Home >Common Problem >What is the range of float?
What is the range of float?
- 烟雨青岚Original
- 2020-07-02 16:33:3859027browse
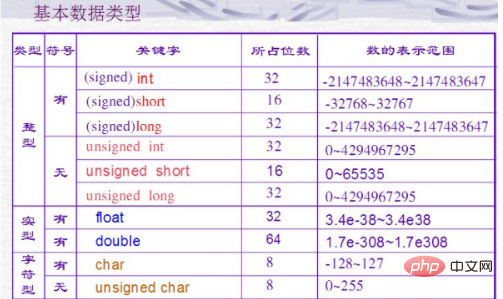
The float range is "-3.4E 38 ~ 3.4E 38". The FLOAT data type is used to store single-precision floating-point numbers or double-precision floating-point numbers; floating-point numbers use the IEEE format. Single-precision values of type floating point have 4 bytes, including a sign bit, an 8-bit binary exponent, and a 23-bit mantissa.

1. Float: The number of bits is 32, the valid digits are 6-7, The value range is -3.4E 38 ~ 3.4E 38
2. Double: The number of bits is 64, the valid digits are 15-16, and the value range is -1.7E-308~1.7E 308
Floating point variables can be declared as float or double according to the needs of the application. The main differences between these two types are the bases in which they can be represented, the storage they require, and their scope.
Extended information
Two types of floating point
1. Single-precision floating-point type (float)
Single-precision floating-point type (float) specifically refers to a single-precision (single-precision) value that occupies 32-bit storage space. Single precision is faster than double precision on some processors and takes up only half the space of double precision, but it will become imprecise when the values are very large or small. Single-precision floating-point variables are useful when you need a fractional part and don't have high precision requirements.
Floating-point data type, FLOAT data type is used to store single-precision floating-point numbers or double-precision floating-point numbers. Floating point numbers use the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) format. Single-precision values of floating-point type have 4 bytes, including a sign bit, an 8-bit binary exponent, and a 23-bit mantissa. Since the high-order bit of the mantissa is always 1, it is not stored as a number. This representation gives float types a range of approximately -3.4E 38 ~ 3.4E 38 .
For example, single-precision floating point types are useful when representing dollars and cents.
These are some examples of declaring single-precision floating-point variables: float hightemp, lowtemp;
2. Double-precision (double) floating-point type
Double precision type, as represented by its keyword "double", occupies 64 bits of storage space. Double-precision is actually faster than single-precision on some modern processors that are optimized for high-speed mathematical calculations.
All mathematical functions beyond human experience, such as sin(), cos(), tan() and sqrt(), return double-precision values. Doubles are the best choice when you need to maintain accuracy over many iterations of a calculation, or when working with very large numbers.
For more related knowledge, please visit PHP Chinese website! !
The above is the detailed content of What is the range of float?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

