How to understand data structures and algorithms (Python)
Understanding of data structures and algorithms in Python: Data structures in Python refer to the static description of the relationship between data elements, and algorithms refer to methods or steps to solve problems. In other words, algorithms are designed to solve practical problems. Designed, the data structure is the carrier of the problem that the algorithm needs to deal with.
Data structures and algorithms are essential basic skills for a program developer, so we need to take the initiative to learn and accumulate them. Next, I will introduce these two knowledge points to you in detail in this article. I hope it will be helpful to you. Everyone helps.

[Recommended course: Python Tutorial]
Introducing concepts
Let’s look at a question first:
If a b c=1000, and a2 b2=c^2 (a, b, c are Natural numbers), how to find all possible combinations of a, b, c?
First try
import time
start_time = time.time()
# 注意是三重循环
for a in range(0, 1001):
for b in range(0, 1001):
for c in range(0, 1001):
if a**2 + b**2 == c**2 and a+b+c == 1000:
print("a, b, c: %d, %d, %d" % (a, b, c))
end_time = time.time()
print("elapsed: %f" % (end_time - start_time))
print("complete!")Running result:
a, b, c: 0, 500, 500 a, b, c: 200, 375, 425 a, b, c: 375, 200, 425 a, b, c: 500, 0, 500 elapsed: 1066.117884 complete!
Run The time was as long as 17.8 minutes
Proposal of algorithm
Concept of algorithm
Algorithm is a computer processing information The essence of a computer program is that it is essentially an algorithm that tells the computer the exact steps to perform a specified task. Generally, when an algorithm is processing information, it will read data from an input device or a storage address of the data, and write the results to an output device or a storage address for later recall.
Algorithms are independent methods and ideas for solving problems.
For algorithms, the language of implementation is not important, what is important is the idea.
Algorithms can have different language description implementation versions (such as C description, C description, Python description, etc.). We are now using Python language to describe and implement it.
Five characteristics of algorithms
Input: The algorithm has 0 or more inputs
Output: The algorithm has at least 1 or more outputs
Finiteness: The algorithm will automatically end after a limited number of steps without looping infinitely, and each step can be completed within an acceptable time
Deterministic: Each step in the algorithm All have definite meanings and there will be no ambiguity
Feasibility: Every step of the algorithm is feasible, which means that each step can be executed a limited number of times
Second attempt
import time
start_time = time.time()
# 注意是两重循环
for a in range(0, 1001):
for b in range(0, 1001-a):
c = 1000 - a - b
if a**2 + b**2 == c**2:
print("a, b, c: %d, %d, %d" % (a, b, c))
end_time = time.time()print("elapsed: %f" % (end_time - start_time))print("complete!")Running results:
a, b, c: 0, 500, 500 a, b, c: 200, 375, 425 a, b, c: 375, 200, 425 a, b, c: 500, 0, 500 elapsed: 0.632128
Note that the running time is 0.632128 seconds
Algorithm efficiency measurement
Execution Time Response Algorithm Efficiency
For the same problem, we gave two solving algorithms. In the implementation of the two algorithms, we measured the program execution time. It is found that the execution time of the two programs is very different. From this, we can draw a conclusion: the execution time of the algorithm program can reflect the efficiency of the algorithm, that is, the quality of the algorithm.
Is the time value alone absolutely reliable?
What if we ran our second attempt at the algorithm on a computer with an ancient configuration and poor performance? Most likely the running time will not be much faster than running Algorithm 1 on our computers.
It is not necessarily objective and accurate to compare the advantages and disadvantages of algorithms based solely on running time!
The running of a program cannot be separated from the computer environment (including hardware and operating system). These objective reasons will affect the speed of program running and be reflected in the execution time of the program. So how can we objectively judge the quality of an algorithm?
Time complexity and "Big O notation"
We assume that the time it takes for the computer to perform each basic operation of the algorithm is a fixed time unit, then how many Basic operations represent how many units of time it will take. Since the exact unit time is different for different machine environments, but the number of basic operations performed by the algorithm (that is, how many time units it takes) is the same in the order of magnitude, so the influence of the machine environment can be ignored and objective The time efficiency of the reaction algorithm.
For the time efficiency of the algorithm, we can use "Big O notation" to express it.
"Big O notation": For a monotonic integer function f, if there is an integer function g and a real constant c>0, such that for a sufficiently large n there is always f(n)
Time complexity: Assume that there is a function g such that the time it takes for algorithm A to process a problem example of size n is T(n)=O(g(n)), then it is called O(g(n)) is the asymptotic time complexity of algorithm A, referred to as time complexity, denoted as T(n)
How to understand the "Big O notation"
对于算法进行特别具体的细致分析虽然很好,但在实践中的实际价值有限。对于算法的时间性质和空间性质,最重要的是其数量级和趋势,这些是分析算法效率的主要部分。而计量算法基本操作数量的规模函数中那些常量因子可以忽略不计。例如,可以认为3n2和100n2属于同一个量级,如果两个算法处理同样规模实例的代价分别为这两个函数,就认为它们的效率“差不多”,都为n2级。
最坏时间复杂度
分析算法时,存在几种可能的考虑:
算法完成工作最少需要多少基本操作,即最优时间复杂度
算法完成工作最多需要多少基本操作,即最坏时间复杂度
算法完成工作平均需要多少基本操作,即平均时间复杂度
对于最优时间复杂度,其价值不大,因为它没有提供什么有用信息,其反映的只是最乐观最理想的情况,没有参考价值。
对于最坏时间复杂度,提供了一种保证,表明算法在此种程度的基本操作中一定能完成工作。
对于平均时间复杂度,是对算法的一个全面评价,因此它完整全面的反映了这个算法的性质。但另一方面,这种衡量并没有保证,不是每个计算都能在这个基本操作内完成。而且,对于平均情况的计算,也会因为应用算法的实例分布可能并不均匀而难以计算。
因此,我们主要关注算法的最坏情况,亦即最坏时间复杂度。
时间复杂度的几条基本计算规则
基本操作,即只有常数项,认为其时间复杂度为O(1)
顺序结构,时间复杂度按加法进行计算
循环结构,时间复杂度按乘法进行计算
分支结构,时间复杂度取最大值
判断一个算法的效率时,往往只需要关注操作数量的最高次项,其它次要项和常数项可以忽略
在没有特殊说明时,我们所分析的算法的时间复杂度都是指最坏时间复杂度
算法分析
第一次尝试的算法核心部分
or a in range(0, 1001):
for b in range(0, 1001):
for c in range(0, 1001):
if a**2 + b**2 == c**2 and a+b+c == 1000:
print("a, b, c: %d, %d, %d" % (a, b, c))时间复杂度:
T(n) = O(n * n * n) = O(n³)
第二次尝试的算法核心部分
for a in range(0, 1001):
for b in range(0, 1001-a):
c = 1000 - a - b
if a**2 + b**2 == c**2:
print("a, b, c: %d, %d, %d" % (a, b, c))时间复杂度:
T(n) = O(n * n * (1+1)) = O(n * n) = O(n²)
由此可见,我们尝试的第二种算法要比第一种算法的时间复杂度好多的。
常见时间复杂度
| 执行次数函数举例 | 阶 | 非正式术语 |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | O(1) | 常数阶 |
| 2n + 3 | O(n) | 线性阶 |
| 3n² +2n + 1 | O(n²) | 平方阶 |
| 5log2n+20 | O(logn) | 对数阶 |
| 2n+3nlog2n+19 | O(nlogn) | nlogn阶 |
| 6n³ +2n² +3n + 1 | O(n³) | 立方阶 |
| 2n | O(2n) | 指数阶 |
注意,经常将log2n(以2为底的对数)简写成logn
常见时间复杂度之间的关系
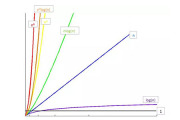
所消耗的时间从小到大
O(1) < O(logn) < O(n) < O(nlogn) < O(n2) < O(n3) < O(2n) < O(n!) < O(nn)
Python内置类型性能分析
timeit模块
timeit模块可以用来测试一小段Python代码的执行速度。
class timeit.Timer(stmt='pass', setup='pass', timer=<timer function>)
Timer是测量小段代码执行速度的类。
stmt参数是要测试的代码语句(statment)
setup参数是运行代码时需要的设置
timer参数是一个定时器函数,与平台有关。
timeit.Timer.timeit(number=1000000)
Timer类中测试语句执行速度的对象方法。number参数是测试代码时的测试次数,默认为1000000次。方法返回执行代码的平均耗时,一个float类型的秒数。
list的操作测试
def test1():
l = [] for i in range(1000):
l = l + [i]def test2():
l = [] for i in range(1000):
l.append(i)def test3():
l = [i for i in range(1000)]def test4():
l = list(range(1000))from timeit import Timer
t1 = Timer("test1()", "from __main__ import test1")
print("concat ",t1.timeit(number=1000), "seconds")
t2 = Timer("test2()", "from __main__ import test2")
print("append ",t2.timeit(number=1000), "seconds")
t3 = Timer("test3()", "from __main__ import test3")
print("comprehension ",t3.timeit(number=1000), "seconds")
t4 = Timer("test4()", "from __main__ import test4")
print("list range ",t4.timeit(number=1000), "seconds")
# ('concat ', 1.7890608310699463, 'seconds')
# ('append ', 0.13796091079711914, 'seconds')
# ('comprehension ', 0.05671119689941406, 'seconds')
# ('list range ', 0.014147043228149414, 'seconds')pop操作测试
x = range(2000000)
pop_zero = Timer("x.pop(0)","from __main__ import x")
print("pop_zero ",pop_zero.timeit(number=1000), "seconds")
x = range(2000000)
pop_end = Timer("x.pop()","from __main__ import x")
print("pop_end ",pop_end.timeit(number=1000), "seconds")
# ('pop_zero ', 1.9101738929748535, 'seconds')
# ('pop_end ', 0.00023603439331054688, 'seconds')测试pop操作:从结果可以看出,pop最后一个元素的效率远远高于pop第一个元素
可以自行尝试下list的append(value)和insert(0,value),即一个后面插入和一个前面插入???
list内置操作的时间复杂度

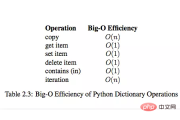
dict内置操作的时间复杂度
数据结构
概念
数据是一个抽象的概念,将其进行分类后得到程序设计语言中的基本类型。如:int,float,char等。数据元素之间不是独立的,存在特定的关系,这些关系便是结构。数据结构指数据对象中数据元素之间的关系。
Python给我们提供了很多现成的数据结构类型,这些系统自己定义好的,不需要我们自己去定义的数据结构叫做Python的内置数据结构,比如列表、元组、字典。而有些数据组织方式,Python系统里面没有直接定义,需要我们自己去定义实现这些数据的组织方式,这些数据组织方式称之为Python的扩展数据结构,比如栈,队列等。
算法与数据结构的区别
数据结构只是静态的描述了数据元素之间的关系。
高效的程序需要在数据结构的基础上设计和选择算法。
程序 = 数据结构 + 算法
总结:算法是为了解决实际问题而设计的,数据结构是算法需要处理的问题载体
抽象数据类型(Abstract Data Type)
抽象数据类型(ADT)的含义是指一个数学模型以及定义在此数学模型上的一组操作。即把数据类型和数据类型上的运算捆在一起,进行封装。引入抽象数据类型的目的是把数据类型的表示和数据类型上运算的实现与这些数据类型和运算在程序中的引用隔开,使它们相互独立。
最常用的数据运算有五种
插入
删除
修改
查找
排序
The above is the detailed content of How to understand data structures and algorithms (Python). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python's Hybrid Approach: Compilation and Interpretation CombinedMay 08, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python's Hybrid Approach: Compilation and Interpretation CombinedMay 08, 2025 am 12:16 AMPythonusesahybridapproach,combiningcompilationtobytecodeandinterpretation.1)Codeiscompiledtoplatform-independentbytecode.2)BytecodeisinterpretedbythePythonVirtualMachine,enhancingefficiencyandportability.
 Learn the Differences Between Python's 'for' and 'while' LoopsMay 08, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Learn the Differences Between Python's 'for' and 'while' LoopsMay 08, 2025 am 12:11 AMThekeydifferencesbetweenPython's"for"and"while"loopsare:1)"For"loopsareidealforiteratingoversequencesorknowniterations,while2)"while"loopsarebetterforcontinuinguntilaconditionismetwithoutpredefinediterations.Un
 Python concatenate lists with duplicatesMay 08, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python concatenate lists with duplicatesMay 08, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python, you can connect lists and manage duplicate elements through a variety of methods: 1) Use operators or extend() to retain all duplicate elements; 2) Convert to sets and then return to lists to remove all duplicate elements, but the original order will be lost; 3) Use loops or list comprehensions to combine sets to remove duplicate elements and maintain the original order.
 Python List Concatenation Performance: Speed ComparisonMay 08, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python List Concatenation Performance: Speed ComparisonMay 08, 2025 am 12:09 AMThefastestmethodforlistconcatenationinPythondependsonlistsize:1)Forsmalllists,the operatorisefficient.2)Forlargerlists,list.extend()orlistcomprehensionisfaster,withextend()beingmorememory-efficientbymodifyinglistsin-place.
 How do you insert elements into a Python list?May 08, 2025 am 12:07 AM
How do you insert elements into a Python list?May 08, 2025 am 12:07 AMToinsertelementsintoaPythonlist,useappend()toaddtotheend,insert()foraspecificposition,andextend()formultipleelements.1)Useappend()foraddingsingleitemstotheend.2)Useinsert()toaddataspecificindex,thoughit'sslowerforlargelists.3)Useextend()toaddmultiple
 Are Python lists dynamic arrays or linked lists under the hood?May 07, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Are Python lists dynamic arrays or linked lists under the hood?May 07, 2025 am 12:16 AMPythonlistsareimplementedasdynamicarrays,notlinkedlists.1)Theyarestoredincontiguousmemoryblocks,whichmayrequirereallocationwhenappendingitems,impactingperformance.2)Linkedlistswouldofferefficientinsertions/deletionsbutslowerindexedaccess,leadingPytho
 How do you remove elements from a Python list?May 07, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How do you remove elements from a Python list?May 07, 2025 am 12:15 AMPythonoffersfourmainmethodstoremoveelementsfromalist:1)remove(value)removesthefirstoccurrenceofavalue,2)pop(index)removesandreturnsanelementataspecifiedindex,3)delstatementremoveselementsbyindexorslice,and4)clear()removesallitemsfromthelist.Eachmetho
 What should you check if you get a 'Permission denied' error when trying to run a script?May 07, 2025 am 12:12 AM
What should you check if you get a 'Permission denied' error when trying to run a script?May 07, 2025 am 12:12 AMToresolvea"Permissiondenied"errorwhenrunningascript,followthesesteps:1)Checkandadjustthescript'spermissionsusingchmod xmyscript.shtomakeitexecutable.2)Ensurethescriptislocatedinadirectorywhereyouhavewritepermissions,suchasyourhomedirectory.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool






