Home >Java >javaTutorial >What are C/S and B/S?
What are C/S and B/S?
- (*-*)浩Original
- 2019-05-06 09:28:5028227browse
This article introduces the C/S and B/S architecture of Java software, hoping to serve as a reference for everyone.
Recommended course: Java Tutorial.

C/S is the abbreviation of Client/Server. The server usually uses a high-performance PC, workstation or minicomputer, and uses a large database system. Such as Oracle, Sybase, Informix or SQLServer. The client needs to install special client software. Examples: QQ, Xunlei, Kuaibo, Baofengyingyin, various online games, etc. As long as there is communication with the server, it counts.
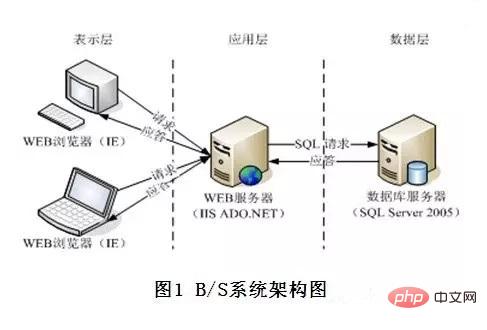
B/S is the abbreviation of Brower/Server. Only one browser needs to be installed on the client, such as Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer, and Oracle or Oracle must be installed on the server. SQL
Server waits for the database. Example: All websites are BS.
B/S is a network structure model after the rise of WEB. The WEB browser is the most important application software on the client. This model unifies the client and concentrates the core parts of system function implementation on the server, simplifying the development, maintenance and use of the system. Under this structure, the user interface is completely implemented through the WWW browser, and part of the transaction logic is implemented on the front end. However, the main transaction logic is implemented on the server side, and the browser interacts with the database through the Web Server.

Client/Server is based on the local area network. Browser/Server is built on the basis of WAN.
Compared with CS management software, BS has unparalleled advantages in installation and deployment, upgrade and maintenance, equipment bandwidth, software learning and promotion costs, etc. The user of the BS management software is on the client computer There is no need to install any software, you can access the system using a browser.
The system eliminates the need to invest more information technology funds for enterprise expansion, makes system training and later promotion very easy, and the management model becomes replicable.
Availability: Any time, any place, any system, as long as you can use a browser to access the Internet, you can use the BS system terminal. When more system users join, they only need to set up an account,
Training is enough, and mobile office and distributed office are supported. CS is a typical centralized mechanized processing with relatively low interactivity.
Stability: J2EE three-tier architecture, using middleware application server. The database, application server, and view are designed in a hierarchical manner, and the system has excellent performance with tens of thousands of users online at the same time.
Easy to upgrade: CS systems are often an indivisible whole. Changes in part of each module will be related to changes in other modules, making system upgrade costs relatively high.
BS is composed of components. You only need to change the page to update it synchronously. Almost all its development and maintenance work are also concentrated on the server side. When an enterprise upgrades its network application, it only needs to update the server. Just the end-of-life software.
Low maintenance: CS requires a special client installation program, and client installation, upgrade, and network debugging are difficult; while BS system only needs to manage the central server.
Compatibility: The CS system relies heavily on fixed development tools, development languages, operating systems, and databases. What software service providers can only provide is a holistic solidified software, which does not support heterogeneous operations. Operating systems and databases are difficult to be compatible with. After the emergence of BS with the help of cross-platform languages such as JAVA, it is compatible with all mainstream databases and operating systems.
Low bandwidth: The typical application of CS is that each client directly connects to the server database. It is generally used on a dedicated network.
It is only suitable for internal users of the LAN or small-scale network environments for broadband users. , not suitable for large-scale applications with widely distributed operating points. BS is built on the wide area network and has low bandwidth requirements. It does not have to be a specialized network hardware environment and is suitable for low-bandwidth and unstable environments.
Rich display: CS is mostly built on the Window platform, and the expression methods are limited. BS is built on the browser and has a richer and more vivid way of expression to communicate with users.
The above is the detailed content of What are C/S and B/S?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

