PHP evolution history — from v5.6 to v8.0
- 藏色散人forward
- 2019-09-20 09:24:504449browse
In this article, we will take 15 minutes to briefly review the PHP v7.x version changes.
After the release of PHP 7.3, in order to better understand the new features and optimizations of this widely popular programming language, I decided to study PHP development in detail: what is being developed and where it is headed.
After looking at a brief list of features implemented in PHP during the development of PHP 7.x, I decided to put together this list myself as a nice addition , I believe some people will also find it useful.
We will start with PHP 5.6 as a baseline and look at what has been added or changed. At the same time, I have also added direct links to the relevant official documentation for each feature mentioned, so if you are interested in reading in depth, please feel free to do so.
PHP 7.0
Anonymous class support\
In the following two situations, anonymous classes may be used In named classes:
● When the class does not need to be recorded
● When the class is only used once during program execution
new class($i) {
public function __construct($i) {
$this->i = $i;
}
}Integer division function—Safe division (even divisible by 0)\
This function will return the integer part of the result after the first parameter is divided by the second parameter. When the divisor (the second parameter) is 0, this function throws an E_WARNING error and returns FALSE.
intdiv(int $numerator, int $divisor)
Added a new empty merge operation assignment—that is, “??”
$x = NULL; $y = NULL; $z = 3; var_dump($x ?? $y ?? $z); // int(3) $x = ["c" => "meaningful_value"]; var_dump($x["a"] ?? $x["b"] ?? $x["c"]); // string(16) "meaningful_value"
Added a new operator—spaceship symbol( )\
The spaceship character is used to optimize and simplify comparison operations.
// 使用 <=> (飞船符)前
function order_func($a, $b) {
return ($a < $b) ? -1 : (($a > $b) ? 1 : 0);
}
// 使用 <=> (飞船符)之后
function order_func($a, $b) {
return $a <=> $b;
}Scalar Type Declaration \
This is just the first step towards implementing stronger typed programming language features in PHP — v0.5.
function add(float $a, float $b): float {
return $a + $b;
}
add(1, 2); // float(3)Return type declaration \
Added the ability to return types other than scalar classes including inheritance. Somehow it's not set as an optional feature (will be explained in v7.1 :blush: )
interface A {
static function make(): A;
}
class B implements A {
static function make(): A {
return new B();
}
}Group usage declaration
// 显式使用语法:
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\ClassA;
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\ClassB;
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\ClassC;
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\ClassD as Fizbo;
// 分组使用语法:
use FooLibrary\Bar\Baz\{ ClassA, ClassB, ClassC, ClassD as Fizbo };Generator Delegate
The following new syntax is allowed in the generator function body:
yield from <expr>
Performance improvement
PHP 7 is faster than PHP 5.6 double.
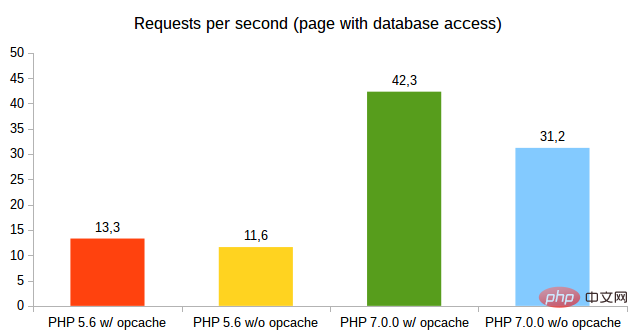
Significantly reduces memory usage
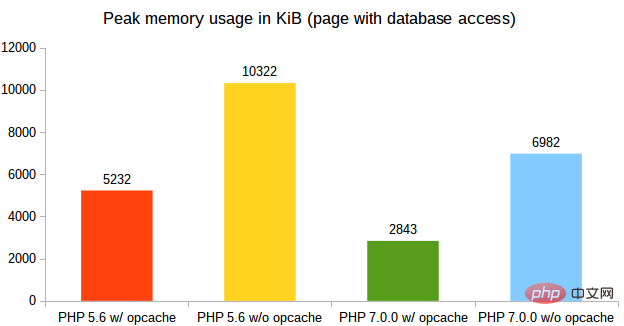
As can be seen from the chart, PHP 7.0 Huge improvements in performance and (reduced) memory usage. For pages with database queries, version 7.0.0 is 3 times faster than version 5.6 with opcache enabled and 2.7 times faster without opcache. In terms of memory usage, the difference between the two is also very obvious.
Throwable interface
The refactored exception class has a non-intuitive naming scheme and can reduce confusion, especially for beginners.
Errors and Exceptions now implement Throwable.
This is the Throwable hierarchy:
interface Throwable
|- Error implements Throwable
|- ArithmeticError extends Error
|- DivisionByZeroError extends ArithmeticError
|- AssertionError extends Error
|- ParseError extends Error
|- TypeError extends Error
|- ArgumentCountError extends TypeError
|- Exception implements Throwable
|- ClosedGeneratorException extends Exception
|- DOMException extends Exception
|- ErrorException extends Exception
|- IntlException extends Exception
|- LogicException extends Exception
|- BadFunctionCallException extends LogicException
|- BadMethodCallException extends BadFunctionCallException
|- DomainException extends LogicException
|- InvalidArgumentException extends LogicException
|- LengthException extends LogicException
|- OutOfRangeException extends LogicException
|- PharException extends Exception
|- ReflectionException extends Exception
|- RuntimeException extends Exception
|- OutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException
|- OverflowException extends RuntimeException
|- PDOException extends RuntimeException
|- RangeException extends RuntimeException
|- UnderflowException extends RuntimeException
|- UnexpectedValueException extends RuntimeException*⚠ Warning! You can only
implement Throwable by inheriting Error and Exception,
That is to say, an interface inherited from Throwable can only be implemented by subclasses of Exception or Error.
Unicode Codepoint escape syntax — “\u{xxxxx}”
echo "\u{202E}Reversed text"; //输出反转文本
echo "mañana"; // "ma\u{00F1}ana"
echo "mañana"; // "man\u{0303}ana" "n" 结合 ~ 字符 (U+0303)Context-sensitive parser \
Globally reserved words have become semi-reserved:
callable class trait extends implements static abstract final public protected private const enddeclare endfor endforeach endif endwhile and global goto instanceof insteadof interface namespace new or xor try use var exit list clone include include_once throw array print echo require require_once return else elseif default break continue switch yield function if endswitch finally for foreach declare case do while as catch die self parent
In addition to still prohibiting the definition of a class constant named class, because class name resolution::class.
Generator return expression
Uniform variable syntax
dirname () function level support
PHP 7.1
Nullable type
function answer(): ?int {
return null; //成功
}
function answer(): ?int {
return 42; // 成功
}
function answer(): ?int {
return new stdclass(); // error
}
function say(?string $msg) {
if ($msg) {
echo $msg;
}
}
say('hello'); // 成功 -- 打印 hello
say(null); // 成功 -- 不打印
say(); // 错误 -- 参数丢失
say(new stdclass); //错误 --错误类型Void Returns
function should_return_nothing(): void {
return 1; // 致命错误: void 函数不能有返回值
}Unlike other return types that are enforced when calling a function, this type is checked at compile time, which means that the error will occur when the function is not called.
Function with void return type or void function can return implicitly or use a return statement without a value:
function lacks_return(): void {
// valid
}Iterable pseudo-type** \
** Functions usually accept or return an array or implement a Traversable object for use with foreach. However, because array is a primitive type and Traversable is an interface, there is currently no way to use a type declaration on a parameter or return type to indicate that the value is iterable.
function foo(iterable $iterable) {
foreach ($iterable as $value) {
// ...
}
}iterable can also be used as a return type, indicating that the function will return an iterable value. If the returned value is not an array or instance of Traversable, a TypeError is thrown.
function bar(): iterable {
return [1, 2, 3];
}Parameters declared as iterable can use null or an array as the default value.
function foo(iterable $iterable = []) {
// ...
}* Callable closure
class Closure {
...
public static function fromCallable(callable $callable) : Closure {...}
...
}Square bracket syntax for array structure assignment
$array = [1, 2, 3]; //为 $a,$b 和 $c 按键值从 0 开始的方式分配 $array 数组元素的值 [$a, $b, $c] = $array; // 使用 “a”,“b” 和 “c” 键分别为 $a,$b 和 $c 分配 $array 中数组元素的值 ["a" => $a, "b" => $b, "c" => $c] = $array;
list() 的方括号语法
$powersOfTwo = [1 => 2, 2 => 4, 3 => 8]; list(1 => $oneBit, 2 => $twoBit, 3 => $threeBit) = $powersOfTwo;
类常量的可见性
class Token {
// 常量默认为 public
const PUBLIC_CONST = 0;
// 常量也可以定义可见性
private const PRIVATE_CONST = 0;
protected const PROTECTED_CONST = 0;
public const PUBLIC_CONST_TWO = 0;
//常量只能有一个可见性声明列表
private const FOO = 1, BAR = 2;
}捕获多个异常类型
try {
// 部分代码...
} catch (ExceptionType1 | ExceptionType2 $e) {
// 处理异常的代码
} catch (\Exception $e) {
// ...
}PHP 7.2
参数类型扩大
<?php
class ArrayClass {
public function foo(array $foo) { /* ... */ }
}
// 这个 RFC 提议允许类型被扩大为无类型,也就是任何类型。
// 类型可以作为参数传递。
// 任何类型的限制都可以通过用户写在方法体中的代码来实现。
class EverythingClass extends ArrayClass {
public function foo($foo) { /* ... */ }
}不可数对象的计数 \
当一个标量或者没有实现 Countable 接口 的对象调用 count() 方法时会返回 1(不合逻辑)。
在 PHP 7.2 版本 中,对以标量、null、或者一个没有实现 Countable 接口 接口的对象作为参数调用 count() 方法的情况,新增了一个 WARNING 警告。
在命名空间的 列表用法中使用尾随逗号
use Foo\Bar\{ Foo, Bar, Baz, };Argon2 密码散列算法 \
现有的 password 函数为散列密码提供了一个向前兼容的简单接口。这个 RFC 提议 password 函数实现 Argon2i (v1.3),用来取代 Bcrypt 密码散列算法。
调试 PDO 预处理语句模拟
$db = new PDO(...); // 生成没有绑定值的语句 $stmt = $db->query('SELECT 1'); var_dump($stmt->activeQueryString()); // => string(8) "SELECT 1" $stmt = $db->prepare('SELECT :string'); $stmt->bindValue(':string', 'foo'); // 返回执行前,未解析的查询 var_dump($stmt->activeQueryString()); // => string(14) "SELECT :string" // 返回执行后,已解析的查询 $stmt->execute(); var_dump($stmt->activeQueryString()); // => string(11) "SELECT 'foo'"
PHP 7.3
JSON_THROW_ON_ERROR
很长一段时间内在使用 JSON 时没有足够的方式去处理错误,全世界的开发人员都认为这是该语言的巨大缺点。
在 PHP v7.2 版本前,我们需要使用一种方法来从 JSON 中获取错误,虽然它既不可靠,也不精通;
例子如下:
json_decode("{");
json_last_error() === JSON_ERROR_NONE //结果是错误的
json_last_error_msg() // 结果是"语法错误"那么让我们看看如何使用这种新语法糖:
use JsonException;
try {
$json = json_encode("{", JSON_THROW_ON_ERROR);
return base64_encode($json);
} catch (JsonException $e) {
throw new EncryptException('Could not encrypt the data.', 0, $e);
}从上面的代码可以看到 json_encode 函数现在有了一个可选参数 JSON_THROW_ON_ERROR — 这将捕获错误并且用下列 异常方法 显示出来:
$e->getMessage(); // 相当于 json_last_error_msg() $e->getCode(); // 相当于 json_last_error()
添加 is_countable 函数
// 之前:
if (is_array($foo) || $foo instanceof Countable) {
// $foo is countable
}
// 之后
if (is_countable($foo)) {
// $foo is countable
}添加数组函数 array_key_first(), array_key_last()
$firstKey = array_key_first($array); $lastKey = array_key_last($array);
原生支持同站点 Cookie 判断
有两种方式使用同站点 Cookie 判断:Lax 和 Strict。它们的区别在于跨域 HTTP GET 请求中 Cookie 的可访问性。 使用 Lax 的 Cookie 允许跨域 GET 访问,而使用 Strict 的 Cookie 不允许跨域 GET 访问。 而 POST 方法则没有区别:因为浏览器不允许在跨域的 POST 请求中访问 Cookie。
Set-Cookie: key=value; path=/; domain=example.org; HttpOnly; SameSite=Lax|Strict
从 PCRE 迁移至 PCRE2
Argon2 哈希密码功能增强
现有的 password_* 函数为散列密码提供了前向兼容的简化接口。此 RFC 建议在 password _* 函数中实现 Argon2id,以用作最初提出的 Argon2i 的安全替代方案。
在函数调用中允许尾随逗号
$newArray = array_merge(
$arrayOne,
$arrayTwo,
['foo', 'bar'], // 函数调用中允许使用逗号结尾
);list () 使用参考
$array = [1, 2]; list($a, &$b) = $array;
相当于:
$array = [1, 2]; $a = $array[0]; $b = &$array[1];
不建议使用不区分大小写的常量
PHP 7.4(开发中)
参数类型(Typed properties)
class User {
public int $id;
public string $name;
public function __construct(int $id, string $name) {
$this->id = $id;
$this->name = $name;
}
}外部函数接口(Foreign Function Interface)
外部函数接口(下简称 FFI)是 Python 和 LuaJIT 在快速原型中非常实用的功能之一。FFI 使得纯脚本语言能直接调用 C 语言函数和数据类型,从而更高效地开发「系统代码」。而 PHP 在 FFI 中开辟了一种使用 PHP 语言编写 PHP 扩展并绑定到 C 语言库的方法。
非空赋值运算符(Null Coalescing Assignment Operator)
// 下面几行代码完成相同功能 $this->request->data['comments']['user_id'] = $this->request->data['comments']['user_id'] ?? 'value'; // 使用非空赋值运算符,替代上面的方法 $this->request->data['comments']['user_id'] ??= 'value';
预加载(Preloading)
PHP 已经使用操作码缓存(opcode caches)很久了(APC、Turck MMCache、Zend OpCache)。它们通过 几乎完全 消除 PHP 代码重新编译的开销,实现了显著的性能提升。新的预加载功能将只需一个新的 php.ini 配置实现 ——opcache.preload。通过该配置指定一个 PHP 文件,该文件将执行预加载任务,然后通过包含其他文件或使用 opcache_compile_file() 函数预加载其他文件。
始终可用的哈希扩展(Always available hash extension)
这将使 hash 扩展(ext/hash)始终可用,类似于 date。hash 扩展提供了非常丰富实用功能与哈希算法,这是不仅有利于 PHP 开发者,也有利于 PHP 本身的开发。
在去 PHP 8.0 的旅途中
JIT.
简而言之。当你启动 PHP 程序时, Zend Engine 会将代码解析为抽象语法树(AST)并将其转换为操作码。操作码是 Zend 虚拟机的执行单元 (Zend VM)。 操作码相当底层(low-leve),转换为机器代码比原始 PHP 代码要快得多。 PHP 在核心中有一个名为 OPcache 的扩展,用于缓存这些操作码。
“JIT” 是一种在运行时编译部分代码的技术,因此可以使用编译版本。
这是仍在讨论的最新和最大的 PHP 优化策略之一。 PHP 工程师正期待这个新的功能可以在他们的应用中挤压出来多少性能。我自己是真的热衷于亲眼看到这一点。
内部函数的一致类型错误 \
如果参数解析失败,则使得内部参数解析 API 始终生成 TypeError 错误。应该要注意的是, 这些错误也包括用来表示传递太少 / 很多参数的情况的 ArgumentCountError (TypeError 的子类) 。
性能比较
我编写了一个简单的测试来帮助轻松比较不同 PHP 版本的性能(使用 Docker )。 这甚至可以通过添加新容器名称轻松检查新 PHP 版本的性能。
在 Macbook pro,2.5 GHz Intel Core i7 上运行。
PHP 版本 : 5.6.40
-------------------------------------- test_math : 1.101 sec. test_stringmanipulation : 1.144 sec. test_loops : 1.736 sec. test_ifelse : 1.122 sec. Mem: 429.4609375 kb Peak mem: 687.65625 kb -------------------------------------- Total time: : 5.103 PHP 版本 : 7.0.33 -------------------------------------- test_math : 0.344 sec. test_stringmanipulation : 0.516 sec. test_loops : 0.477 sec. test_ifelse : 0.373 sec. Mem: 421.0859375 kb Peak mem: 422.2109375 kb -------------------------------------- Total time: : 1.71 PHP 版本 : 7.1.28 -------------------------------------- test_math : 0.389 sec. test_stringmanipulation : 0.514 sec. test_loops : 0.501 sec. test_ifelse : 0.464 sec. Mem: 420.9375 kb Peak mem: 421.3828125 kb -------------------------------------- Total time: : 1.868 PHP 版本 : 7.2.17 -------------------------------------- test_math : 0.264 sec. test_stringmanipulation : 0.391 sec. test_loops : 0.182 sec. test_ifelse : 0.252 sec. Mem: 456.578125 kb Peak mem: 457.0234375 kb -------------------------------------- Total time: : 1.089 PHP 版本 : 7.3.4 -------------------------------------- test_math : 0.233 sec. test_stringmanipulation : 0.317 sec. test_loops : 0.171 sec. test_ifelse : 0.263 sec. Mem: 459.953125 kb Peak mem: 460.3984375 kb -------------------------------------- Total time: : 0.984 PHP 版本 : 7.4.0-dev -------------------------------------- test_math : 0.212 sec. test_stringmanipulation : 0.358 sec. test_loops : 0.205 sec. test_ifelse : 0.228 sec. Mem: 459.6640625 kb Peak mem: 460.109375 kb -------------------------------------- Total time: : 1.003
如果你有兴趣自己测试,可以在仓库中找到相关代码 meskis/php-bench.
PHP 5.6 及更高版本的基准测试
我非常喜欢在 servebolt.com 上对 5.6 及以上的所有主要版本进行可视化性能编译。结果请查看下面表格。
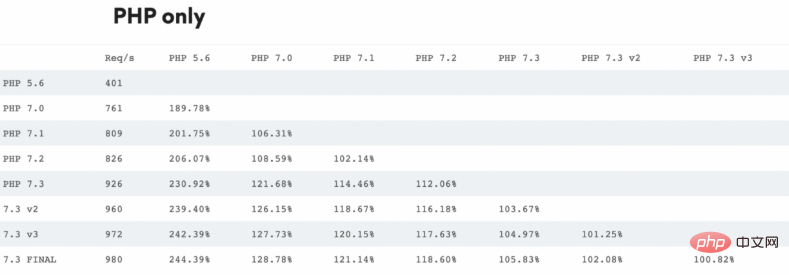
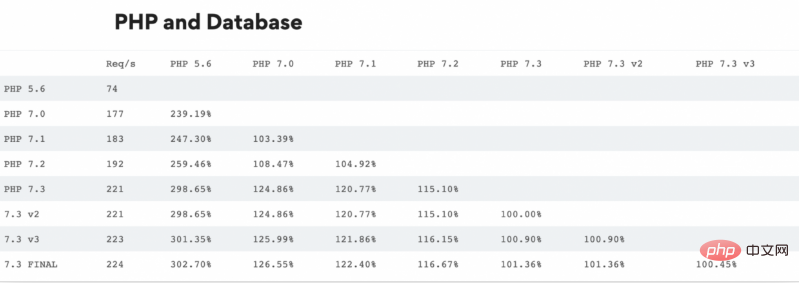
性能摘要
PHP 7.0.0 是一个重要的里程碑,它现住地提高了性能,降低了内存使用量,但 PHP 的维护人员没办法再改进它了。 剩下的一个要点是 JIT (Just in time) 编译。 它是 PHP 8.0 的一部分。
发展方向
在整个 PHP 7.x 版本中,有一条通往更多类型化(和更客观)和现代编程语言的可见路径。尽管如此,PHP 还是喜欢采用其他编程语言中简洁有用的特性。
很快我们就能看到一些更好的功能,例如:
● 命名参数
● Nullsafe 调用
● 枚举类型 (ENUMs)
● 箭头函数
有了这些, PHP 开发人员将加入现代编程语言采用者的行列。没有一种语言是完美的,但 PHP 为它的未来铺平了道路。
太长了,读不下去了
为了让篇幅更短,我已经根据最新版本的 PHP 7.3 列出了相对重要的变动。 它们是:
● 添加了新的空合并运算符
● 标量类型声明
● 返回类型声明
● Throwable 接口
● 可为空类型
● 空返回
● 用于数组析构的方括号语法
● 类常量可见性

