 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance Best way to manage ssh hosts and private keys
Best way to manage ssh hosts and private keysAs a system administrator, handle multiple remote systems on a regular basis. Need to use ssh system many times during work. Many remote Linux servers are accessed via passwords, many via private keys. So that's more typical for managing all of this stuff. This article will introduce you to the details about using key files to correctly organize the ssh server.

Configuration file syntax:
We can add multiple ssh host details to the ~/.ssh/config file . Edit the configuration file in your favorite editor such as vi, vim or nano.
$ vi~/.ssh/config
The syntax is as follows:
Host<NICK_NAME>
HostName<IP地址远程>
IdentityFile <PATH TO私有文件>
User<LOGIN AS USERNAME>
Port<SSH要使用的端口>
LocalForward <本地端口> <REMOTE_LOCATION:PORT>1. Add the first SSH host
For example, our first ssh host is running A php development web server with details name php-web1, user root, port 22, and accessible via password. Add the following content in the configuration file.
Host php-web1
HostName 192.168.1.100
User rootNow try using SSH as the following command.
$ ssh php-web1
2. Add a second SSH host
Our second host server (php-web2) can use ssh with user root on the default port 22 Key pair access. Add the following content in the configuration file.
Host php-web2
HostName 192.168.1.101
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-web2.pem
User rootNow try using SSH as the following command.
$ ssh php-web2
3. Add a third SSH host
Our third ssh host server (php-db1) is running on port 2222 and can be accessed through user ubuntu key pair access. Add the following content in the configuration file.
Host php-db1
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
User ubuntuNow try using SSH as the following command.
$ ssh php-db1
4. Set up forwarding using SSH
In this setup we need to forward the local system port 3306 to the remote server (php-db1) on port 3306 ) host. Add the following content in the configuration file.
Host php-db1-mysql-tunnel
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
LocalForward 3306 127.0.0.1:3306Now try using SSH as the following command.
$ ssh php-db1-mysql-tunnel
Final configuration file
The final configuration file ~/.ssh/config is as follows.
Host php-web1
HostName 192.168.1.100
User root
Host php-web2
HostName 192.168.1.101
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-web2.pem
User root
Host php-db1
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
User ubuntu
Host php-db1-mysql-tunnel
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
LocalForward 3306 127.0.0.1:3306The above is the detailed content of Best way to manage ssh hosts and private keys. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
![Windows 11 中的 Telnet 完整教程 [安装/启用和故障排除]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/164/168476253791019.jpg) Windows 11 中的 Telnet 完整教程 [安装/启用和故障排除]May 22, 2023 pm 09:35 PM
Windows 11 中的 Telnet 完整教程 [安装/启用和故障排除]May 22, 2023 pm 09:35 PM<p>Telnet是“终端网络”的简称。它是用户可以用来将一台计算机连接到本地计算机的协议。</p><p>这里,本地计算机是指启动连接的设备,而连接到本地计算机的计算机称为远程计算机。</p><p>Telnet在客户端/服务器主体上运行,虽然它已经过时,但在2022年它仍然被许多人使用。许多人已经转向Windows11操作系统,这是微软提供的最新操作系统。&
 如何从 iPad SSH 到 MacApr 14, 2023 pm 12:22 PM
如何从 iPad SSH 到 MacApr 14, 2023 pm 12:22 PM如何从 iPad SSH 到 Mac这是一个两部分的演练。首先,您将在 Mac 上启用 SSH 服务器,然后您将使用 ssh 客户端应用程序从 iPad 连接到它。在 Mac 上,启动 SSH 服务器您可以通过打开名为 Remote Login 的功能在 Mac 上启用 SSH 服务器。转到 Apple 菜单 > 系统偏好设置 > 共享 > 启用“远程登录”,并选中“允许远程用户完全访问磁盘”框Mac 现在是一个 SSH 服务器,为您提供从 iPad 连接的 shell。注意
 Python服务器编程:使用Paramiko实现SSH远程操作Jun 18, 2023 pm 01:10 PM
Python服务器编程:使用Paramiko实现SSH远程操作Jun 18, 2023 pm 01:10 PM随着云计算和物联网的发展,远程操作服务器变得越来越重要。在Python中,我们可以使用Paramiko模块来轻松实现SSH远程操作。在本文中,我们将介绍Paramiko的基本用法,以及如何在Python中使用Paramiko来远程管理服务器。什么是ParamikoParamiko是一个用于SSHv1和SSHv2的Python模块,可以用于连接和控制SSH客户
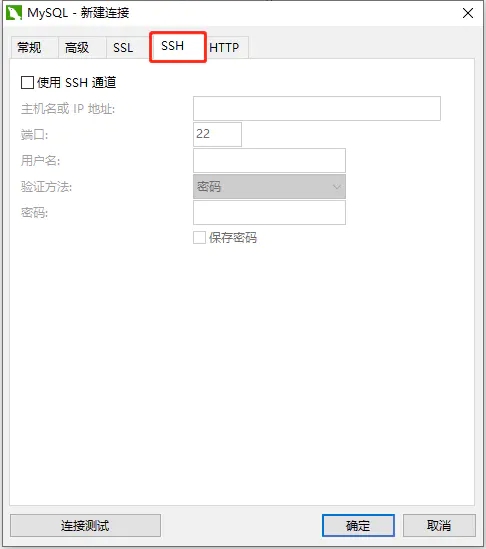 Python基于ssh远程怎么连接Mysql数据库May 27, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
Python基于ssh远程怎么连接Mysql数据库May 27, 2023 pm 04:07 PM背景如果需要访问远程服务器的Mysql数据库,但是该Mysql数据库为了安全期间,安全措施设置为只允许本地连接(也就是你需要登录到该台服务器才能使用),其他远程连接是不可以直接访问,并且相应的端口也做了修改,那么就需要基于ssh来连接该数据库。这种方式连接数据库与Navicat里面界面化基于ssh连接一样。Navicat连接数据库安装支持库如果要连接Mysql,首先需要安装pymysqlpipinstallpymysql安装基于ssh的库sshtunnelpipinstallsshtunnel#
 linux自带有ssh吗Apr 06, 2023 pm 03:55 PM
linux自带有ssh吗Apr 06, 2023 pm 03:55 PMlinux自带有ssh。linux系统会自带ssh软件,默认就是OpenSSH相关软件包,并将ssh服务添加为开机自启动,可以通过“ssh -V”命令来查看安装的ssh版本信息。执行“systemctl start sshd”命令即可启动sshd服务,默认端口使用的22端口。
 CentOS 7.9 安装及centos 7.9 安装sshFeb 13, 2024 pm 10:30 PM
CentOS 7.9 安装及centos 7.9 安装sshFeb 13, 2024 pm 10:30 PM在进行服务器搭建或者系统管理时,CentOS7.9是一个非常常用的操作系统版本,本文将为您提供关于CentOS7.9安装以及安装SSH的详细步骤和说明。CentOS7.9是一个免费且开源的Linux操作系统,它是基于RedHatEnterpriseLinux(RHEL)的二进制兼容版本,下面是CentOS7.9安装的步骤:1.您需要下载CentOS7.9的ISO镜像文件,您可以从CentOS官方网站上下载最新的CentOS7.9ISO镜像文件。2.在您的计算机上创建一个新的虚拟机或者物理机,并将
 Ansible工作原理详解Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:40 PM
Ansible工作原理详解Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:40 PMAnsible工作原理从上面的图上可以了解到:管理端支持local、ssh、zeromq三种方式连接被管理端,默认使用基于ssh的连接,这部分对应上面架构图中的连接模块;可以按应用类型等方式进行HostInventory(主机清单)分类,管理节点通过各类模块实现相应的操作,单个模块,单条命令的批量执行,我们可以称之为ad-hoc;管理节点可以通过playbooks实现多个task的集合实现一类功能,如web服务的安装部署、数据库服务器的批量备份等。playbooks我们可以简单的理解为,系统通过
 Linux怎么检查SSH版本Feb 15, 2023 am 11:28 AM
Linux怎么检查SSH版本Feb 15, 2023 am 11:28 AM检查方法:1、用文本编辑器打开“/etc/ssh/sshd_config”,查看“Protocol”字段,若显示“Protocol 2”就代表服务器只支持SSH2,若显示“Protocol 1”就代表服务器同时支持两者。2、强制ssh使用特定的SSH协议,通过查看SSH服务器的响应来判断。3、使用scanssh工具,语法“sudo scanssh -s ssh ip地址”。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.





