
The principle is: extract total RNA from tissues or cells, use the mRNA in it as a template, and use Oligo (dT) or random primers to reverse transcriptase into cDNA. Then use cDNA as a template for PCR amplification to obtain the target gene or detect gene expression.
This technology is mainly used to: analyze gene transcription products, obtain target genes, synthesize cDNA probes, and construct efficient RNA transcription systems.
RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a technology that combines RNA reverse transcription (RT) and cDNA polymerase chain amplification (PCR).
First, cDNA is synthesized from RNA through the action of reverse transcriptase, and then the cDNA is used as a template to amplify and synthesize the target fragment. RT-PCR technology is sensitive and versatile and can be used to detect gene expression levels in cells, the content of RNA viruses in cells, and to directly clone cDNA sequences of specific genes.
The RNA used as template can be total RNA, mRNA or in vitro transcribed RNA product. Regardless of the type of RNA used, the key is to ensure that the RNA is free of RNase and genomic DNA contamination.
The primers used for reverse transcription can be selected from random primers, Oligo dT and gene-specific primers according to the specific conditions of the experiment. For short eukaryotic cell mRNAs that do not have a hairpin structure, all three are available.
For more FAQ, please visit the PHP Chinese website.
The above is the detailed content of What are the principles and applications of rtPCR. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 趣谈ChatGPT原理及算法Apr 27, 2023 pm 08:46 PM
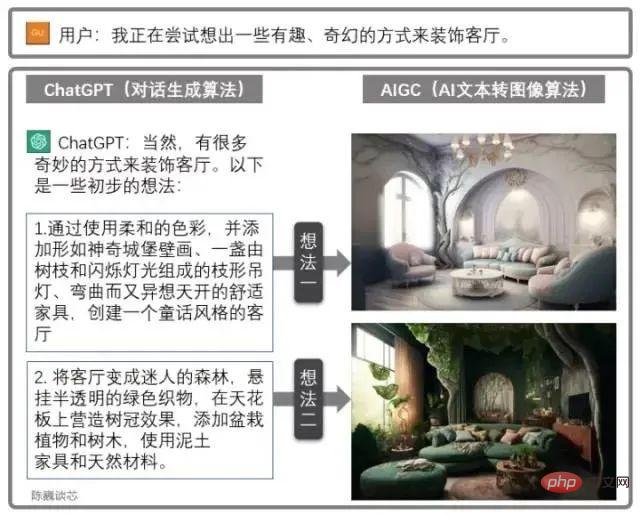
趣谈ChatGPT原理及算法Apr 27, 2023 pm 08:46 PM去年12月1日,OpenAI推出人工智能聊天原型ChatGPT,再次赚足眼球,为AI界引发了类似AIGC让艺术家失业的大讨论。ChatGPT是一种专注于对话生成的语言模型。它能够根据用户的文本输入,产生相应的智能回答。这个回答可以是简短的词语,也可以是长篇大论。其中GPT是GenerativePre-trainedTransformer(生成型预训练变换模型)的缩写。通过学习大量现成文本和对话集合(例如Wiki),ChatGPT能够像人类那样即时对话,流畅的回答各种问题。(当然回答速度比人还是
 深入解析MySQL MVCC 原理与实现Sep 09, 2023 pm 08:07 PM
深入解析MySQL MVCC 原理与实现Sep 09, 2023 pm 08:07 PM深入解析MySQLMVCC原理与实现MySQL是目前最流行的关系型数据库管理系统之一,它提供了多版本并发控制(MultiversionConcurrencyControl,MVCC)机制来支持高效并发处理。MVCC是一种在数据库中处理并发事务的方法,可以提供高并发和隔离性。本文将深入解析MySQLMVCC的原理与实现,并结合代码示例进行说明。一、M
 深入解析Struts2框架的工作原理与实现方式Jan 05, 2024 pm 04:08 PM
深入解析Struts2框架的工作原理与实现方式Jan 05, 2024 pm 04:08 PM解读Struts2框架的原理及实现方式引言:Struts2作为一种流行的MVC(Model-View-Controller)框架,被广泛应用于JavaWeb开发中。它提供了一种将Web层与业务逻辑层分离的方式,并且具有灵活性和可扩展性。本文将介绍Struts2框架的基本原理和实现方式,同时提供一些具体的代码示例来帮助读者更好地理解该框架。一、框架原理:St
 Golang实现继承方法的基本原理和方式Jan 20, 2024 am 09:11 AM
Golang实现继承方法的基本原理和方式Jan 20, 2024 am 09:11 AMGolang继承方法的基本原理与实现方式在Golang中,继承是面向对象编程的重要特性之一。通过继承,我们可以使用父类的属性和方法,从而实现代码的复用和扩展性。本文将介绍Golang继承方法的基本原理和实现方式,并提供具体的代码示例。继承方法的基本原理在Golang中,继承是通过嵌入结构体的方式实现的。当一个结构体嵌入另一个结构体时,被嵌入的结构体就拥有了嵌
 深入探究Maven生命周期的功能和机制Jan 04, 2024 am 09:09 AM
深入探究Maven生命周期的功能和机制Jan 04, 2024 am 09:09 AM深入理解Maven生命周期的作用与原理Maven是一款非常流行的项目管理工具,它使用一种灵活的构建模型来管理项目的构建、测试和部署等任务。Maven的核心概念之一就是生命周期(Lifecycle),它定义了一系列阶段(Phase)和每个阶段的目标(Goal),帮助开发人员和构建工具按照预定的顺序执行相关操作。Maven的生命周期主要分为三套:Clean生命周
 深入理解Java反射机制的原理与应用Dec 23, 2023 am 09:09 AM
深入理解Java反射机制的原理与应用Dec 23, 2023 am 09:09 AM深入理解Java反射机制的原理与应用一、反射机制的概念与原理反射机制是指在程序运行时动态地获取类的信息、访问和操作类的成员(属性、方法、构造方法等)的能力。通过反射机制,我们可以在程序运行时动态地创建对象、调用方法和访问属性,而不需要在编译时知道类的具体信息。反射机制的核心是java.lang.reflect包中的类和接口。其中,Class类代表一个类的字节
 了解PHP底层开发原理:基础知识和概念介绍Sep 10, 2023 pm 02:31 PM
了解PHP底层开发原理:基础知识和概念介绍Sep 10, 2023 pm 02:31 PM了解PHP底层开发原理:基础知识和概念介绍作为一名PHP开发者,了解PHP底层开发原理是非常重要的。正因为如此,本文将介绍PHP底层开发的基础知识和概念,帮助读者更好地理解和应用PHP。一、什么是PHP?PHP(全称:HypertextPreprocessor)是一门开源的脚本语言,主要用于Web开发。它可以嵌入到HTML文档中,通过服务器解释执行,并生成
 PHP邮件队列系统的原理和实现方式是什么?Sep 13, 2023 am 11:39 AM
PHP邮件队列系统的原理和实现方式是什么?Sep 13, 2023 am 11:39 AMPHP邮件队列系统的原理和实现方式是什么?随着互联网的发展,电子邮件已经成为人们日常生活和工作中必不可少的通信方式之一。然而,随着业务的增长和用户数量的增加,直接发送电子邮件可能会导致服务器性能下降、邮件发送失败等问题。为了解决这个问题,可以使用邮件队列系统来通过串行队列的方式发送和管理电子邮件。邮件队列系统的实现原理如下:邮件入队列当需要发送邮件时,不再直

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool







