Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Check key_len in the explain to determine which index is used
Check key_len in the explain to determine which index is used
- 藏色散人forward
- 2020-03-30 08:51:372092browse
Check the key_len in the explain to determine which index is used?
There are multiple indexes in a table, and the conditions in our where field have multiple index values, so which one should we use?
Recommended: " mysql video tutorial》
We can use explain to view, the key_len field can be seen
For example, the following sql
explain select * from ent_calendar_diary where email='xxxx' and diary_id=1784; +----+-------------+--------------------+------------+-------+-------------------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+--------------------+------------+-------+-------------------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | ent_calendar_diary | NULL | const | PRIMARY,idx_email_stime | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+--------------------+------------+-------+-------------------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
There are two index fields in possible_keys, but key_len is 4 bytes
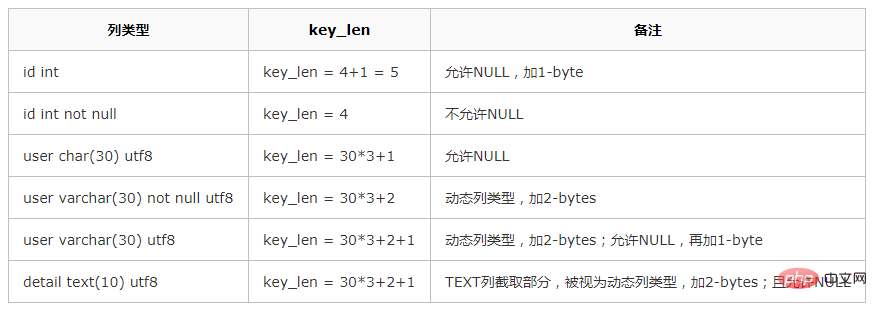
Remarks, key_len only indicates The index column selected for conditional filtering in WHERE does not contain ORDER BY/GROUP BY
int type and not null is 4 bytes, so the above sql uses the primary key index
explain select * from ent_calendar_diary where email='xxxx'; +----+-------------+--------------------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+--------------------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | ent_calendar_diary | NULL | ref | idx_email_stime | idx_email_stime | 767 | const | 111 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+--------------------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
This is 767 bytes, varchar(255) not null 255 * 3 2 exactly matches, so it is the ordinary index of email used
CREATE TABLE `ent_calendar_diary` ( `diary_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `email` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `title` varchar(100) NOT NULL, `summary` varchar(500) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `stime` bigint(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `ctime` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', PRIMARY KEY (`diary_id`), KEY `idx_email_stime` (`email`,`stime`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1809 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
The above is the detailed content of Check key_len in the explain to determine which index is used. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

