Implementation of double-ended linked list in Redis
- 尚forward
- 2020-04-03 09:40:232312browse

adlist, as a double-ended linked list in Redis, is widely used in many places in Redis, such as the storage of slowlog, error reporting client in master-slave replication, and the implementation of list data structure etc., many are related to this, so it is also a very important data structure.
1) Data structure of double-ended linked list in Redis
(Recommended: redis video tutorial)
Double-ended linked list (the following code is defined in src/adlist.h):
typedef struct list {
listNode *head; //指向链表的第一个节点
listNode *tail; //指向链表的最后一个节点
//复制链表节点时候的回调函数,由于链表节点可以任意类型的数据,不同类型操作不同,故而用回调函数去特殊处理
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
void (*free)(void *ptr); //释放链表节点内存时候的回调函数,理由同上
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key); //比较链表节点值的回调函数,用于自定义比较,理由同上
unsigned long len; //当前列表节点数量
} list;Node of double-ended linked list (the following code is defined in src/adlist.h):
typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *prev; //当前节点的上一个节点
struct listNode *next; //当前节点的下一个节点
void *value; //当前节点存储的值,可以任意类型
} listNode;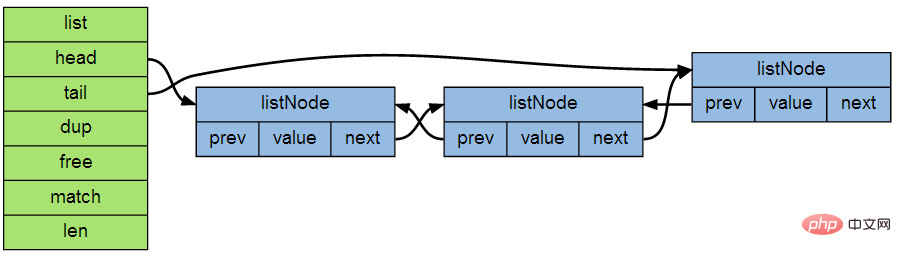
list through head The two pointers and tail point to the head and tail of the linked list respectively, so that the linked list can be traversed in both positive and negative orders. The void *value of listNode can save any data and can be customized through dup, free, and match. How to handle the value of listNode.
2. Simple operation of double-ended linked list
Create a linked list (the following code is defined in src/adlist.c):
list *listCreate(void)
{
struct list *list; //初始化链表
//为链表分配内存
if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)
return NULL;
//为空链表设置初始值
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
list->len = 0;
list->dup = NULL;
list->free = NULL;
list->match = NULL;
return list;
}Append to the end of the linked list (below The code is defined in src/adlist.c):
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node; //初始化node节点
//为新的node节点分配内存
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
//为node节点设置值
node->value = value;
if (list->len == 0) {
//如果空链表则 将头尾指向 新节点 并后继前驱节点设置为NULL
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
//否则将节点的前驱节点设置为原来的尾部节点
node->prev = list->tail;
//由于追加到尾部,后继节点为NULL
node->next = NULL;
//之前的尾部节点的后继节点设置为新增的节点
list->tail->next = node;
//将列表的尾部节点指针指向新增的节点
list->tail = node;
}
//增加链表长度
list->len++;
return list;
}Traverse the linked list:
There are two commonly used ways to traverse the linked list, one is to manually traverse the linked list through a while loop according to the length of the linked list, and the other is It is traversed using the iterator provided by Redis double-ended linked list.
Manual traversal (the following code is defined in the memory release function in src/adlist.c):
void listRelease(list *list)
{
unsigned long len;
//current表示当前遍历的游标指针,next表示下次遍历的游标指针(next作为临时变量用于保存下一个节点)
listNode *current, *next;
//将current指向头部节点
current = list->head;
//计算长度(其实就是 listLength(list))
len = list->len;
//通过长度递减的方式进行遍历,便利到长度为0的时候,遍历结束
while(len--) {
//保存下次循环的节点指针
next = current->next;
//释放掉当前节点,如果设置释放节点的回调函数,则执行用户自定义的函数
if (list->free) list->free(current->value);
zfree(current);
//将游标指向下个节点
current = next;
}
zfree(list);
}Please see below for iterator mode traversal.
3) Iterator of double-ended linked list
In order to facilitate the iteration of the linked list, Redis encapsulates the iterator of the linked list. The iterator structure is as follows (the following code is defined in src/adlist .h):
typedef struct listIter {
listNode *next; //迭代器指向的下一个节点
//迭代方向,由于双端链表保存了head和tail的值,所以可以进行两个方向的迭代
//AL_START_HEAD表示从头向后遍历,AL_START_TAIL表示从尾部向前遍历
int direction;
} listIter;Iterator usage examples:
//l表示list结构,n表示listNode结构,listNode的值保存的是sds字符串
//创建迭代器对象
iter = listGetIterator(l, AL_START_HEAD);
//循环获取下一个需要遍历的节点
while ((n = listNext(iter))) {
//输出返回的节点n的value值
printf("Node Value: %s\n", listNodeValue(n));
}For more redis knowledge, please pay attention to the redis introductory tutorial column.
The above is the detailed content of Implementation of double-ended linked list in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

