Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Pitfalls in the front-end written test-JS implicit conversion problem
Pitfalls in the front-end written test-JS implicit conversion problem
- hzcforward
- 2020-06-17 10:00:322132browse
When we write written test questions, we often encounter questions involving implicit conversion, such as
"1" + 2 obj + 1 [] == ![] [null] == false
=== and ==
=== It is called a strict operator. The object type points to the same address or the same original type (numeric value, string, Boolean value) value; == is called an equality operator. Different types will be converted and compared. Undefined and null are equal. , the object type is still a reference. The == operator treats the original value and its wrapped object as equal, but the === operator treats them as unequal.
All obj.a==null (equivalent to obj.a=== null || obj.a ===undefined).
The equality operator is a trap that often causes implicit conversion in JS. It also often appears in our interview questions. However, in real development, in order to avoid unnecessary problems, we require the use of strict operators. But it is still necessary to understand.
If you want to understand JS implicit conversion, you must first start with three knowledge points.
Primitive types
Primitive types (basic types, basic data types, primitive data types) are data that are neither objects nor methods. In JavaScript, there are 7 types: string, number, bigint, boolean, null, undefined, symbol (new in ECMAScript 2016).
falsy value (virtual value)
falsy value (virtual value) is a value that is considered false in a Boolean context. There are only seven falsy values in JavaScript.
- false false Keyword
- 0 Value zero
- 0n When BigInt is used as a Boolean value, follow its rules as a value. 0n is a falsy value.
- An empty string (the length of the string is zero). Strings in JavaScript can be defined with double quotes "", single quotes '', or template literal ``.
- null null - missing value
- undefined undefined - original value
- NaN NaN - non-numeric value
In particular, except for this All seven objects have true values, such as new Number and new Boolean.
let b = new Boolean(false);i
f(b){
//会执行到这里。
}
Four major conversion rules
-
toString rules: Operations for converting other types of values into string types
- null => "null"
- undefined => "undefined"
- true => "true" false=>"false"
- 10 = > "10" "1e21"=>"1e 21"
- [1,2,3] => "1,2,3"
- Object object=> " [Object Object]" is actually calling the toString method
-
ToPrimitive rule: the operation of converting an object type array to a primitive type
- When the object type needs to be converted to a primitive type, it will first look for the valueOf method of the object. If the valueOf method returns a value of the primitive type, the result of ToPrimitive is this value
- If valueOf does not exist or valueOf If the method returns a value that is not a primitive type, it will try to call the object's toString method, which means it will follow the object's ToString rules, and then use the return value of toString as the result of ToPrimitive
- Date is toString first and then ValueOf
- If the original type cannot be obtained after toString and ValueOf, then it will be thrown when judging equality, addition and subtraction
Uncaught TypeError: Cannot convert object to primitive value
-
ToNumber Rule
- ##null=> 0
- undefined => NaN
- "123" =>123 "12ssd"=>NaN ""=>0
- false => 0 true=>1
- Array, objectToPrimitive
-
ToBoolean rules
- The seven falsy values (virtual values) in js are false, and the others are true
-
== 的过程(优先换成数字、字符串)
- 首先看==前后有没有NaN,有的话都是返回false。NaN不等于任何值,包括其本身
- 布尔值会转成数字类型,true转成1,false转成0
- 数字和字符串比较,字符串会转成数字
- undefined和null除了和undefined或null相等,和其他相比都是false
- 数字或者字符串和对象相比,对象使用ToPrimitive规则转换。
- 当两个操作数都是对象时,JavaScript会比较其内部引用,当且仅当他们的引用指向内存中的相同对象(区域)时才相等,即他们在栈内存中的引用地址相同。
-
+的过程(优先换成字符串、数字)
- 如果至少有一个操作数是对象,它会被转换成原始值(字符串,数字或布尔);
- 转换之后,如果至少有一个操作数是字符串类型,第二个操作数会被转换成字符串,并且会执行连接。
- 在其他的情况下,两个操作数都会转换成数字并执行算数加法运算。
-
-的过程(转换成数字) 这个就很简单了,全部用ToNumber规则转换成数字
检测学习成果
我们根据以上所学看几个笔试题。如果你都知道结果,就不用看我的废解释了。
[] == [] [] == ![] [null] == false
第一个,==左右都是对象,比较引用地址,这个两个不同的实例,肯定不相等啊。
第二个,!的优先级高于==,所以先 [] 是真值,求非当让是false了,转成数字0,==左是对象右是数字,对象使用ToPrimitive规则转换成"",再用ToNumber规则就转成0了,判断为相等。
第三个,[null]ToPrimitive再ToNumber规则就转成0,false也转成0。
var a = 1;
var b = "3";
var obj1 = {
i:1,
toString:function() {
return "1";
},
valueOf:function() {
return 1;
}
};
var obj2 = {
i:1,
toString:function() {
return "2";
}
};
var obj3 = {
i:1,
valueOf:function() {
return 3;
}
};
var obj = {
i:1,
};
var objE = {
i:1,
valueOf:function() {
return [];
},
toString:function() {
return {};
}
};
a+b
a + obj
a + objE
a+obj1
a+obj2
a+obj3
b+obj1
b+obj2
b+obj3
a==obj2
a==obj1
这道题比较简单你只要熟练掌握我上面说的那几个知识点可以了。下面直接写出结果啦。
a + b //"13" a + obj //"1[object Object]" a + objE //Uncaught TypeError: Cannot convert object to primitive value a+obj1 //2 a+obj2 //"12" a+obj3 // 4 b+obj1 //"31" b+obj2 //"32" b+obj3 //“33” a==obj2 //false a==obj1 //true
最后提一个比较奇葩的题目。
定义一个变量a,使得下面的表达式结果为true
a == 1 && a == 2 && a == 3
这里我简单提示下,a要是一个对象,重写valueOf方法,让它每次隐式转换的时候,调用时i++。
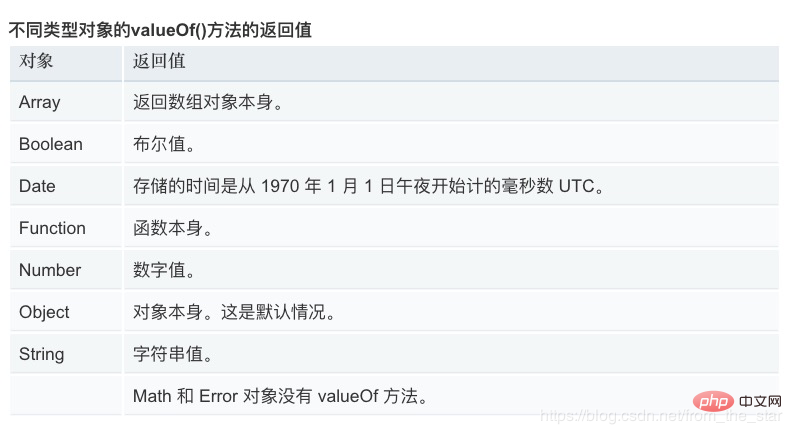
valueOf()在Object上默认返回的是对象不是原始类型,它会再调用toString。所以只要重写toString也可以。
如果还是没有思路,你们可以去看下这道题的文章原文从一道面试题说起—js隐式转换踩坑合集。
推荐教程:《JS教程》
The above is the detailed content of Pitfalls in the front-end written test-JS implicit conversion problem. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

