Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed understanding of Generator function in JavaScript
Detailed understanding of Generator function in JavaScript
- 不言forward
- 2019-03-20 10:26:502190browse
This article brings you a detailed understanding of the Generator function in JavaScript. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
This article is about the summary and understanding of generator functions in ES6...
The definition of Generator function
In teacher Ruan Yifeng's The book says:
Generator function has multiple understanding angles. Syntactically, it can be understood first that the Generator function is a state machine that encapsulates multiple internal states. Executing the Generator function will return a traverser object. In other words, in addition to the state machine, the Generator function is also a traverser object generation function. The returned traverser object can traverse each state inside the Generator function in sequence.
My understanding:
The generator function can be understood as: the interior of the function is composed of multiple small functions, and the yield keyword is used to divide the interior of the function into multiple block areas; and when the function is executed , it will stop when it encounters yield, and output the expression result after yield (of course the next() method must be called externally); the next time the next() method is called, execution will start from where it stopped (this means The function has a memory function); if no yield is encountered again, it will be like a normal function. The return value of the function is an iterable object (traverser object); I like to call it iterable object, or traversable object ...
Let’s talk about the next() method of iterable objects (iterator)
function CreateIterator(iterator) {
// 定义一个初始下标用来判断
let nextIndex = 0;
// 返回对象: 包含的next方法,
return {
next: function () {
// 返回一个对象: value是当前对象下标对应的值, done是是否遍历完成
return nextIndex <p style="white-space: normal;"><strong>The use of generator functions</strong></p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">generator生成器函数的使用:
function *fn() {
代码1;
yield;
代码2;
}
普通函数: 执行到底
生成器函数: 遇到yield会暂停,交出执行权,下次执行从上次的停止的位置继续
生成器函数返回值为: 生成器对象
生成器对象.next()方法才能执行 函数体中的代码
// 可以解决函数回调嵌套的问题; 解决耗时操作
function *func() {
// 请求数据.
// yield ajax()
// 处理数据
}
// generator函数本质上 分割成多个小函数来执行... yield关键字前后
// 遇到yield就暂停; 没有就往下执行...
// yield 起到了 暂停函数执行的作用About the understanding of yield keyword
yield pass value
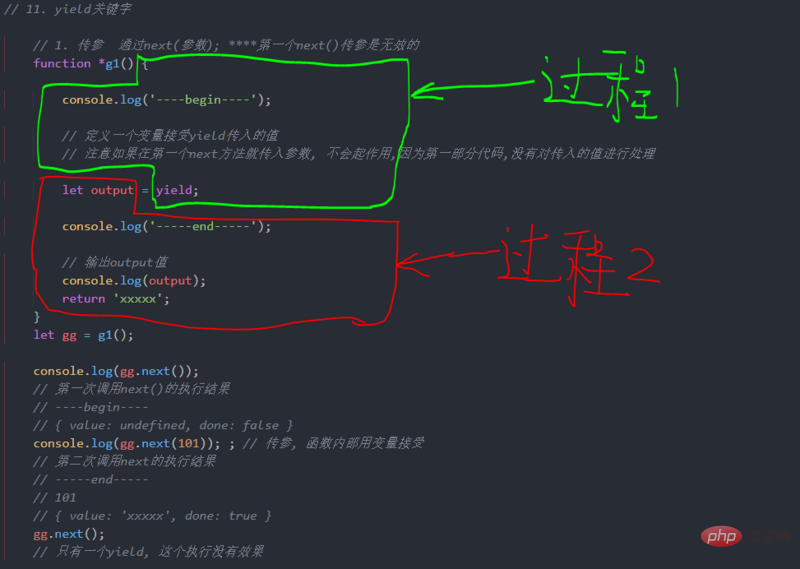
yield output value
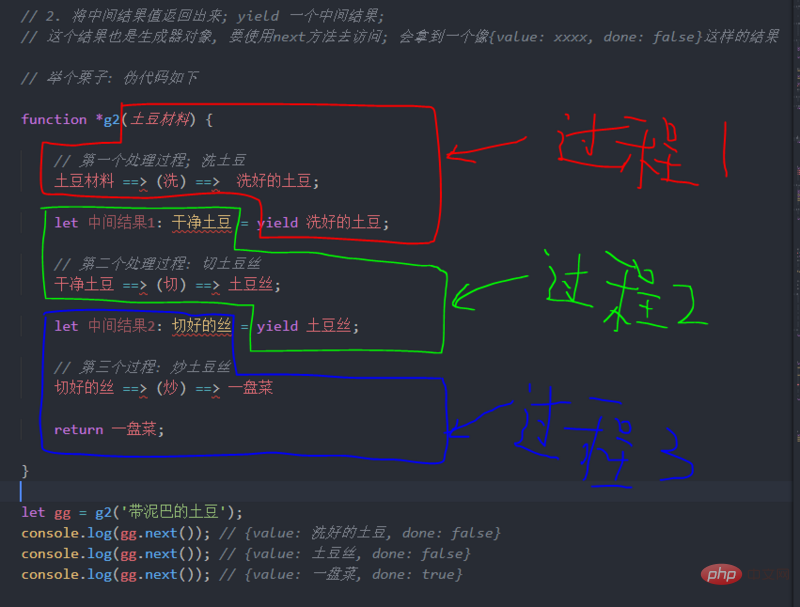
function *g2(x, y) {
let sum = x+y;
yield sum; // sum是第一个输出结果
let agv = sum / 2;
yield agv; // agv 是第二个输出的结果
return {"和": sum, "平均数": agv}; // 最后一个结果
}
let gg2 = g2(100, 20);
console.log(gg2.next().value); // 120
console.log(gg2.next().value); // 60
console.log(gg2.next().value); // { '和': 120, '平均数': 60 }Application of Generator
Here is just a simple example, like the async function in ES7 that we usually use; he is the generator An application of functions; it is actually syntactic sugar for the Generator function. Borrow an example from ES6 Getting Started: Two ways to read filesconst fs = require('fs');
const readFile = function (fileName) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
fs.readFile(fileName, function(error, data) {
if (error) return reject(error);
resolve(data);
});
});
};
// 1.使用生成器函数 读取文件
const gen = function* () {
const f1 = yield readFile(__dirname + '/first.json');
const f2 = yield readFile(__dirname + '/second.json');
console.log(f1.toString()); // 没有输出; 因为 f1 拿到是一个 Iterator 对象
console.log(f2.toString());
};
// 使用 async + await 读取; 注意两种需配合使用
const asyncReadFile = async function () {
const f1 = await readFile(__dirname + '/first.json');
const f2 = await readFile(__dirname + '/second.json');
console.log(f1.toString()); //async函数的返回值是 Promise 对象
console.log(f2.toString());
};
gen(); // 没有值, 需要用 next()方法去取值
asyncReadFile() // 返回值 {"hello": "first"} {"hello": "second"}So; let’s compare here; the async function replaces the asterisk (*) in the Generator function with async , replacing yield with await greatly facilitates our use. We can use async await to implement usual asynchronous code...For example, an ajax request in vue to obtain data
methods: {
async getApi() {
let res = await axios.get('url')
// 这里的执行顺序是同步的...
console.log(res)
}
}This article ends here It's all over. For more other exciting content, you can pay attention to the JjavaScript tutorial video column on the PHP Chinese website!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed understanding of Generator function in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Detailed introduction to JavaScript event delegation (with code)
- Parsing JavaScript scopes and scope chains (with examples)
- Detailed introduction to JavaScript execution context (with code)
- Detailed introduction to JavaScript high-order functions (with code)
- Differences in using for...in and Object.keys() to enumerate object properties in JavaScript (code attached)
- Understanding code composition (compose) in JavaScript functional programming

