Home >Common Problem >What are the characteristics of linked lists?
What are the characteristics of linked lists?
- 藏色散人Original
- 2020-06-30 09:05:1518894browse
The characteristic of the linked list is to use a set of arbitrary storage units to store the data elements of the linear list. Therefore, in order to express the logical relationship between each data element and its direct successor data elements, for the data elements, in addition to storage In addition to its own information, it is also necessary to store information indicating its immediate successor.

Features
Singly linked list, the end of the arrow is the node
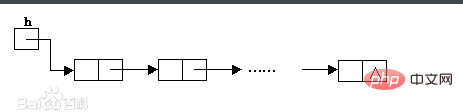
The linked storage representation of a linear table is characterized by using a set of arbitrary storage units to store the data elements of the linear table (this set of storage units can be continuous or discontinuous). Therefore, in order to represent the logical relationship between each data element and its direct successor data element, for the data element, in addition to storing its own information, it is also necessary to store information indicating its direct successor (that is, the storage of the direct successor Location). These two pieces of information form a "node" (as shown in the figure next to the overview), which represents a data element in the linear table. One disadvantage of the linked storage representation of linear tables is that to find a number, you have to start from scratch, which is very troublesome.
Depending on the situation, you can also design other extensions of the linked list yourself. However, data is generally not appended to the edges, because the points and edges of the linked list are basically in one-to-one correspondence (except for the first or last node, but no special circumstances will occur). However, a special case is that if the linked list supports reversing the front and back pointers in a section of the linked list, it may be more convenient to add a reverse mark to the edge.
For non-linear linked lists, you can refer to other related data structures, such as trees and graphs. There is also a data structure based on multiple linear linked lists: skip lists. The speed of basic operations such as insertion, deletion and search can reach O(nlogn), the same as a balanced binary tree.
The domain that stores data element information is called the data domain (let the domain name be data), and the domain that stores the direct successor storage location is called the pointer domain (let the domain name be next). The information stored in the pointer field is also called a pointer or chain.
A linked list consisting of N nodes that respectively represent,,..., are linked in sequence, is called a linked storage representation of a linear list, because each node of such a linked list only contains one pointer field , so it is also called a singly linked list or a linear linked list.
The above is the detailed content of What are the characteristics of linked lists?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

