 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance CentOS
CentOS Detailed explanation of two methods for configuring IP address in centos7
Detailed explanation of two methods for configuring IP address in centos7The following column centos introductory tutorial will introduce to you two methods of configuring IP addresses in centos7. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!

There are two main ways to obtain an IP address on centos7, 1: obtain the IP dynamically; 2: set a static IP address
Before configuring the network, we first need to know the name of the centos network card. Centos7 no longer uses the ifconfig command. You can view it through the command IP addr. As shown in the figure, the network card name is ens32 and has no IP address.

1. Dynamically obtain ip (provided that your router has enabled DHCP)
Modify the network card configuration file vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens32 (the last one is the network card name)
You need to modify the dynamically obtained IP address Just two places
(1)bootproto=dhcp
(2)onboot=yes

After modification, restart the network service. Systemctl restart network
[root@mini ~]# systemctl restart network [root@mini ~]#
In this way, the dynamically configured IP address is set. Check again at this time. Click ip addr and you will see that you have obtained the IP address and can access the Internet (ping Baidu)

2. Configure a static IP address
Setting a static IP address is similar to a dynamic iIP. You also need to modify the network card configuration file vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens32 (the last one is the network card name)
(1)bootproto=static
(2)onboot=yes
(3) ) Add a few lines at the end, IP address, subnet mask, gateway, dns server
IPADDR=192.168.1.160 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 DNS1=119.29.29.29 DNS2=8.8.8.8
(4) Restart the network service
[root@mini ~]# systemctl restart network [root@mini ~]#
You can configure only one DNS server. I use two free dns servers. Check the IP address and test the network connection

[root@mini ~]# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens32: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:d2:42:55 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.160/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global noprefixroute ens32
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::f86e:939e:ff9b:9aec/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@mini ~]# ping www.baidu.com
PING www.a.shifen.com (163.177.151.109) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 163.177.151.109 (163.177.151.109): icmp_seq=1 ttl=55 time=27.5 ms
64 bytes from 163.177.151.109 (163.177.151.109): icmp_seq=2 ttl=55 time=35.2 ms
^C
--- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1008ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 27.570/31.425/35.281/3.859 msFor more centos related technical articles, please visit the centos system tutorial column!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of two methods for configuring IP address in centos7. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 CentOS7怎么安装Mysql并设置开机自启动Jun 02, 2023 pm 08:36 PM
CentOS7怎么安装Mysql并设置开机自启动Jun 02, 2023 pm 08:36 PMcentos7不带mysql数据库了,默认的数据库是mariadb(mysql的一个分支)。可以按照以下步骤手动安装mysql数据库。1.下载rpm安装文件wgethttp://repo.mysql.com/mysql-community-release-el7.rpm2.执行rpm安装rpm-ivhmysql-community-release-el7.rpm依赖解析完成后,出现下列选项:dependenciesresolved=================================
 centos7怎么查看php安装目录?三种方法分享Mar 22, 2023 am 10:38 AM
centos7怎么查看php安装目录?三种方法分享Mar 22, 2023 am 10:38 AM如果你正在使用 CentOS 7 操作系统,需要查看 PHP 安装目录以便定位配置文件、扩展等相关信息,那么就需要了解一些相关命令和技巧。下面,我们将为您介绍一些方法来查看 CentOS 7 上的 PHP 安装目录。
 怎么在CentOS7中使用Nginx和PHP7-FPM安装NextcloudMay 24, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
怎么在CentOS7中使用Nginx和PHP7-FPM安装NextcloudMay 24, 2023 pm 08:13 PM先决条件64位的centos7服务器的root权限步骤1-在centos7中安装nginx和php7-fpm在开始安装nginx和php7-fpm之前,我们还学要先添加epel包的仓库源。使用如下命令:yum-yinstallepel-release现在开始从epel仓库来安装nginx:yum-yinstallnginx然后我们还需要为php7-fpm添加另外一个仓库。互联网中有很个远程仓库提供了php7系列包,我在这里使用的是webtatic。添加php7-fpmwebtatic仓库:rpm
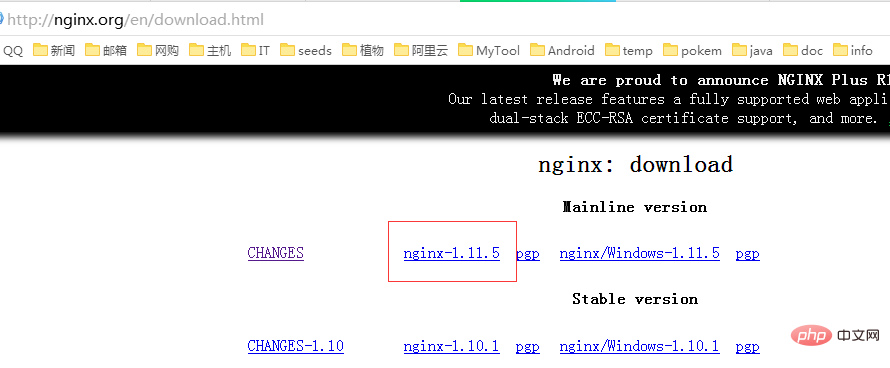 CentOS7如何安装Nginx并配置自动启动May 14, 2023 pm 03:01 PM
CentOS7如何安装Nginx并配置自动启动May 14, 2023 pm 03:01 PM1、官网下载安装包选择适合linux的版本,这里选择最新的版本,下载到本地后上传到服务器或者centos下直接wget命令下载。切换到/usr/local目录,下载软件包#cd/usr/local#wgethttp://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.11.5.tar.gz2、安装nginx先执行以下命令,安装nginx依赖库,如果缺少依赖库,可能会安装失败,具体可以参考文章后面的错误提示信息。#yuminstallgcc-c++#yuminstallpcre#yumins
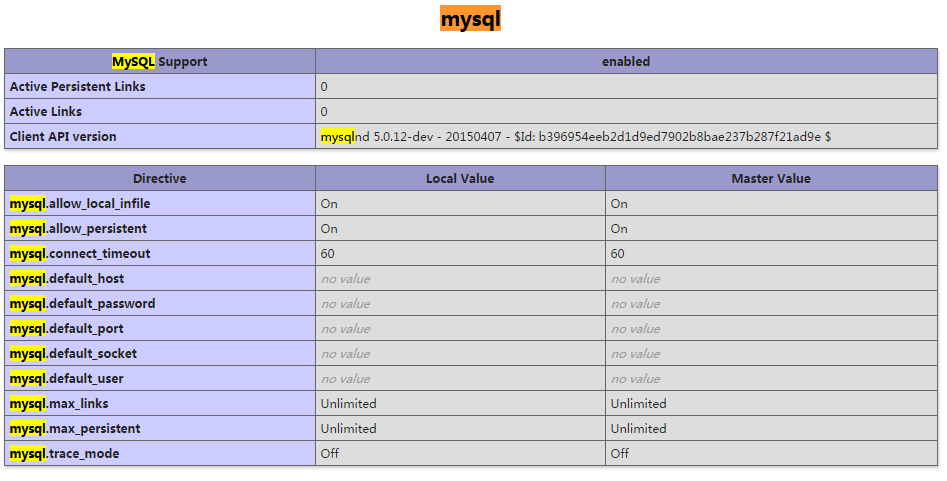 CentOS7下怎么部署php7.1和开启MySQL扩展May 28, 2023 pm 03:01 PM
CentOS7下怎么部署php7.1和开启MySQL扩展May 28, 2023 pm 03:01 PM简单安装(yum方式)安装软件源添加epel源[root@opstrip.comopt]#rpm--import/etc/pki/rpm-gpg/rpm-gpg-key*[root@opstrip.comopt]#rpm-uvhhttp://mirrors.rit.edu/fedora/epel//7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-9.noarch.rpm添加remi源[root@opstrip.comopt]#rpm-uvhhttp://rpms.remirepo.net/e
 如何在 CentOS 7 中安装并配置 Java 环境变量?Apr 22, 2023 pm 04:28 PM
如何在 CentOS 7 中安装并配置 Java 环境变量?Apr 22, 2023 pm 04:28 PM安装环境:Centos764位Jdk1.864位Xshell免费版win10*64位一、先进来,你需要检查自己的openjdk是否卸载(或者判断是否存在,因为一般centos都会预装openjdk):在xshell或rpm-qa|grepjdk中输入rpm-qa|grepjavarpm-qa|grepjava第二,如果有一个对应的openjdk,并且显示了一个响应列表,那么就需要卸载它。在xshell中输入rpm-e-nodepstzdata-文件名(这个文件名是你查看的openjdk文件列表中
 Centos7改系统时区方法有哪些Mar 03, 2023 am 10:47 AM
Centos7改系统时区方法有哪些Mar 03, 2023 am 10:47 AMCentos7修改系统时区的两种方法:1、使用timedatectl命令,可设定和修改时区信息,语法“timedatectl set-timezone 时区标识”;2、修改用户目录下的“.bash_profile”文件,在文件末尾追加“TZ='时区标识'; export TZ”即可。
 centos7使用rpm安装mysql5.7的方法May 27, 2023 am 08:05 AM
centos7使用rpm安装mysql5.7的方法May 27, 2023 am 08:05 AM1.下载4个rpm包mysql-community-client-5.7.26-1.el7.x86_64.rpmmysql-community-common-5.7.26-1.el7.x86_64.rpmmysql-community-libs-5.7.26-1.el7.x86_64.rpmmysql-community-server-5.7.26-1.el7.x86_64.rpm想要用迅雷进行下载得先找到对应的rpm下载路径首先浏览器打开mysql官网:在打开的界面,按键盘f12打开开发者工具


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version





