前面的话
CSS有三种基本的定位机制:普通流、浮动和绝对定位。利用定位,可以准确地定义元素框相对于其正常位置应该出现的位置,或者相对于父元素、另一个元素甚至浏览器窗口本身的位置。但元素究竟如何定位,定位到什么位置,主要依靠top/right/bottom/left这四个偏移属性。本文就定位中的偏移做详细介绍。
position定位
值: static | relative | absolute | fixed | inherit
初始值: static
应用于: 所有元素
继承性: 无
static:元素框正常生成。块级元素生成一个矩形框,作为文档流的一部分,行内元素则会创建一个或多个行框,置于其父元素中
relative:元素框偏移某个距离。元素仍保持其未定位前的形状,它原本所占的空间仍保留
absolute:元素框从文档流完全删除,并相对于其包含块定位,包含块可能是文档中的另一个元素或者是初始包含块。元素原先在正常文档流中所占的空间会关闭,就好像 该元素原来不存在一样。元素定位后生成一个块级框,而不论原来它在正常流中生成何种类型的框
fixed:元素框的表现类似于将position设置为absolute,不过其包含块是视窗本身
[注意]相对定位实际上被看作普通流定位模型的一部分,因为元素的位置相对于它在普通流中的位置
包含块
【1】根元素
根元素HTML的包含块(也称为初始包含块)是一个视窗大小的矩形,即HTML的父级document
【2】非根元素
如果position值是relative或static,包含块由最近的块级框、表单元格或行内祖先框的内容边界构成
如果position值是absolute,包含块设置为最近的position值不是static的祖先元素(可以是任何类型),过程如下:
[1]如果这个祖先是块级元素,包含块则设置为该元素的内边距边界。换句话说,就是由边框界定的区域
[2]如果这个祖先是行内元素,包含块则设置为该祖先元素的内容边界
[3]如果没有祖先,元素的包含块定义为初始包含块,即document
[注意]由于元素可以定位到其包含块的外面。这与浮动元素使用负外边距浮动到其父元素内容区外面很类似。所以这里包含块实际上应该是定位上下文,或者定位父级
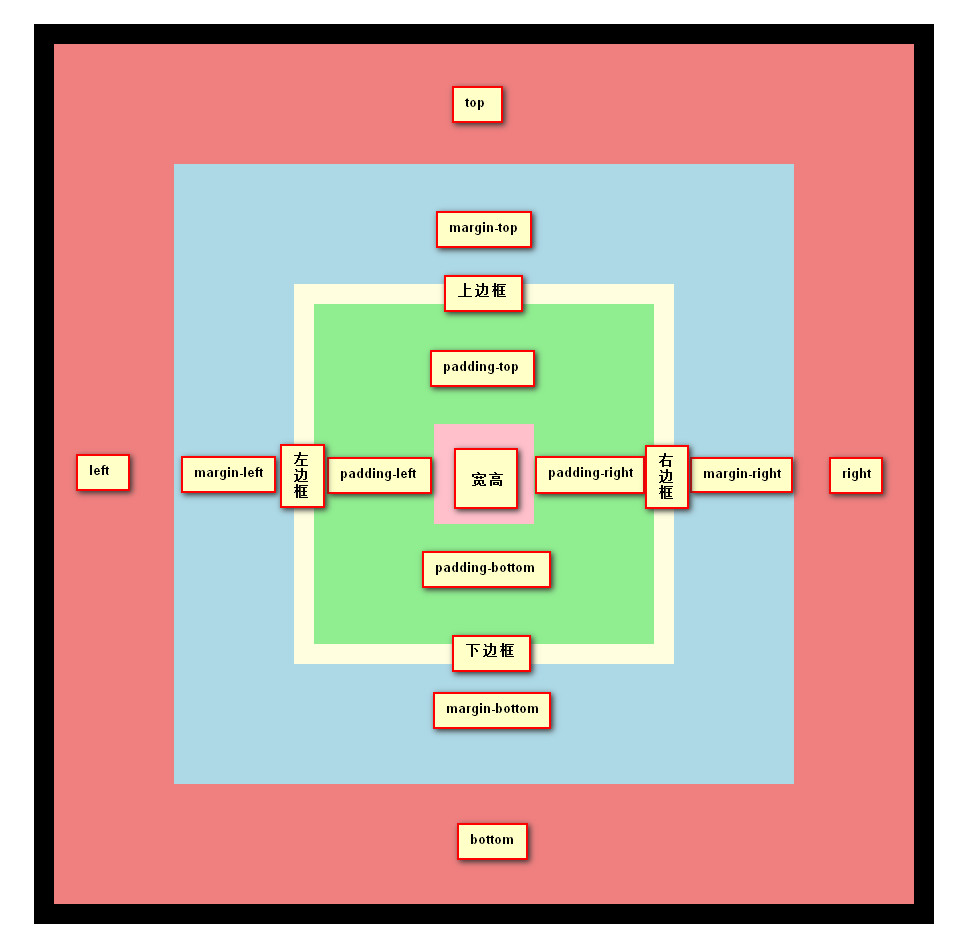
偏移属性
三种定位机制使用了4个属性来描述定位元素各边相对于其包含块的偏移。这4个属性被称为偏移属性。
top/right/bottom/left
值:
初始值: auto
应用于: 定位元素(也就是position值不是static的元素)
继承性: 无
百分数: 对于top和bottom,相对于包含块的clientHeight;对于right和left,相对于包含块的clientWidth
这些属性描述了距离包含块最近边的偏移。top描述了定位元素上外边界离其包含块的顶端有多远。如果top为正值,会把定位元素的上外边距边界下移,若为负值,则会把定位元素的上外边距移到其包含块的顶端之上。类似地,left描述了定位元素的左外边距边界在其包含块左边界右边(正值)或左边(负值)有多远。如果是正值,会把定位元素的外边距边界移到包含块左边界右边,而负值则将其移到包含块左边界左边。所以,正值会导致向内偏移,使边界朝着包含块的中心移动,而负值会导致向外偏移。
偏移定位元素的外边距边界时,带来的影响是元素的所有一切(包含外边距、边框、内边距和内容)都会在定位的过程中移动
[注意]定位元素的边界是指定位元素margin外侧的边界;包含块的包含区域是指包含块的border内侧的padding+content区域
绝对定位
元素绝对定位时,会从文档流中完全删除。然后相对于其包含块定位,其边界根据偏移属性(top、left等)放置。定位元素不会流入其他元素的内容,反之亦然。元素绝对定位时,会为其后代元素建立一个包含块
[注意]如果文档可滚动,绝对定位元素会随着它滚动,因为元素最终会相对于正常流的某一部分定位
当元素绝对定位时,偏移属性表现如下:
left:<span style="color: #800080;">0</span> 元素的左边界(margin-left外侧)位于包含块的左边界内侧(border-<span style="color: #000000;">left内侧)
top:</span><span style="color: #800080;">0</span> 元素的上边界(margin-rop外侧)位于包含块的上边界内侧(border-<span style="color: #000000;">top内侧)
right:</span><span style="color: #800080;">0</span> 元素的右边界(margin-right外侧)位于包含块的右边界内侧(border-<span style="color: #000000;">right内侧)
bottom:</span><span style="color: #800080;">0</span> 元素的下边界(margin-bottom外侧)位于包含块的下边界内侧(border-<span style="color: #000000;">bottom内侧)<br></span>
<span style="color: #000000;"> 当top、right、bottom、left四个值都为auto时(即都处于默认状态时),
left:auto 元素的左边界位于元素处于静态位置时的左边界
top:auto 元素的上边界位于元素处于静态位置时的上边界
right:auto 元素的右边界位于正好能包裹住元素的横向区域的右边界(margin</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">right外侧)
bottom:auto 元素的下边界位于正好能包裹住元素的纵向区域的下边界(margin</span>-bottom外侧)
[注意]元素的静态位置是指元素在正常流中原本的位置,更确切的讲,顶端的静态位置是从包含块的上边界到假想框的上外边距边界之间的距离。假想框是假设元素position属性为static时元素的第一个框。如果这个假想框在包含块的上面,则这个值为负
<span style="color: #008000;">//</span><span style="color: #008000;">DEMO中,包含块的width和height都是180px,padding为10px,所以包含块的clientWidth和clientHeight都是200px</span>
格式化
对于普通流的元素来说,水平格式化的7大属性是margin-left、border-left、padding-left、width、padding-right、border-right、margin-right7个属性的值加在一起必须是元素包含块的宽度,这往往是块元素的父元素的width值(因为块级元素的父级元素几乎都是块级元素)。垂直方向也类似。关于元素格式化的详细信息移步至此
但是对于绝对定位元素则不相同。它的水平格式化等式为:
left + margin-left + border-left-width + padding-left + width + padding-right + border-right-width + margin-right + right = 包含块的clientWidth
类似的,垂直格式化等式为:
top + margin-top + border-top-width + padding-top + height + padding-bottom + border-bottom-width + margin-bottom + bottom = 包含块的clientHeight
auto
auto值是用来弥补实际值与所需总和的差距。
水平方向上,可以为auto的属性有left、margin-left、width、margin-right、right。类似地,垂直方向上,可以为auto的属性有top、margin-top、height、margin-bottom、bottom
【0个auto】
当水平方向上9个值的和不等于包含块的clientWidth时,属于过度受限的情况,right值会被重置为auto;类似地,当垂直方向上9个值的和不等于包含块的clientHeight时,属于过度受限的情况,bottom值会被重置为auto
【1个auto】
根据水平和垂直格式化等式,auto为计算值
【2个auto】
当margin-left和margin-right同时为auto时,margin-left和margin-right都为等式计算值且相等
[注意]在margin-left和margin-right同时为auto的情况下,只有当left和right值相等时,元素才能水平居中显示;否则,虽然margin-left和margin-right依然相等,但由于left和right并不相等,元素也不能水平居中
当margin-left或margin-right不同时为auto时,值为auto的margin-left或margin-right被置为0
当width与left或right同时为auto时,width被置为宽度最小值(内容宽度)
当left和right同时为auto时,则left为置为0
类似地,
当margin-top和margin-bottom同时为auto时,margin-top和margin-bottom都为等式计算值且相等
[注意]在margin-top和margin-bottom同时为auto的情况下,只有当top和bottom值相等时,元素才能垂直居中显示;否则,虽然margin-top和margin-bottom依然相等,但由于top和bottom并不相等,元素也不能垂直居中
当margin-top或margin-bottom不同时为auto时,值为auto的margin-top或margin-bottom被置为0
当height与top或bottom同时为auto时,height被置为高度最小值(行高)
当top和bottom同时为auto时,则top为置为0
【3个auto】
当margin-left和margin-right同时为auto时,margin-left和margin-right都被置为0
当margin-left和margin-right不同时为auto时,值为auto的margin-left或margin-right被置为0
除了width、margin-left和margin-right同时为auto时,margin-left和margin-right都置为0,width为等式计算值;其他情况下,width都被置为宽度最小值(内容宽度)
当left和right同时为auto时,则left为置为0
类似地,
当margin-top和margin-bottom同时为auto时,margin-top和margin-bottom都被置为0
当margin-top和margin-bottom不同时为auto时,值为auto的margin-top或margin-bottom被置为0
除了height、margin-top和margin-bottom同时为auto时,margin-top和margin-bottom都置为0,height为等式计算值;其他情况下,height都被置为高度最小值(行高)
当top和bottom同时为auto时,则top为置为0
【4个auto】
当width不为auto时,margin-left和margin-right被置为0,left被置为0,right为计算值
当left不为auto时,margin-left和margin-right被置为0,width被置为宽度最小值(内容宽度),right为计算值
当right不为auto时,margin-left和margin-right被置为0,width被置为宽度最小值(内容宽度),left为计算值
当margin-left不为auto时,left和margin-right被置为0,width被置为宽度最小值(内容宽度),right为计算值
当margin-right不为auto时,left和margin-left被置为0,width被置为宽度最小值(内容宽度),right为计算值
类似地,
当height不为auto时,margin-top和margin-bottom被置为0,top被置为0,bottom为计算值
当top不为auto时,margin-top和margin-bottom被置为0,height被置为高度最小值(行高),bottom为计算值
当bottom不为auto时,margin-top和margin-bottom被置为0,height被置为高度最小值(行高),top为计算值
当margin-top不为auto时,top和margin-bottom被置为0,height被置为高度最小值(行高),bottom为计算值
当margin-bottom不为auto时,top和margin-top被置为0,height被置为高度最小值(行高),bottom为计算值
【5个auto】
left、margin-left和margin-right被置为0,width被置为宽度最小值(内容宽度),right为计算值
类似地,top、margin-top和margin-bottom被置为0,height被置为高度最小值(行高),bottom为计算值
总结
auto值的赋值顺序为:margin先置0或其他值,然后宽高置为最小值,然后left/top置为0,最后right/bottom为等式计算值
[注意1]IE7-浏览器不支持绝对定位元素通过将上下外边距设置为auto来实现垂直居中的行为
[注意2]IE6-浏览器不支持绝对定位元素不设置宽度,而通过设置top/left/right/bottom来撑开宽高的行为
<span style="color: #008000;">//</span><span style="color: #008000;">DEMO中,定位元素的padding、border都为0。而父级元素也就是包含块的width和height都设为200px,边框为2px</span>
 What is the purpose of the <datalist> element?Mar 21, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
What is the purpose of the <datalist> element?Mar 21, 2025 pm 12:33 PMThe article discusses the HTML <datalist> element, which enhances forms by providing autocomplete suggestions, improving user experience and reducing errors.Character count: 159
 How do I use HTML5 form validation attributes to validate user input?Mar 17, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How do I use HTML5 form validation attributes to validate user input?Mar 17, 2025 pm 12:27 PMThe article discusses using HTML5 form validation attributes like required, pattern, min, max, and length limits to validate user input directly in the browser.
 What is the purpose of the <iframe> tag? What are the security considerations when using it?Mar 20, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
What is the purpose of the <iframe> tag? What are the security considerations when using it?Mar 20, 2025 pm 06:05 PMThe article discusses the <iframe> tag's purpose in embedding external content into webpages, its common uses, security risks, and alternatives like object tags and APIs.
 What is the purpose of the <progress> element?Mar 21, 2025 pm 12:34 PM
What is the purpose of the <progress> element?Mar 21, 2025 pm 12:34 PMThe article discusses the HTML <progress> element, its purpose, styling, and differences from the <meter> element. The main focus is on using <progress> for task completion and <meter> for stati
 What is the purpose of the <meter> element?Mar 21, 2025 pm 12:35 PM
What is the purpose of the <meter> element?Mar 21, 2025 pm 12:35 PMThe article discusses the HTML <meter> element, used for displaying scalar or fractional values within a range, and its common applications in web development. It differentiates <meter> from <progress> and ex
 What are the best practices for cross-browser compatibility in HTML5?Mar 17, 2025 pm 12:20 PM
What are the best practices for cross-browser compatibility in HTML5?Mar 17, 2025 pm 12:20 PMArticle discusses best practices for ensuring HTML5 cross-browser compatibility, focusing on feature detection, progressive enhancement, and testing methods.
 What is the viewport meta tag? Why is it important for responsive design?Mar 20, 2025 pm 05:56 PM
What is the viewport meta tag? Why is it important for responsive design?Mar 20, 2025 pm 05:56 PMThe article discusses the viewport meta tag, essential for responsive web design on mobile devices. It explains how proper use ensures optimal content scaling and user interaction, while misuse can lead to design and accessibility issues.
 How do I use the HTML5 <time> element to represent dates and times semantically?Mar 12, 2025 pm 04:05 PM
How do I use the HTML5 <time> element to represent dates and times semantically?Mar 12, 2025 pm 04:05 PMThis article explains the HTML5 <time> element for semantic date/time representation. It emphasizes the importance of the datetime attribute for machine readability (ISO 8601 format) alongside human-readable text, boosting accessibilit


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor







