JavaScript is a scripting language that supports advanced features such as functional programming, closures, and prototype-based inheritance. JavaScript seems to be easy to get started with at first, but as you use it more deeply, you will find that JavaScript is actually very difficult to master, and some basic concepts are confusing. Among them, the this keyword in JavaScript is a relatively confusing concept. In different scenarios, this will be transformed into different objects. There is a view that only by correctly mastering the this keyword in JavaScript can you enter the threshold of the JavaScript language. In mainstream object-oriented languages (such as Java, C#, etc.), the meaning of this is clear and specific, that is, it points to the current object. Usually bound at compile time. In JavaScript, this is bound at runtime. This is the essential reason why the this keyword in JavaScript has multiple meanings.
Due to the nature of JavaScript binding at runtime, this in JavaScript can be the global object, the current object, or any object. It all depends on how the function is called. There are several ways to call functions in JavaScript: as an object method, as a function, as a constructor, and using apply or call. As the saying goes, words are not as good as words, and expressions are not as good as pictures. In order to better understand what JavaScript this points to? Let’s use a picture to explain:
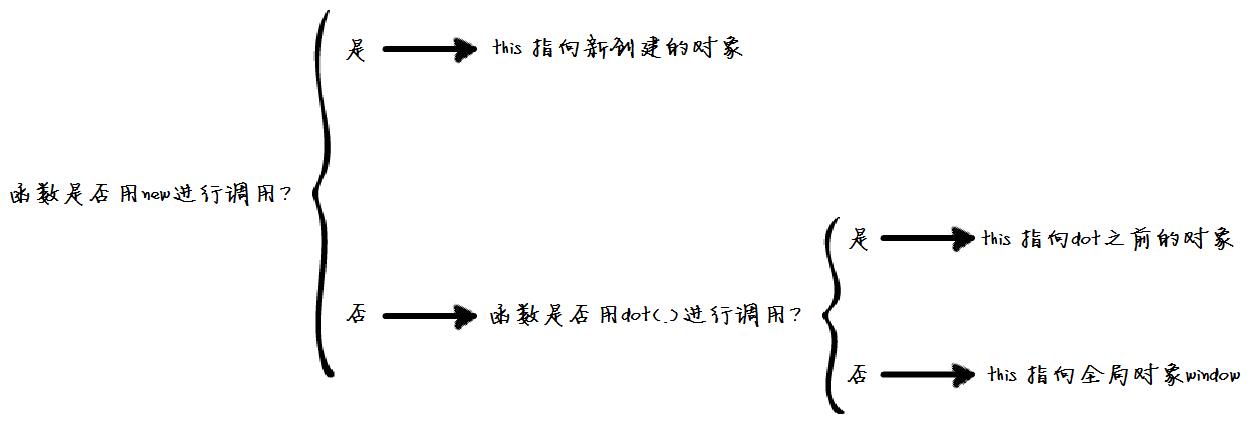
I call the above picture "JavaScript this decision tree" (in non-strict mode). The following uses an example to illustrate how this picture can help us judge this:
var point = {
x : 0,
y : 0,
moveTo : function(x, y) {
this.x = this.x + x;
this.y = this.y + y;
}
};
//决策树解释:point.moveTo(1,1)函数不是new进行调用,进入否决策,
//是用dot(.)进行调用,则指向.moveTo之前的调用对象,即point
point.moveTo(1,1); //this 绑定到当前对象,即point对象
The decision process of the point.moveTo() function in "JavaScript this decision tree" is as follows:
1) Is the point.moveTo function called using new? This is obviously not the case. Go to the "No" branch, that is, is the function called with dot(.)? ;
2) The point.moveTo function is called using dot(.), that is, it enters the "yes" branch, that is, this here points to the previous object point in point.moveTo;
The analytical diagram illustrating what this points to in the point.moveTo function is as shown below:

For another example, look at the following code:
function func(x) {
this.x = x;
}
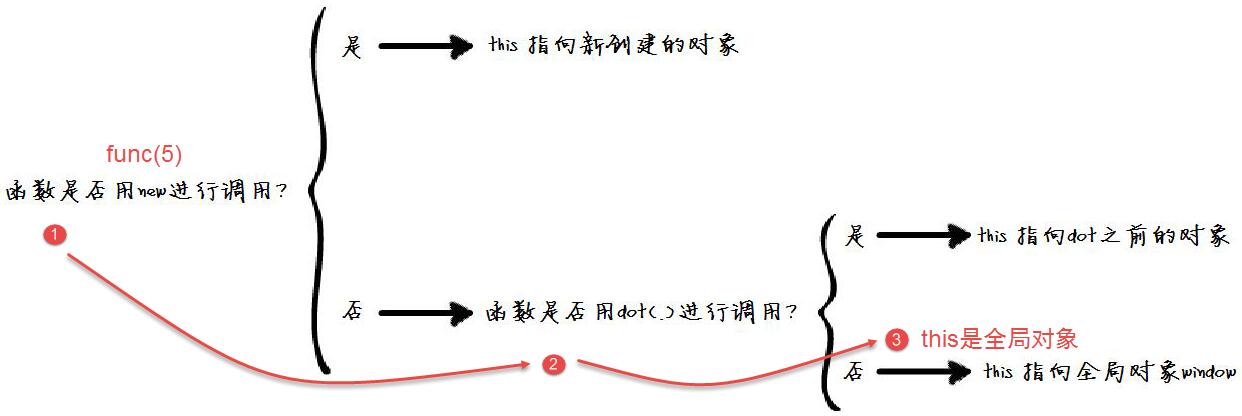
func(5); //this是全局对象window,x为全局变量
//决策树解析:func()函数是用new进行调用的么?为否,进入func()函数是用dot进行调用的么?为否,则 this指向全局对象window
x;//x => 5
The process of the func() function making decisions in "JavaScript this decision tree" is as follows:
1) Is the func(5) function called using new? This is obviously not the case. Go to the "No" branch, that is, is the function called with dot(.)? ;
2) The func(5) function is not called with dot(.), that is, it enters the "No" branch, that is, this here points to the global variable window, then this.x is actually window.x;
The analytical diagram illustrating what this points to in the func function is as shown below:
For the direct call as a function, let’s look at a complex example:
var point = {
x : 0,
y : 0,
moveTo : function(x, y) {
// 内部函数
var moveX = function(x) {
this.x = x;//this 指向什么?window
};
// 内部函数
var moveY = function(y) {
this.y = y;//this 指向什么?window
};
moveX(x);
moveY(y);
}
};
point.moveTo(1,1);
point.x; //=>0
point.y; //=>0
x; //=>1
y; //=>1
The point.moveTo(1,1) function actually calls the moveX() and moveY() functions internally. The this inside the moveX() function is determined in the "JavaScript this decision tree" The process is like this:
1) Is the moveX(1) function called using new? This is obviously not the case. Go to the "No" branch, that is, is the function called with dot(.)? ;
2) The moveX(1) function is not called with dot(.), that is, it enters the "No" branch, that is, this here points to the global variable window, then this.x is actually window.x;
Let’s look at an example of calling a constructor:
function Point(x,y){
this.x = x; // this ?
this.y = y; // this ?
}
var np=new Point(1,1);
np.x;//1
var p=Point(2,2);
p.x;//error, p是一个空对象undefined
window.x;//2
The process of the Point(1,1) function judging this in var np=new Point(1,1) in the "JavaScript this decision tree" is as follows:
1) Is the call to var np=new Point(1,1) using new? This is obviously, entering the "yes" branch, that is, this points to np;
2) Then this.x=1, that is, np.x=1;
The process of the Point(2,2) function determining this in var p= Point(2,2) in the "JavaScript this decision tree" is as follows:
1) Is the call to var p= Point(2,2) using new? This is obviously not the case. Go to the "No" branch, that is, is the function called with dot(.)? ;
2) The Point(2,2) function is not called with dot(.)? If the judgment is no, it enters the "No" branch, that is, this here points to the global variable window, then this.x is actually window.x;
3) this.x=2 means window.x=2.
Finally, let’s take a look at an example of a function being called using call and apply:
function Point(x, y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.moveTo = function(x, y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
var p1 = new Point(0, 0);
var p2 = {x: 0, y: 0};
p1.moveTo.apply(p2, [10, 10]);//apply实际上为p2.moveTo(10,10)
p2.x//10
The process of the p1.moveTo.apply(p2,[10,10]) function in "JavaScript this decision tree" is as follows:
We know that the two methods apply and call are extremely powerful. They allow switching the context of function execution, that is, the object bound to this. p1.moveTo.apply(p2,[10,10]) is actually p2.moveTo(10,10). Then p2.moveTo(10,10) can be interpreted as:
1) Is the p2.moveTo(10,10) function called using new? This is obviously not the case. Go to the "No" branch, that is, is the function called with dot(.)? ;
2) The p2.moveTo(10,10) function is called with dot(.), that is, it enters the "yes" branch, that is, this here points to the previous object p2 in p2.moveTo(10,10). , so p2.x=10;
Regarding the process of JavaScript function execution environment, there is a very good description in the IBM developerworks document library. The excerpt is as follows:
"Function in JavaScript can be executed as an ordinary function or as a method of an object. This is the main reason why this has such rich meaning. When a function is executed, an execution environment (ExecutionContext) will be created , all the behavior of the function occurs in this execution environment. When building the execution environment, JavaScript will first create the arguments variable, which contains the parameters passed in when calling the function. Then it will create the scope chain and initialize it first. The formal parameter list of the function, the value is the corresponding value in the arguments variable. If there is no corresponding value in the arguments variable, the formal parameter is initialized to undefined. If the function contains internal functions, these internal functions are initialized. If not, continue to initialize. For the local variables defined in this function, it should be noted that these variables are initialized to undefined at this time, and their assignment operations will not be executed until the function is executed after the execution environment (ExecutionContext) is successfully created. This is very important for us to understand the role of variables in JavaScript. The domain is very important. In view of the space, we will not discuss this topic here. Finally, assign a value to this variable. As mentioned above, it will be assigned to this global object, current object, etc. according to the function calling method (up to this point). ExecutionContext) is created successfully, the function begins to execute line by line, and the required variables are read from the previously constructed execution environment (ExecutionContext) ”
.Understanding this paragraph will be of great benefit to understanding Javascript functions.
The above is a detailed introduction to the this keyword in JavaScript. Generally, pictures are easier for everyone to understand than text. I hope this article will be helpful to everyone's learning.
 es6数组怎么去掉重复并且重新排序May 05, 2022 pm 07:08 PM
es6数组怎么去掉重复并且重新排序May 05, 2022 pm 07:08 PM去掉重复并排序的方法:1、使用“Array.from(new Set(arr))”或者“[…new Set(arr)]”语句,去掉数组中的重复元素,返回去重后的新数组;2、利用sort()对去重数组进行排序,语法“去重数组.sort()”。
 JavaScript的Symbol类型、隐藏属性及全局注册表详解Jun 02, 2022 am 11:50 AM
JavaScript的Symbol类型、隐藏属性及全局注册表详解Jun 02, 2022 am 11:50 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于Symbol类型、隐藏属性及全局注册表的相关问题,包括了Symbol类型的描述、Symbol不会隐式转字符串等问题,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 原来利用纯CSS也能实现文字轮播与图片轮播!Jun 10, 2022 pm 01:00 PM
原来利用纯CSS也能实现文字轮播与图片轮播!Jun 10, 2022 pm 01:00 PM怎么制作文字轮播与图片轮播?大家第一想到的是不是利用js,其实利用纯CSS也能实现文字轮播与图片轮播,下面来看看实现方法,希望对大家有所帮助!
 JavaScript对象的构造函数和new操作符(实例详解)May 10, 2022 pm 06:16 PM
JavaScript对象的构造函数和new操作符(实例详解)May 10, 2022 pm 06:16 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于对象的构造函数和new操作符,构造函数是所有对象的成员方法中,最早被调用的那个,下面一起来看一下吧,希望对大家有帮助。
 javascript怎么移除元素点击事件Apr 11, 2022 pm 04:51 PM
javascript怎么移除元素点击事件Apr 11, 2022 pm 04:51 PM方法:1、利用“点击元素对象.unbind("click");”方法,该方法可以移除被选元素的事件处理程序;2、利用“点击元素对象.off("click");”方法,该方法可以移除通过on()方法添加的事件处理程序。
 JavaScript面向对象详细解析之属性描述符May 27, 2022 pm 05:29 PM
JavaScript面向对象详细解析之属性描述符May 27, 2022 pm 05:29 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于面向对象的相关问题,包括了属性描述符、数据描述符、存取描述符等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 foreach是es6里的吗May 05, 2022 pm 05:59 PM
foreach是es6里的吗May 05, 2022 pm 05:59 PMforeach不是es6的方法。foreach是es3中一个遍历数组的方法,可以调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传给回调函数进行处理,语法“array.forEach(function(当前元素,索引,数组){...})”;该方法不处理空数组。
 整理总结JavaScript常见的BOM操作Jun 01, 2022 am 11:43 AM
整理总结JavaScript常见的BOM操作Jun 01, 2022 am 11:43 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于JavaScript的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于BOM操作的相关问题,包括了window对象的常见事件、JavaScript执行机制等等相关内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)





