Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Ajax complete and detailed tutorial (1)
Ajax complete and detailed tutorial (1)
- 王林forward
- 2019-08-26 14:44:584251browse
Introduction to Ajax
Composed of HTML, JavaScript™ technology, DHTML, and the DOM, Ajax is a brilliant way to transform clumsy Web interfaces into interactive Ajax applications. It is a powerful way to build a website.
Ajax attempts to build a bridge between the functionality and interactivity of desktop applications and the constantly updated web applications. You can use dynamic user interfaces and beautiful controls like those found in desktop applications, but in a web application.
Basic technologies used in Ajax applications:
1. HTML is used to create Web forms and determine fields used by other parts of the application.
2. JavaScript code is the core code that runs Ajax applications and helps improve communication with server applications.
3. DHTML or Dynamic HTML, used to dynamically update forms. We will mark up HTML using divs, spans, and other dynamic HTML elements.
4. Document Object Model DOM is used to process (through JavaScript code) the HTML structure and (in some cases) the XML returned by the server.
The definition of Ajax
Ajax= Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (and DHTML, etc.) Asynchronous asynchronous JS and XML.
XMLHttpRequest This is a JavaScript object; it is the object that handles all server communication. Creating this object is simple, as shown in Listing 1.
Listing 1. Creating a new XMLHttpRequest object
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();</script>It is JavaScript technology that talks to the server through the XMLHttpRequest object. This is not ordinary application flow, and this is where the power of Ajax comes from.
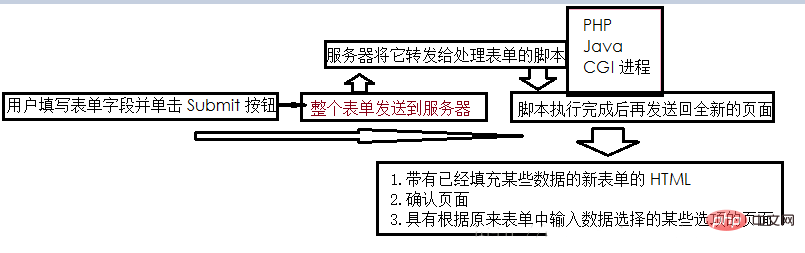
Ajax basically puts JavaScript technology and the XMLHttpRequest object between the web form and the server.

After getting the handle of XMLHttpRequest, use JavaScript code to complete the following tasks:
1. Get form data: JavaScript code can easily extract data from HTML forms. and sent to the server.
2、修改表单上的数据:更新表单也很简单,从设置字段值到迅速替换图像。
3、解析 HTML 和 XML:使用 JavaScript 代码操纵 DOM(请参阅 下一节),处理 HTML 表单服务器返回的 XML数据的结构
对于前两点,需要非常熟悉 getElementById() 方法,如 清单 2 所示。
清单 2. 用 JavaScript 代码捕获和设置字段值
//捕获字段值:
// 获得字段"phone"的值并用其创建一个变量phone
var phone = document.getElementById("phone").value;
//设置字段值:
// 从response的数组中获得值并将其写到标签中
document.getElementById("order").value = response[0];
document.getElementById("address").value = response[1];DOM的功能
当需要在 JavaScript 代码和服务器之间传递 XML 和改变 HTML 表单的时候,我们再深入研究 DOM。
获取 Request 对象
XMLHttpRequest 是 Ajax 应用程序的核心.
var xmlhttp;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
{// 从 IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari 中获得XMLHttpRequest对象
xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else
{//从 IE6, IE5 中获得XMLHttpRequest对象
xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}清单 4. 以支持多种浏览器的方式创建 XMLHttpRequest 对象
/* Create a new XMLHttpRequest object to talk to the Web server */
var xmlHttp = false;
/*@cc_on @*/
/*@if (@_jscript_version >= 5)
try {
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Msxml2.XMLHTTP");
} catch (e) {
try {
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
} catch (e2) {
xmlHttp = false;
}
}
@end @*/
if (!xmlHttp && typeof XMLHttpRequest != 'undefined') {
xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}这段代码的核心分为三步:
1、建立一个变量 xmlHttp 来引用即将创建的 XMLHttpRequest 对象。
2、尝试在 Microsoft 浏览器中创建该对象:
1)尝试使用 Msxml2.XMLHTTP 对象创建它。
如果失败,再尝试 Microsoft.XMLHTTP 对象。
3、如果仍然没有建立 xmlHttp,则以非 Microsoft 的方式创建该对象。 最后,xmlHttp 应该引用一个有效的XMLHttpRequest 对象,无论运行什么样的浏览器。
Ajax 的请求/响应
与服务器上的 Web 应用程序打交道的是 JavaScript 技术,而不是直接提交给那个应用程序的 HTML 表单。
发出请求
如何使用XMLHttpRequest 对象?
首先–需要一个能够调用JavaScript 方法 的Web 页面 。
接下来就是在所有 Ajax 应用程序中基本都雷同的流程:
1、从 Web 表单中获取需要的数据。
2、建立要连接的 URL。
3、打开到服务器的连接。
4、设置服务器在完成后要运行的函数。
5、发送请求。
清单 5 中的示例 Ajax 方法就是按照这个顺序组织的:
清单 5. 发出 Ajax 请求
function callServer() {
// 获得city和state的值
var city = document.getElementById("city").value;
var state = document.getElementById("state").value;
// 当它们的值任一个不存在的时候结束JS
if ((city == null) || (city == "")) return;
if ((state == null) || (state == "")) return;
// 创建连接的URL对象
var url = "/scripts/getZipCode.php?city=" + escape(city) + "&state=" + escape(state);
// 打开一个连接服务器的连接
xmlHttp.open("GET", url, true);
// 设置一个方法,当请求返回的时候调用这个方法
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = updatePage;
//xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function()
//{
// if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200)
// {
// document.getElementById("myDiv").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText;
// }
//}
// 发生链接
xmlHttp.send(null);
}开始的代码使用基本 JavaScript 代码获取几个表单字段的值。 然后设置一个 PHP 脚本作为链接的目标。 要注意脚本 URL 的指定方式,city 和 state(来自表单)使用简单的 GET 参数附加在 URL 之后。 最后一个参数如果设为 true,那么将请求一个异步连接(这就是 Ajax 的由来)。 如果使用 false,那么代码发出请求后将等待服务器返回的响应。 如果设为 true,当服务器在后台处理请求的时候用户仍然可以使用表单(甚至调用其他 JavaScript 方法)。 onreadystatechange属性可以告诉服务器在运行完成后做什么。因为代码没有等待服务器,必须让服务器知道怎么做以便您能作出响应。
在这个示例中,如果服务器处理完了请求,一个特殊的名为 updatePage() 的方法将被触发。
最后,使用值 null 调用send()。因为已经在请求 URL 中添加了要发送给服务器的数据(city 和state),所以请求中不需要发送任何数据。这样就发出了请求,服务器按照您的要求工作。
处理响应
1.什么也不要做,直到 xmlHttp.readyState 属性的值等于 4。
2.服务器将把响应填充到 xmlHttp.responseText 属性中。
其中的第一点,即就绪状态;
第二点,使用 xmlHttp.responseText 属性获得服务器的响应,清单 6中的示例方法可供服务器根据 清单 5 中发送的数据调用。
清单 6. 处理服务器响应
function updatePage() {
if (xmlHttp.readyState == 4) { var response = xmlHttp.responseText;
document.getElementById("zipCode").value = response;
}
}它等待服务器调用,如果是就绪状态,则使用服务器返回的值(这里是用户输入的城市和州的 ZIP 编码)设置另一个表单字段的值。
一旦服务器返回 ZIP 编码,updatePage() 方法就用城市/州的 ZIP 编码设置那个字段的值,用户就可以改写该值。这样做有两个原因:
保持例子简单,说明有时候可能希望用户能够修改服务器返回的数据。
要记住这两点,它们对于好的用户界面设计来说很重要。
连接 Web 表单
一个 JavaScript 方法捕捉用户输入表单的信息并将其发送到服务器,另一个 JavaScript 方法监听和处理响应,并在响应返回时设置字段的值。所有这些实际上都依赖于调用 第一个 JavaScript 方法,它启动了整个过程。
利用 JavaScript 技术更新表单。
清单 7. 启动一个 Ajax 过程
<form>
<p>City: <input type="text" name="city" id="city" size="25"
onChange="callServer();" /></p>
<p>State: <input type="text" name="state" id="state" size="25"
onChange="callServer();" /></p>
<p>Zip Code: <input type="text" name="zipCode" id="city" size="5" /></p>
</form>结束语
在下一期文章中,您将掌握:
1、XMLHttpRequest 对象
2、学会如何处理 JavaScript 和服务器的通信
3、如何使用 HTML 表单以及如何获得 DOM 句柄。
更多相关问题请访问PHP中文网:Ajax视频教程
本文系列文章:
The above is the detailed content of Ajax complete and detailed tutorial (1). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

