Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >ES6 Map principle analysis
ES6 Map principle analysis
- angryTomforward
- 2019-11-27 15:05:324981browse

The keys of ES6 Map can be any data structure and are not repeated.
So what is the underlying principle of map?
Map is implemented using linked lists and hash ideas.
First of all, Map can be deleted, and the deleted data can be intermediate values. The advantage of a linked list is that adding and deleting elements anywhere in the middle is very fast. There is no need to move other elements, just change the pointing of the pointer.
[Related course recommendations: JavaScript video tutorial]
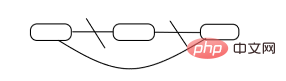 .
.
When a lot of data is stored, the chain will be too long and the search efficiency will be slow. Therefore, we can create a bucket (a container for storing objects) and change the hash value according to the hash algorithm. into a fixed value) to evenly distribute data to prevent the chain from being too long.
As shown below: There are 3 positions in the bucket, each position is an object, and the next attribute points to the next object to connect unrelated objects together.

Save the Map attribute value and attribute name into the value of the object.
Simple simulation of Map, the code is as follows:
function Mymap() { //构造函数
this.init();
}
//初始化函数,创建桶(数组),每个位置都是一个对象,每个对象的属性上设置next属性,并且初始化为null。
Mymap.prototype.init = function () {
this.tong = new Array(8);
for (var i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
this.tong[i] = new Object();
this.tong[i].next = null;
}
};
//添加数据。
Mymap.prototype.set = function (key, value) {
var index = this.hash(key); //获取到当前设置的key设置到那个位置上
var TempBucket = this.tong[index]; //获取当前位置的对象
while (TempBucket.next) { //遍历如果当前对象链接的下一个不为空
if (TempBucket.next.key == key) { //如果要设置的属性已经存在,覆盖其值。
TempBucket.next.value = value;
return; //return ,不在继续遍历
} else {
TempBucket = TempBucket.next; //把指针指向下一个对象。 }
}
TempBucket.next = { //对象的next是null ,添加对象。
key: key,
value: value,
next: null
}
};
//查询数据
Mymap.prototype.get = function (key) {
var index = this.hash(key);
var TempBucket = this.tong[index];
while(TempBucket){
if(TempBucket.key == key){
return TempBucket.value;
}else{
TempBucket = TempBucket.next;
}
}
return undefined;
}
//删除数据
Mymap.prototype.delete = function(key){
var index = this.hash(key);
var TempBucket = this.tong[index];
while(TempBucket){
if(TempBucket.next.key == key){
TempBucket.next = TempBucket.next.next;
return true;
}else{
TempBucket = TempBucket.next;
}
}
}
//看当前属性是否存在
Mymap.prototype.has = function(key){
var index = this.hash(key);
var TempBucket = this.tong[index];
while(TempBucket){
if(TempBucket.key == key){
return true;
}else{
TempBucket = TempBucket.next;
}
}
return false;
}
//清空这个map
Mymap.prototype.clear = function(){
this.init();
}
//使设置的属性平均分配到每个位置上,使得不会某个链条过长。
Mymap.prototype.hash = function (key) {
var index = 0;
if (typeof key == "string") {
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
index = index + isNaN(key.charCodeAt(i)) ? 0 : key.charCodeAt(i);
}
}
else if (typeof key == 'object') {
index = 0;
}
else if (typeof key == 'number') {
index = isNaN(key) ? 7 : key;
} else {
index = 1;
}
return index % 8;
}
var map = new Mymap(); //使用构造函数的方式实例化map
map.set('name','zwq');
map.get('name');
map.has('name);
This article comes from the js tutorial column, welcome to learn!
The above is the detailed content of ES6 Map principle analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

