Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >How to use python's import
How to use python's import
- 爱喝马黛茶的安东尼Original
- 2019-06-26 15:02:0223566browse
In the process of learning Python, import is a keyword that I came into contact with earlier. Python has many built-in libraries, which can be used after importing, or imported using pip after installation. Import also organizes the project structure for us. It provides the possibility that when developing a large system, the entire project has many folders and files, which are all connected through import, so it is necessary to understand the working mechanism of import.

1. Basic usage of import
1. Import package name
import os
2. From package Import function
from math import pow
3.Import the package and give it an alias
import math as m
4.Import constants from the package and give it an alias
from math import pi as p
5.Import all the contents in the package
from math import *
Related recommendations: "Python Video Tutorial"
2. The way Python organizes code
1. A file Elements in
If the entire program has only one file, there will be elements such as variables, functions, and classes in this file for operation.
2. Module
Simply speaking, a module is a .py file. For example: there are two files a.py and b.py in the same path, then in a You can import b in .py, and then you can use the variables, functions, and classes in b.py through b.xxx.
3. Package
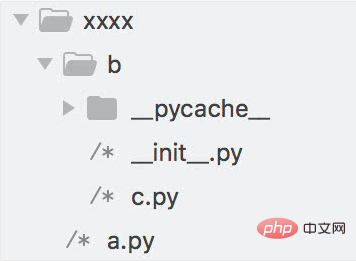
A simple understanding of a package is a folder containing an __init__.py. For example: there is an a.py file and a b folder in the same path. , there is an __init__.py file in the b folder. Import b in a means importing the package b, which is actually the file __init__.py.

4.__all__
The __all__ variable defined in the __init__.py of the package, so that the package can be called by importing the package name Elements in each file, for example: there is an a.py file and a b folder in the same path, and there are two files __init__.py and c.py in the b folder,
The contents of 
c.py are:
__init__.py’s contents are:
a.py’s contents are:
Run results :
After the program runs, there is an additional __pycache__ folder. When a module is imported for the first time, it is assembled into byte code and the byte code is written into a .pyc with the same name. document. Subsequent import operations will directly read the .pyc file instead of the .py file. (Unless the modification date of the .py file is updated, in this case the .pyc file will be regenerated)
5. Why use .c to import?
The previous a.py can use import b to import elements in b.py. Why can't __init__.py in the b folder import c? Because __init__.py actually represents the folder b, and c is not in the first-level directory with it, so .c must be used to introduce elements in c.py.
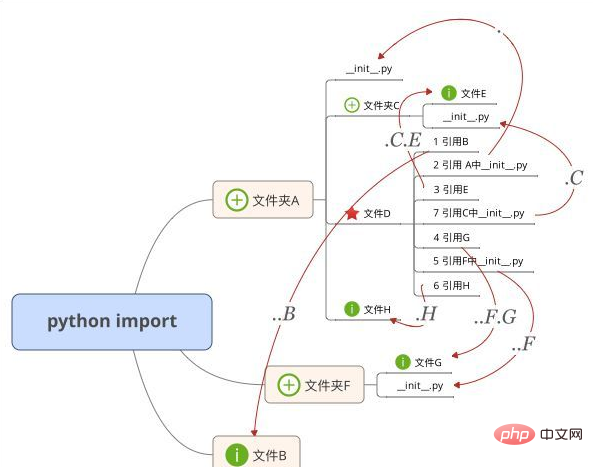
6. How to import multi-layer directories?
It is enough to look at the following picture:
3. Search path
When importing the module, The interpreter searches the sys.path list, which contains a list of directories.
sys.path is different in different environments. Python will search for the path of the list in sequence and return after finding it, so the order is very important. The first '' refers to the current directory or the specified Relative path, for example, there is a math.py file in your current directory. When you import math, it is equivalent to importing this math.py file instead of the standard library math.
The above is the detailed content of How to use python's import. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

