Home >Java >Javagetting Started >Examples to explain variable types in java
Examples to explain variable types in java
- 王林Original
- 2020-05-23 18:12:132352browse

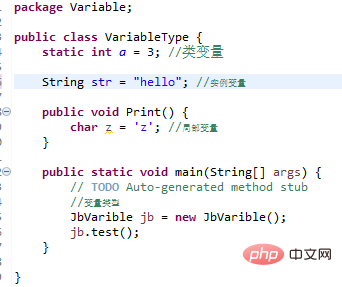
First of all, there are three types of variables supported by the Java language, namely:
Class variables: variables independent of methods, modified with static.
Instance variables: variables independent of methods, but without static modification.
Local variables: variables in class methods.
Example:
(Video tutorial recommendation: java video)
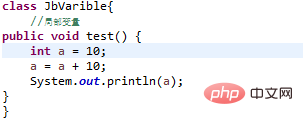
Local variables
Local variables are declared in methods, constructors, or statement blocks;
Local variables are created when methods, constructors, or statement blocks are executed. When they are executed, the variables will be destroyed;
Access modifiers cannot be used for local variables;
Local variables are only visible in the method, constructor or statement block in which they are declared;
Local Variables are allocated on the stack.
Local variables have no default value, so after a local variable is declared, it must be initialized before it can be used.
Example:

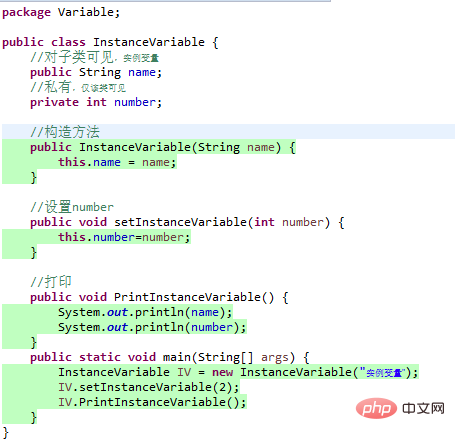
Instance variables

Class variable
Class variables are also called static variables. They are declared with the static keyword in the class, but must be outside the method. No matter how many objects a class creates, the class only has one copy of the class variable. Static variables are rarely used except when declared as constants. Constants refer to variables declared as public/private, final and static types. Constants cannot be changed after initialization. Static variables are stored in the static storage area. Often declared as constants, variables are rarely declared using static alone. Static variables are created when they are accessed for the first time and are destroyed when the program ends. Have similar visibility to instance variables. But in order to be visible to users of the class, most static variables are declared as public types. Default values are similar to instance variables. The default value of numeric variables is 0, the default value of Boolean variables is false, and the default value of reference types is null. The value of a variable can be specified when declaring it or in the constructor. In addition, static variables can also be initialized in static statement blocks. Static variables can be accessed through: ClassName.VariableName. When a class variable is declared as a public static final type, it is generally recommended to use uppercase letters for the class variable name. If the static variable is not of public or final type, its naming method is consistent with the naming method of instance variables and local variables.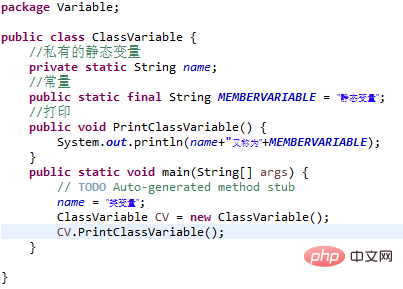

Recommended tutorial: Getting started with java development
The above is the detailed content of Examples to explain variable types in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

