
In Excel, there are two functions to extract characters of a specified length, namely the Mid function and the Midb function. The former is used to extract the number of characters of a specified length, and the latter is used to extract The number of bytes of the specified length. When using the Mid function to extract, whether it is Chinese characters, letters or numbers, they are counted as one character; when using the Midb function to extract, Chinese characters are counted as two bytes, and numbers and letters are counted as one byte. Normally, they are extracted from left to right; but they can also be extracted from right to left. The following are specific examples of how to use the Excel Mid function and the Midb function and include forward and reverse values. The versions used in the examples are Excel 2016.
1. Excel Mid function syntax
1. Expression that returns the number of characters: MID(Text, Start_Num, Num_Chars)
Chinese expression Display: MID (text, starting position, extracted character length)
2. Expression that returns the number of bytes: MIDB(Text, Start_Num, Num_Bytes)
Chinese expression: MIDB (Text, starting position, extracted byte length)
3. Description:
A. start_num is the starting position of the characters to be extracted, it must be greater than or equal to 1, otherwise an error will be returned; if start_num is greater than the text length, null will be returned; if start_num is less than the text length plus Num_Chars is greater than the text length, only the characters at the end of the text will be returned.
B. Num_Chars is the number of characters to be extracted. It must be greater than 0, otherwise a #VALUE! error will be returned.
C, Num_Bytes is the number of bytes to extract characters, it must be greater than 0, otherwise #VALUE! error will also be returned.
2. How to use Excel Mid function
(1) Intercept Chinese characters
1. Select cell H4 , enter the formula =MID(B4,3,2), press Enter, return to "Short Sleeves", the operation process steps are shown in Figure 1:

Figure 1
2. Description: The content of B4 is "pink short-sleeved shirt", start_num is 3, Num_Chars is 2, that is, extraction starts from the third character, and the length of the extracted string is 2, so "short-sleeved shirt" is returned. "Sleeve"; indicates that the MID function counts each Chinese character as one character.
(2) Intercept the string composed of letters and numbers, and demonstrate the situation when Num_Chars Start_num exceeds the text length and Start_num is 0
1. Put the formula =MID ("Excel 2016",7,4) Copy to cell A1, press Enter, return to 2016; change 4 to 6, the result will also return to 2016; then change 7 to 0, the result will return #VALUE! Error; operation process Steps, as shown in Figure 2:
2. Description: The first formula =MID("Excel 2016",7,4) starts from the 7th position (a space counts as one character) and takes 4 , returns 2016; the second formula =MID("Excel 2016",7,6) also starts from the 7th position, taking 6 characters, but there are only 4 characters from the 7th position to the end of the text, so only 4 characters are taken. 4; the third formula =MID("Excel 2016",0,6) starts extracting from 0. Since the Mid function counts from 1, it returns #VALUE! error.
(3) Intercept the string consisting of Chinese characters, letters and numbers, and demonstrate the situation when Start_num is greater than the text length
1. Change the formula =MID("Excel 2016 Basic Tutorial",12,4) Copy to cell A1, press Enter, return to "Basic Tutorial"; change 12 to 18, press Enter, return to the "empty" operation process steps, as shown in Figure 3:
2. Description: The first formula =MID("Excel 2016 Basic Tutorial",12,4) intercepts from the 12th character, that is, intercepts from the "base" character, intercepts 4 characters, and intercepts exactly Go to the "Basic Tutorial" to explain that whether it is a Chinese character, a letter or a number, the Mid function counts as one character; the second formula =MID("Excel 2016 Basic Tutorial",18,4) starts from the 18th position. Due to the length of the text With only 15 digits, the starting position is greater than the text length, and a space is returned.
(4) Reverse value taking (i.e. taking value from right to left)
1. If you want to take the value from the 4th digit from the bottom and only take 4 character. Copy the formula =MID(A1,LEN(A1) - 4 1,4) to cell B1, as shown in Figure 4:

Figure 4
2. Press Enter to return to "Basic Tutorial", as shown in Figure 5:

3. Description: The formula first uses the Len function to return the length of the string A1, and then uses it to subtract the 4th digit and add 1, so that the position where the string is to be intercepted can be located. The interception length is 4, so Return to the four words "Basic Tutorial". If you want to intercept the third to last digit, just change 4 to 3, then the formula becomes =MID(A1,LEN(A1) - 3 1,3), as shown in Figure 6:

Figure 6
The result returns to "Basic Tutorial", as shown in Figure 7:

Figure 7
3. How to use Excel Midb function
(1) Intercept a string composed of Chinese characters, letters and numbers
1. Put the formula =MIDB(A1,12,8) Copy to cell B1, press Enter, return to the four words "Basic Tutorial", the operation process steps are as shown in Figure 8:

Figure 8
2. Description: The formula is intercepted from the 12th position, which is the "base" character. The interception length is 8 bytes, and each Chinese character occupies two bytes, so Get four Chinese characters.
(2) Reverse value acquisition
1. If you want to intercept from the fourth byte from the bottom and only take four bytes. Copy the formula =MIDB(A1,LEN(A1) - 4 1,4) to cell B1, press Enter, and return to the word "Basic". The operation process steps are as shown in Figure 9:

Figure 9
#2. Description: The reverse value of the Midb function is the same as the Mid function. The last few bytes are intercepted, subtract the number, and then add 1; for example Then intercept the second to last byte, and the formula becomes: =MIDB(A1,LEN(A1) - 2 1,2).
For more technical articles related to Excel, please visit the Excel Tutorial## column to learn!
The above is the detailed content of How to use Excel Mid function. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PMThis tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
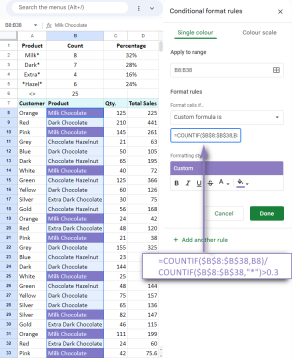 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PMMaster Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AMThis tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
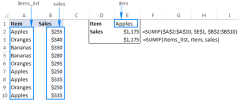 Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AMThis tutorial clarifies the function of Excel names and demonstrates how to define names for cells, ranges, constants, or formulas. It also covers editing, filtering, and deleting defined names. Excel names, while incredibly useful, are often overlo
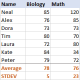 Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis tutorial clarifies the distinction between standard deviation and standard error of the mean, guiding you on the optimal Excel functions for standard deviation calculations. In descriptive statistics, the mean and standard deviation are intrinsi
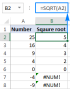 Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AMThis Excel tutorial demonstrates how to calculate square roots and nth roots. Finding the square root is a common mathematical operation, and Excel offers several methods. Methods for Calculating Square Roots in Excel: Using the SQRT Function: The
 Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AMUnlock the Power of Google Sheets: A Beginner's Guide This tutorial introduces the fundamentals of Google Sheets, a powerful and versatile alternative to MS Excel. Learn how to effortlessly manage spreadsheets, leverage key features, and collaborate


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)





