Image.open(baseImgPath)
base = base.convert('RGBA')
# 获取图片文件夹图片并打乱顺序
files = glob.glob(imagesPath + '/*.*')
random.shuffle(files)
# 图片数量
num = len(files)
# 底图大小
x = base.size[0]
y = base.size[1]
# 每张图片数量 这个公式是为了xNum * yNum 的总图片数量<num又成比例的最大整数
yNum = int((num / (y / x)) ** 0.5)
if yNum == 0:
yNum = 1
xNum = int(num / yNum)
# 图片大小 因为像素没有小数点 为防止黑边所以+1
xSize = int(x / xNum) + 1
ySize = int(y / yNum) + 1
2. Traverse the pictures in the folder and fill them in order to generate the final composite picture
for file in files:
fromImage = Image.open(file)
i = int(num % xNum)
j = int(num / xNum)
out = fromImage.resize((xSize, ySize), Image.ANTIALIAS).convert('RGBA')
toImage.paste(out, (i * xSize, j * ySize))
toImage = toImage.convert('RGBA')
img = Image.blend(base, toImage, 0.3)
# 显示图片
photo = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img)
showLabel.config(image=photo)
showLabel.image = photo
if num < xNum * yNum:
num = num + 1 3. Save the image after generation
toImage.save('generator.png')
img.save("final.png")

4.Establish a visual interface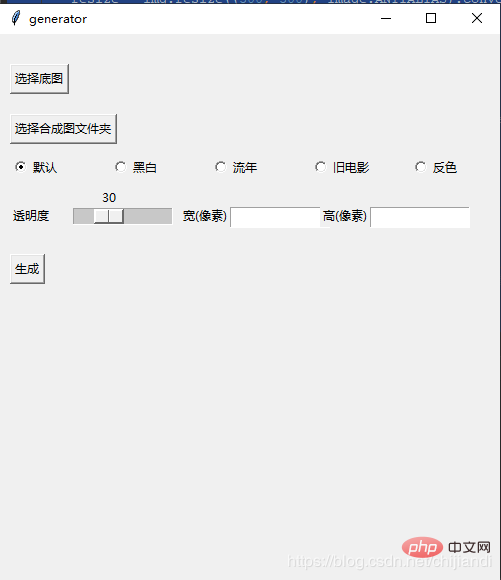
5.Pyinstaller generates exe executable file
Install the pyinstaller module and execute the command to generate exe file
pyinstaller -F -w test.py (-w就是取消窗口)
Overall code
I haven’t learned Python’s syntax and design specifications yet, so code specifications, code reuse, etc. may not be in place. This blog post is mainly a record of ideas and the overall process.
Subsequently, some special effects were optimized, such as using random positions for composite pictures, adding black and white, fleeting and other display special effects, and optional transparency, etc.
import PIL.Image as Image
import glob
import random
import tkinter.filedialog
from tkinter.filedialog import askdirectory, Label, Button, Radiobutton, Entry
import threading
import numpy as np
from PIL import ImageTk
alpha = 0.3
imagesPath = ''
# 滑动条回调 修改透明度
def resize(ev=None):
global alpha
alpha = scale.get() / 100
# 黑白
def blackWithe(image):
# r,g,b = r*0.299+g*0.587+b*0.114
im = np.asarray(image.convert('RGB'))
trans = np.array([[0.299, 0.587, 0.114], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114]]).transpose()
im = np.dot(im, trans)
return Image.fromarray(np.array(im).astype('uint8'))
# 流年
def fleeting(image, params=12):
im = np.asarray(image.convert('RGB'))
im1 = np.sqrt(im * [1.0, 0.0, 0.0]) * params
im2 = im * [0.0, 1.0, 1.0]
im = im1 + im2
return Image.fromarray(np.array(im).astype('uint8'))
# 旧电影
def oldFilm(image):
im = np.asarray(image.convert('RGB'))
# r=r*0.393+g*0.769+b*0.189 g=r*0.349+g*0.686+b*0.168 b=r*0.272+g*0.534b*0.131
trans = np.array([[0.393, 0.769, 0.189], [0.349, 0.686, 0.168], [0.272, 0.534, 0.131]]).transpose()
# clip 超过255的颜色置为255
im = np.dot(im, trans).clip(max=255)
return Image.fromarray(np.array(im).astype('uint8'))
# 反色
def reverse(image):
im = 255 - np.asarray(image.convert('RGB'))
return Image.fromarray(np.array(im).astype('uint8'))
def chooseBaseImagePath():
name = tkinter.filedialog.askopenfilename()
if name != '':
global baseImgPath
baseImgPath = name
baseImageLabel.config(text=name)
baseImg = Image.open(baseImgPath)
widthEntry.delete(0, tkinter.END)
heightEntry.delete(0, tkinter.END)
widthEntry.insert(0, baseImg.size[0])
heightEntry.insert(0, baseImg.size[1])
else:
baseImageLabel.config(text="您没有选择任何文件")
def chooseImagesPath():
name = askdirectory()
if name != '':
global imagesPath
imagesPath = name
ImagesLabel.config(text=name)
else:
ImagesLabel.config(text="您没有选择任何文件")
def thread_it(func, *args):
# 创建
t = threading.Thread(target=func, args=args)
# 守护 !!!
t.setDaemon(True)
# 启动
t.start()
def test():
MyThread(1, "Thread-1", 1).start()
baseImgPath = ''
def generator():
baseImg = Image.open(baseImgPath)
baseImg = baseImg.convert('RGBA')
files = glob.glob(imagesPath + '/*.*') # 获取图片
random.shuffle(files)
num = len(files)
# 模板图片大小
x = baseImg.size[0]
y = baseImg.size[1]
# 每张图片数量 这个公式是为了xNum * yNum 的总图片数量<num又成比例的最大整数
yNum = int((num / (y / x)) ** 0.5)
if yNum == 0:
yNum = 1
xNum = int(num / yNum)
# 图片大小 因为像素没有小数点 为防止黑边所以+1
xSize = int(x / xNum) + 1
ySize = int(y / yNum) + 1
# 生成数量的随机列表 用于随机位置合成图片
l = [n for n in range(0, xNum * yNum)]
random.shuffle(l)
toImage = Image.new('RGB', (x, y))
num = 1
for file in files:
if num <= xNum * yNum:
num = num + 1
else:
break
fromImage = Image.open(file)
temp = l.pop()
i = int(temp % xNum)
j = int(temp / xNum)
out = fromImage.resize((xSize, ySize), Image.ANTIALIAS).convert('RGBA')
toImage.paste(out, (i * xSize, j * ySize))
toImage = toImage.convert('RGBA')
img = Image.blend(baseImg, toImage, alpha)
# 特效 但是会读取像素会降低效率
choose = v.get()
if choose == 1:
img = blackWithe(img)
elif choose == 2:
img = fleeting(img)
elif choose == 3:
img = oldFilm(img)
elif choose == 4:
img = reverse(img)
resize = img.resize((300, 300), Image.ANTIALIAS).convert('RGBA')
# 显示图片
photo = ImageTk.PhotoImage(resize)
showLabel.config(image=photo)
showLabel.image = photo
toImage.save('generator.png')
img = img.resize((int(widthEntry.get()),int(heightEntry.get())), Image.ANTIALIAS).convert('RGBA')
img.save("final.png")
resize.save("resize.png")
class MyThread(threading.Thread): # 继承父类threading.Thread
def __init__(self, threadID, name, counter):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadID = threadID
self.name = name
self.counter = counter
def run(self): # 把要执行的代码写到run函数里面 线程在创建后会直接运行run函数
generator()
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title('generator')
root.geometry('500x550')
baseImageLabel = Label(root, text='')
baseImageLabel.place(x=10, y=10)
baseImageBtn = Button(root, text="选择底图", command=chooseBaseImagePath).place(x=10, y=30)
ImagesLabel = Label(root, text='')
ImagesLabel.place(x=10, y=60)
ImagesBtn = Button(root, text="选择合成图文件夹", command=chooseImagesPath).place(x=10, y=80)
v = tkinter.IntVar()
v.set(0)
Radiobutton(root, variable=v, text='默认', value=0, ).place(x=10, y=120)
Radiobutton(root, variable=v, text='黑白', value=1, ).place(x=110, y=120)
Radiobutton(root, variable=v, text='流年', value=2, ).place(x=210, y=120)
Radiobutton(root, variable=v, text='旧电影', value=3, ).place(x=310, y=120)
Radiobutton(root, variable=v, text='反色', value=4, ).place(x=410, y=120)
scaleLabel = Label(root, text='透明度').place(x=10, y=170)
scale = tkinter.Scale(root, from_=0, to=100, orient=tkinter.HORIZONTAL, command=resize)
scale.set(30) # 设置初始值
scale.pack(fill=tkinter.X, expand=1)
scale.place(x=70, y=150)
Label(root, text='宽(像素)').place(x=180, y=170)
widthEntry = Entry(root, bd=1)
widthEntry.place(x=230, y=173, width=100)
Label(root, text='高(像素)').place(x=320, y=170)
heightEntry = Entry(root, bd=1)
heightEntry.place(x=370, y=173, width=100)
generatorBtn = Button(root, text="生成", command=test).place(x=10, y=220)
showLabel = Label(root)
showLabel.place(x=100, y=220)
root.mainloop()If you want to learn more about programming, please pay attention to the php training column!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Python photo synthesis method. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

