Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >How to open excel with python
How to open excel with python
- silencementOriginal
- 2019-06-24 10:53:0224800browse

Recently I have seen several people in the group ask questions about xlwt and wlrd. How should I put it? If office 2007 has just come out and everyone is not used to using xlsx files, it is understandable. It's been 10 years. Even if I haven't evolved to Office 2016, I still use Office 2003. It doesn't make sense. Can someone use xlsx to save it as xls? —— Deliberately do a few extra steps. What’s the purpose? For compatibility? Compatible with the ancient office2003? Moreover, since we use python to operate excel, we still need to save the file manually. Is this a crazy idea?
So, I still think that we should give up xls and transform to xlsx. That's why this article is written - xlwt and wlrd can only read and write xls files, but cannot operate xlsx files.
Solution: openpyxl. This is a very simple library that can be used in a few minutes. The installation is very simple. pip install openpyxl can be done in one step. I will mainly talk about the operation of excel. Of course, with all the nonsense mentioned above, students can probably guess that openpyxl can only operate xlsx files but not xls files.
1. Basic concepts
In openpyxl, three concepts are mainly used: Workbooks, Sheets, and Cells. Workbook is an excel worksheet; Sheet is a table page in the worksheet; Cell is a simple cell. openpyxl revolves around these three concepts. Regardless of reading and writing, it is "three things": open the Workbook, locate the Sheet, and operate the Cell. Below we introduce several common methods respectively for reading and writing.
2. Read xlsx
In order to do the experiment, I prepared an excel document in advance, which has three pages: Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3. The following content is filled in:

First use
from openpyxl import load_workbook
to introduce the library
wb = load_workbook("template.xlsx") to open an xlsx file
print(wb.sheetnames) # ['Sheet1', 'Sheet2', 'Sheet3']
You can see which sheet pages are in the open Excel
sheet = wb.get_sheet_by_name("Sheet3")After reading the specified Sheet page, the sheet becomes magical, with the desired content It's all here. For example:
print(sheet["C"]) # (<Cell Sheet3.C1>, <Cell Sheet3.C2>, <Cell Sheet3.C3>, <Cell Sheet3.C4>, <Cell Sheet3.C5>, <Cell Sheet3.C6>, <Cell Sheet3.C7>, <Cell Sheet3.C8>, <Cell Sheet3.C9>, <Cell Sheet3.C10>) <-第C列 print(sheet["4"]) # (<Cell Sheet3.A4>, <Cell Sheet3.B4>, <Cell Sheet3.C4>, <Cell Sheet3.D4>, <Cell Sheet3.E4>) <-第4行 print(sheet["C4"].value) # c4 <-第C4格的值 print(sheet.max_row) # 10 <-最大行数 print(sheet.max_column) # 5 <-最大列数 for i in sheet["C"]: print(i.value, end=" ") # c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8 c9 c10 <-C列中的所有值
Write to xlsx
First create a worksheet with
from openpyxl import Workbook wb = Workbook()
, and then
sheet = wb.active
find Active sheet. The default sheet page of an empty excel sheet is called Sheet. If you want to change the name, you can directly assign a value to the title attribute.
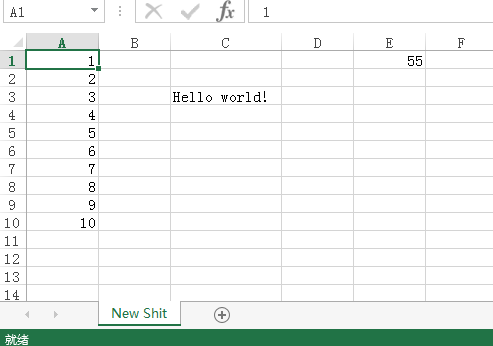
sheet.title = "New Shit"
This attribute is readable and writable. Of course, this only applies to the current active page. For other pages, you can use create_sheet and remove_sheet to add and delete them.
It is relatively simple to write content into the sheet page, just like reading it above,
sheet['C3'] = 'Hello world!' for i in range(10): sheet["A%d" % (i+1)].value = i + 1
We can also perform fancy operations, such as writing formulas:
sheet["E1"].value = "=SUM(A:A)"
Finally Remember to save
wb.save('保存一个新的excel.xlsx')
The above is the detailed content of How to open excel with python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

