 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Summary of method examples of dynamically loading scripts in js_javascript skills
Summary of method examples of dynamically loading scripts in js_javascript skillsSummary of method examples of dynamically loading scripts in js_javascript skills
The example in this article describes the method of dynamically loading scripts in js. Share it with everyone for your reference, the details are as follows:
Recently, the company's front-end map product needs to be divided into modules. It is hoped that users will load which module according to which function they use. This can improve the user experience.
So I searched everywhere to study the loading of js dynamic scripts, but it’s really sad! , there are almost the same articles on the Internet, 4 methods. I hate people who copy other people's results and don't add a link to the original article. Why! The point is that the last method is still a little wrong. After two days of research and information, I would like to share it with you here.
First we need a js file to be loaded. I created a package.js in a fixed folder. After opening it, I wrote a method functionOne in it. It is very simple. The code is as follows:
function functionOne(){
alert("成功加载");
}
The subsequent html files are all created in the same directory.
Method 1: Direct document.write
Create a function1.html under the same folder with the following code:
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init()
{
//加载js脚本
document.write("<script src='package.js'><\/script>");
//加载一个按钮
document.write("<input type=\"button\" value=\"测试运行效果\" onclick=\"operation()\"\/>");
//如果马上使用会找不到,因为还没有加载进来,此处会报错
functionOne();
}
function operation()
{
//可以运行,显示“成功加载”
functionOne();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="初始化加载" onclick="init()"/>
</body>
</html>
You can write scripts to the page through document.write. As shown in the code, you can load the package.js file after clicking the button "Initial Load", but if you run the method functionOne immediately, you will not be able to find this method. Report Error, but clicking the second button ("Test Running Effect" dynamically created through document.write) found that it can be executed. At this time, the script has been loaded. Since this method is asynchronous loading (while continuing to execute the following code, an additional thread is opened to execute the script that needs to be loaded), and document.write will rewrite the interface, which is obviously not practical.
Method 2: Dynamically change the src attribute of an existing script
Create a function2.html under the same folder with the following code:
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript" id="yy" src=""></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init()
{
yy.src = "package.js";
//如果马上使用会找不到,因为还没有加载进来,此处会报错
functionOne();
}
function operation()
{
//可以运行,显示“成功加载”
functionOne();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="测试按钮" onclick="init()"/>
<input type="button" value="测试运行效果" onclick="operation()"/>
</body>
</html>
The advantage of this method is that it does not change the interface elements and does not rewrite the interface elements. However, it is also loaded asynchronously and will have the same problem.
Method 3: Dynamically create script elements (asynchronous)
Create a function3.html under the same folder with the following code:
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init()
{
var myScript= document.createElement("script");
myScript.type = "text/javascript";
myScript.src="package.js";
document.body.appendChild(myScript);
//如果马上使用会找不到,因为还没有加载进来
functionOne();
}
function operation()
{
//可以运行,显示“成功加载”
functionOne();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="测试按钮" onclick="init()"/>
<input type="button" value="测试运行效果" onclick="operation()"/>
</body>
</html>
The advantage of this method compared to the second method is that there is no need to write a script tag in the interface at the beginning. The disadvantage is asynchronous loading and the same problem.
These three methods are all executed asynchronously, so while loading these scripts, the scripts on the main page continue to run. If the above methods are used, the following code will not have the expected effect.
However, you can add an alert in front of functionOne to block the running of the main page script. Then you find that functionOne can run, or your later code needs to be executed under another button. Do it step by step, or else Just define a timer and execute the following code after a fixed time. However, it is definitely impossible to use these methods in the project.
In fact, the third method can be changed to synchronous loading with a few changes.
Method 4: Dynamically create script elements (synchronously)
Create a function4.html under the same folder with the following code:
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init()
{
var myScript= document.createElement("script");
myScript.type = "text/javascript";
myScript.appendChild(document.createTextNode("function functionOne(){alert(\"成功运行\"); }"));
document.body.appendChild(myScript);
//此处发现可以运行
functionOne();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="测试按钮" onclick="init()"/>
</body>
</html>
This method does not load external js files, but adds sub-items to myScript. In Firefox, Safari, Chrome, Opera and IE9, this code works fine. However, it will cause errors in IE8 and lower versions. IE treats <script> as a special element and does not allow DOM access to its child nodes. However, you can use the text attribute of the <script> element to formulate js code, as in the following example: </script>
var myScript= document.createElement("script");
myScript.type = "text/javascript";
myScript.text = "function functionOne(){alert(\"成功运行\"); }";
document.body.appendChild(myScript);
//此处可以运行
functionOne();
The code modified in this way can run in IE, Firefox, Opera and Safari3 and later versions. Versions of Safari prior to 3.0, although they did not correctly support the text attribute, did allow the use of text node technology to specify code. If you need to be compatible with earlier versions of Safari, you can use the following code:
var myScript= document.createElement("script");
myScript.type = "text/javascript";
var code = "function functionOne(){alert(\"成功运行\"); }";
try{
myScript.appendChild(document.createTextNode(code));
}
catch (ex){
myScript.text = code;
}
document.body.appendChild(myScript);
//此处发现可以运行
functionOne();
Here, first try the standard DOM text node method, because all browsers except IE8 and below support this method. If this line of code throws an error, it means IE8 or below, so the text attribute must be used. The whole process can be represented by the following function:
function loadScriptString(code)
{
var myScript= document.createElement("script");
myScript.type = "text/javascript";
try{
myScript.appendChild(document.createTextNode(code));
}
catch (ex){
myScript.text = code;
}
document.body.appendChild(myScript);
}
You can then use this method elsewhere to load the code you need to use. In fact, executing the code this way is the same as passing the same string to eval() in the global function. But we can only use string-form codes here, and there are limitations. Users generally want to provide methods in the form of loadScriptAddress("package.js"), so we need to continue discussing.
Method 5: XMLHttpRequest/ActiveXObject asynchronous loading
Create a function5.html under the same folder with the following code:
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init()
{
//加载package.js文件,设置script的id为yy
ajaxPage("yy","package.js");
//此方法为package.js里面的方法,此处执行方法成功
functionOne();
}
function ajaxPage(sId,url)
{
var oXmlHttp = getHttpRequest();
oXmlHttp.onreadystatechange = function()
{
//4代表数据发送完毕
if ( oXmlHttp.readyState == 4 )
{
//0为访问的本地,200代表访问服务器成功,304代表没做修改访问的是缓存
if(oXmlHttp.status == 200 || oXmlHttp.status == 0 || oXmlHttp.status == 304)
{
includeJS(sId,oXmlHttp.responseText);
}
else
{
}
}
}
oXmlHttp.open("GET",url,true);
oXmlHttp.send(null);
}
function getHttpRequest()
{
if(window.ActiveXObject)//IE
{
return new ActiveXObject("MsXml2.XmlHttp");
}
else if(window.XMLHttpRequest)//其他
{
return new XMLHttpRequest();
}
}
function includeJS(sId,source)
{
if((source != null)&&(!document.getElementById(sId)))
{
var myHead = document.getElementsByTagName("HEAD").item(0);
var myScript = document.createElement( "script" );
myScript.language = "javascript";
myScript.type = "text/javascript";
myScript.id = sId;
try{
myScript.appendChild(document.createTextNode(source));
}
catch (ex){
myScript.text = source;
}
myHead.appendChild( myScript );
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="测试按钮" onclick="init()"/>
</body>
</html>
ActiveXObject只有IE里面才有,其他浏览器大部分支持XMLHttpRequest,通过此办法我们可以实现动态加载脚本了,不过是异步加载,也没法运行functionOne,第二次就可以运行了,但是可惜的是在IE、Firefox、Safari下可以运行,在Opera、Chrome下会出错,Chrome下的错误如下:
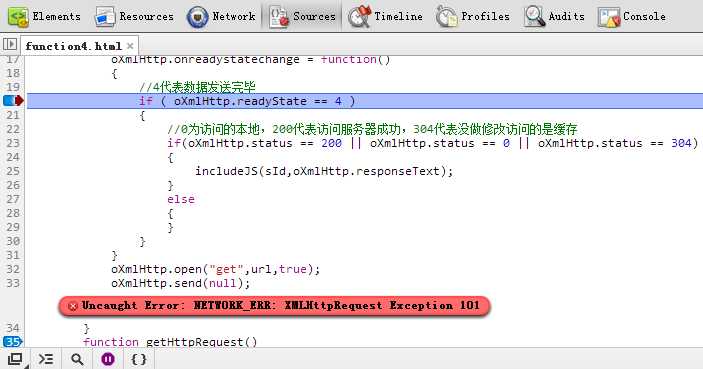
不过只要发布之后在Chrome和Opera下就不会出现错误了。
其实这里把open里面设置为false就是同步加载了,同步加载不需要设置onreadystatechange事件。
方法六:XMLHttpRequest/ActiveXObject同步加载
在这里我把一些情况考虑在内,写成了一个方法,封装为loadJS.js,方便以后直接调用,代码如下:
/**
* 同步加载js脚本
* @param id 需要设置的<script>标签的id
* @param url js文件的相对路径或绝对路径
* @return {Boolean} 返回是否加载成功,true代表成功,false代表失败
*/
function loadJS(id,url){
var xmlHttp = null;
if(window.ActiveXObject)//IE
{
try {
//IE6以及以后版本中可以使用
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Msxml2.XMLHTTP");
}
catch (e) {
//IE5.5以及以后版本可以使用
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
}
else if(window.XMLHttpRequest)//Firefox,Opera 8.0+,Safari,Chrome
{
xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
//采用同步加载
xmlHttp.open("GET",url,false);
//发送同步请求,如果浏览器为Chrome或Opera,必须发布后才能运行,不然会报错
xmlHttp.send(null);
//4代表数据发送完毕
if ( xmlHttp.readyState == 4 )
{
//0为访问的本地,200到300代表访问服务器成功,304代表没做修改访问的是缓存
if((xmlHttp.status >= 200 && xmlHttp.status <300) || xmlHttp.status == 0 || xmlHttp.status == 304)
{
var myHead = document.getElementsByTagName("HEAD").item(0);
var myScript = document.createElement( "script" );
myScript.language = "javascript";
myScript.type = "text/javascript";
myScript.id = id;
try{
//IE8以及以下不支持这种方式,需要通过text属性来设置
myScript.appendChild(document.createTextNode(xmlHttp.responseText));
}
catch (ex){
myScript.text = xmlHttp.responseText;
}
myHead.appendChild( myScript );
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
此处考虑到了浏览器的兼容性以及当为Chrome、Opera时必须是发布,注释还是写的比较清楚的,以后需要加载某个js文件时,只需要一句话就行了,如loadJS("myJS","package.js")。方便实用。
如果想要实现不发布还非要兼容所有浏览器,至少我还没找出这样的同步加载的办法,我们只能通过异步加载开出回调函数来实现。
方法七:回调函数方式
在同一个文件夹下面创建一个function7.html,代码如下:
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init()
{
//加载package.js文件,设置script的id为yy
loadJs("yy","package.js",callbackFunction);
}
function callbackFunction()
{
functionOne();
}
function loadJs(sid,jsurl,callback){
var nodeHead = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
var nodeScript = null;
if(document.getElementById(sid) == null){
nodeScript = document.createElement('script');
nodeScript.setAttribute('type', 'text/javascript');
nodeScript.setAttribute('src', jsurl);
nodeScript.setAttribute('id',sid);
if (callback != null) {
nodeScript.onload = nodeScript.onreadystatechange = function(){
if (nodeScript.ready) {
return false;
}
if (!nodeScript.readyState || nodeScript.readyState == "loaded" || nodeScript.readyState == 'complete') {
nodeScript.ready = true;
callback();
}
};
}
nodeHead.appendChild(nodeScript);
} else {
if(callback != null){
callback();
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="测试按钮" onclick="init()"/>
</body>
</html>
这种方式所有浏览器都支持,但是后面的代码必须放在回调函数里面,也就是异步加载了。看需求使用把!我还是比较喜欢第六种方法的。如果是异步加载的话,方法还有好几种,不过我的出发点是希望实现同步加载,这里就不对异步加载做总结了。
希望本文所述对大家JavaScript程序设计有所帮助。
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor





