Home >Backend Development >PHP Problem >Do you really understand the PHP coding style specification?
Do you really understand the PHP coding style specification?
- 王林forward
- 2019-08-27 18:01:142113browse
Due to the flexibility of PHP, many people do not pay attention to a good code specification when writing code, making the already flexible PHP code look messy. In fact, PSR-1 and PSR-2 in the PSR specification have been defined. There are some specifications in PHP coding. As long as we abide by these specifications, we can write very beautiful and neat code even if we use a flexible scripting language. First, let’s take a look at the PSR specifications that have been passed, and then briefly explain some specific requirements of the PSR-1 and PSR-2 specifications
Passed PSR:
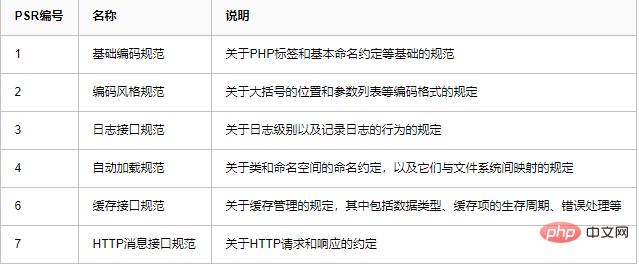
PSR-1 basic coding specification:
1. Open and close Tags
First of all, the PHP code must start with a
2. Side effects
PHP files either declare classes, interfaces, functions, etc., or perform logical operations (such as reading and writing files or sending output to the browser), but not both.
3. Naming
#The naming of the class must comply with the camel case naming convention starting with an uppercase letter. In other words, class names should start with a capital letter. There is no requirement to name properties, but they should be consistent. Method names must conform to the camelCase naming convention starting with lowercase. All letters in class constants must be capitalized, and words are separated by underscores.
PSR2-Coding Style Specification:
1. PSR-1 requires PHP code to start with tag, but should end with a blank line.
2. A blank line should be inserted after the namespace statement, and there should also be a blank line after the use statement block. Don't make multiple use statements in the same line of code.
3. The beginning and end of the class
The class keyword, class name, and the extends and implements keywords must be on the same line. If a class implements multiple interfaces, the interface names can be on the same line of the class declaration, or they can occupy separate lines. If you choose to place these interface names on multiple lines, the first interface name must be on its own line and not follow the implements keyword. The opening brace ({) of a class should be written on its own line after the function declaration, and the closing brace (}) should also be written on its own line after the class body. That is, the class declaration looks like this:
class EarthGame extends Game implements
Playable,
Savable
{
//类体
}You can also put the class name on the same line as the class declaration.
class EarthGame extends Game implements Playble, Savable
{
//类体
}4. Attribute declaration
Each attribute must have an access modifier (public, private or protected). Attributes cannot be declared using the keyword var. The specification of attribute names is already covered in PSR-1: you can use underscores, lowercase camelCase naming, or uppercase camelCase naming, but should remain consistent. (Personally recommend using lowercase camel case for attributes)
5. The beginning and end of the method
All methods must have access modifiers (public, private or protected). The access modifier must be after abstract or final and before static. Method parameters with default values should be placed at the end of the parameter list.
Single-line declaration
The opening curly brace ({) of the method should be written on its own line after the method name, and the closing curly brace (}) should also be written on its own line after the method body (directly following the method after the code). Method parameter lists should not start or end with spaces (i.e. they should follow the parentheses surrounding them). For each parameter, there should be a comma after the parameter name (or default value), and a space after the comma. This may sound complicated, as shown below:
final public static function generateTile(int $diamondCount, bool $polluted = false)
{
//方法体
}Multi-line declaration
A single-line method declaration is not practical if the method has many parameters. At this point we can split the parameter list so that each parameter (including type, parameter variable, default value, and comma) is on its own indented line. In this case, the closing parenthesis should be placed on the line after the parameter list, aligned with the beginning of the method declaration. The opening curly brace ({) should follow the closing parenthesis on the same line, separated by a space. The method body should start on a new line. Again, this may sound complicated, but the following example should help you understand this rule.
public function __construct(
int $size,
string $name,
bool $warparound = false,
bool $aliens = false
) {
//方法体
}6. Lines and indentation
Code should be indented using 4 spaces instead of tabs. We can check the editor settings and set it to use 4 spaces instead of tabs when the tab key is pressed. Each line of code should be no longer than 120 characters.
7、方法与函数调用
方法名称和开始圆括号之间不能有空格。方法调用中的参数列表的规则与方法声明中的参数列表规则相同。换言之,对于单行调用,开始圆括号后或结束圆括号前不能有空格。每个参数之后应该紧跟一个逗号,下一个参数前应该有一个空格。如果需要使用多行代码进行方法调用,那么每个参数应该自成一行并缩进,而且结束圆括号也应该自成一行。
$earthGanme = new EarthGame( 5, 'earth', true, true ); $earthGame::generateTile(5, true);
8、流程控制
流程控制关键字(if、for、while等)后面必须紧跟一个空格。但是,开始圆括号后不能有空格。同样,结束圆括号前不能有空格。因此内容应该紧贴在括号内的。与类和(单行)函数声明相比,流程控制代码的开始花括号应该与结束圆括号在同一行。结束花括号应该自成一行。以下是一个简单的示例。
$title = [];for ($x = 0; $x < $diamondCount; $x++) { if ($polluted) {
$title[] = new PollutionDecorator(new DiamondDecorator(new Plains()));
} else {
$title[] = new DiamondDecorator(new Plains());
}
}想了解更多相关问题请访问PHP中文网:PHP视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Do you really understand the PHP coding style specification?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

