 Java
Java javaTutorial
javaTutorial Resolving the contradiction between singleton mode and thread safety under Spring
Resolving the contradiction between singleton mode and thread safety under SpringThe content of this article is about resolving the contradiction between singleton mode and thread safety under Spring. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
How many people often don’t know or ignore multi-threading issues when using the Spring framework?
Because when writing a program or doing unit testing, it is difficult to encounter multi-threading problems because it is not easy to simulate a multi-threading testing environment. Then when multiple threads call the same bean, there will be thread safety issues. If the bean creation mode in Spring is non-singleton, there will be no such problem.
But if you don’t consider potential vulnerabilities, they will become invisible killers of the program and break out when you don’t know it. Moreover, it is usually very troublesome to trigger in the production environment when the program is delivered for use.
Spring uses ThreadLocal to solve thread safety issues
We know that in general, only stateless beans can be shared in a multi-threaded environment. In Spring, most beans can Declared as singleton scope. It is because Spring uses ThreadLocal to process non-thread-safe states in some beans (such as RequestContextHolder, TransactionSynchronizationManager, LocaleContextHolder, etc.), making them thread-safe, because stateful beans can be shared among multiple threads.
General Web applications are divided into three levels: presentation layer, service layer and persistence layer. Corresponding logic is written in different layers, and the lower layer opens function calls to the upper layer through interfaces. Under normal circumstances, all program calls from receiving a request to returning a response belong to the same thread.
ThreadLocal is a good idea to solve thread safety problems. It solves the conflict of concurrent access to variables by providing an independent copy of the variable for each thread. In many cases, ThreadLocal is simpler and more convenient than directly using the synchronized synchronization mechanism to solve thread safety problems, and the resulting program has higher concurrency.
If there are multiple threads running at the same time in the process where your code is located, these threads may run this code at the same time. If the results of each run are the same as those of single-threaded runs, and the values of other variables are the same as expected, it is thread-safe. In other words: the interface provided by a class or program is an atomic operation for threads or switching between multiple threads will not cause ambiguity in the execution results of the interface, which means that we do not need to consider synchronization issues. Thread safety issues are caused by global variables and static variables.
If there are only read operations and no write operations on global variables and static variables in each thread, generally speaking, this global variable is thread-safe; if multiple threads perform write operations at the same time , generally thread synchronization needs to be considered, otherwise thread safety may be affected.
1) Constants are always thread-safe because there are only read operations.
2) Creating a new instance before each method call is thread-safe because shared resources will not be accessed.
3) Local variables are thread-safe. Because every time a method is executed, a local variable will be created in a separate space, which is not a shared resource. Local variables include method parameter variables and method-internal variables.
Being stateful means having data storage function. Stateful objects (Stateful Beans) are objects with instance variables that can save data and are not thread-safe. No state is retained between method calls.
Stateless is an operation and cannot save data. A stateless object (Stateless Bean) is an object without instance variables. It cannot save data, it is an immutable class, and it is thread-safe.
Stateful objects:
Stateless beans are suitable for immutable mode. The technology is singleton mode, so that instances can be shared and performance improved. Stateful beans are not safe in a multi-threaded environment, so the Prototype prototype mode is suitable. Prototype: Each request for a bean creates a new bean instance.
The default implementation of Struts2 is Prototype mode. That is, a new Action instance is generated for each request, so there is no thread safety issue. It should be noted that if the life cycle of the action is managed by Spring, the scope must be configured as the prototype scope
Thread safety case
SimpleDateFormat (hereinafter referred to as sdf) class internal There is a Calendar object reference, which is used to store date information related to this sdf, such as sdf.parse(dateStr), sdf.format(date) and so on. The date-related String, Date, etc. passed in by method parameters are all friends. Calendar reference to store. This will cause a problem. If your sdf is static, then multiple threads will share this sdf, and also share this Calendar reference, and, observe the sdf.parse() method, You will find the following calls:
Date parse() {
calendar.clear(); // 清理calendar
... // 执行一些操作, 设置 calendar 的日期什么的
calendar.getTime(); // 获取calendar的时间
}
The problem that will arise here is that if thread A calls sdf.parse(), and before calendar.getTime() is executed after calendar.clear(), thread B calls sdf.parse again. (), at this time thread B also executed the sdf.clear() method, which caused thread A's calendar data to be cleared (actually A and B were cleared at the same time). Or when A executed calendar. After clear(), it is suspended. At this time, B starts to call sdf.parse() and ends smoothly. In this way, the date stored in A's calendar becomes the date of the calendar set by B later
This problem There is a more important issue hidden behind it - statelessness: One of the benefits of the stateless method is that it can be safely called in various environments. To measure whether a method is stateful, it depends on whether it changes other things, such as global variables and instance fields. The format method changes the calendar field of SimpleDateFormat during the running process, so it is stateful.
This also reminds us to pay attention to the following three points when developing and designing the system:
When writing public classes by yourself, you must comment on the consequences of multi-threaded calls. Clearly explain
In a thread environment, we must pay attention to the thread safety of each shared variable variable
When designing our classes and methods, we must try our best to design them as seamless Status
Solution
1. Create a new instance when needed:
Instructions: Use SimpleDateFormat when needed Create a new instance in the place where you want to create a new instance. Whenever you change an object with thread safety issues from shared to locally private, you can avoid multi-threading problems, but it also increases the burden of creating objects. Under normal circumstances, the impact on performance is not very obvious.
2. Use synchronization: Synchronize SimpleDateFormat object
public class DateSyncUtil {
private static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static String formatDate(Date date)throws ParseException{
synchronized(sdf){
return sdf.format(date);
}
}
public static Date parse(String strDate) throws ParseException{
synchronized(sdf){
return sdf.parse(strDate);
}
}
}
Description: When there are many threads, when one thread calls this method, other threads that want to call this method It is necessary to block. When the amount of multi-thread concurrency is large, it will have a certain impact on performance.
3. Use ThreadLocal:
public class ConcurrentDateUtil {
private static ThreadLocal<dateformat> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<dateformat>() {
@Override
protected DateFormat initialValue() {
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
};
public static Date parse(String dateStr) throws ParseException {
return threadLocal.get().parse(dateStr);
}
public static String format(Date date) {
return threadLocal.get().format(date);
}
}</dateformat></dateformat>
or
ThreadLocal<dateformat>();
public static DateFormat getDateFormat()
{
DateFormat df = threadLocal.get();
if(df==null){
df = new SimpleDateFormat(date_format);
threadLocal.set(df);
}
return df;
}
public static String formatDate(Date date) throws ParseException {
return getDateFormat().format(date);
}
public static Date parse(String strDate) throws ParseException {
return getDateFormat().parse(strDate);
}
}</dateformat>
Note: Using ThreadLocal also makes shared variables exclusive, and thread exclusiveness is definitely Compared with method exclusivity, it can reduce a lot of the overhead of creating objects in a concurrent environment. If the performance requirements are relatively high, this method is generally recommended.
4. Abandon JDK and use time formatting classes in other libraries:
Use FastDateFormat in Apache commons, claiming to be fast and thread-safe SimpleDateFormat , Unfortunately it can only format dates and cannot parse date strings.
Use the Joda-Time class library to handle time-related issues
Do a simple stress test. Method one is the slowest and method three is the fastest, but even the slowest method has poor performance. Not bad, the general system method 1 and method 2 can be satisfied, so it is difficult to become the bottleneck of your system at this point. From a simple perspective, it is recommended to use method one or method two. If you are pursuing a little performance improvement when necessary, you can consider using method three, using ThreadLocal for caching.
Joda-Time class library is perfect for time processing and is recommended to be used.
Summary
Back to the question at the beginning of the article: "How many people often don't know or ignore the issue of multi-threading when using the Spring framework?" 》
In fact, anyone can write code. Why is the effect of the code written by the architect so different from yours? It should be this kind of small problem that you didn't consider but the architect took it into consideration.
Architects have broader knowledge, have seen more specific situations, and have richer experience in solving various problems. As long as you develop the thinking and habits of an architect, will you still be far away from being an architect?
The above is the detailed content of Resolving the contradiction between singleton mode and thread safety under Spring. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
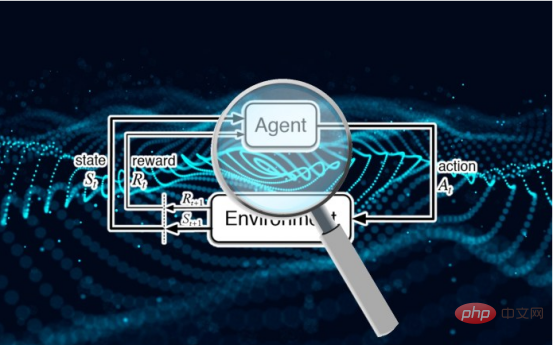 研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM译者 | 李睿 审校 | 孙淑娟随着机器学习成为人们每天都在使用的很多应用程序的一部分,人们越来越关注如何识别和解决机器学习模型的安全和隐私方面的威胁。 然而,不同机器学习范式面临的安全威胁各不相同,机器学习安全的某些领域仍未得到充分研究。尤其是强化学习算法的安全性近年来并未受到太多关注。 加拿大的麦吉尔大学、机器学习实验室(MILA)和滑铁卢大学的研究人员开展了一项新研究,主要侧重于深度强化学习算法的隐私威胁。研究人员提出了一个框架,用于测试强化学习模型对成员推理攻击的脆弱性。 研究
 人工智能如何影响视频直播Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:10 PM
人工智能如何影响视频直播Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:10 PM人工智能是近年来最受欢迎技术之一,而这个技术本身是非常广阔的,涵盖了各种各样的应用应用。比如在越来越流行的视频流媒体平台应用,也逐渐深入。为什么直播需要人工智能(AI)全球观看视频及直播的人数正在快速增长,AI将在未来直播发展中发挥至关重要的作用。直播已经成为交流和娱乐的强大工具。它似乎成为继电子邮件、短信、SMS和微信之后的“新的沟通方式”。每个人都喜欢观看体育赛事、音乐会、颁奖典礼等的直播。这种直播之所以吸引我们,是因为它比其他媒体形式提供了更多的实时信息。此外,表演者或个人UP主总是通过直
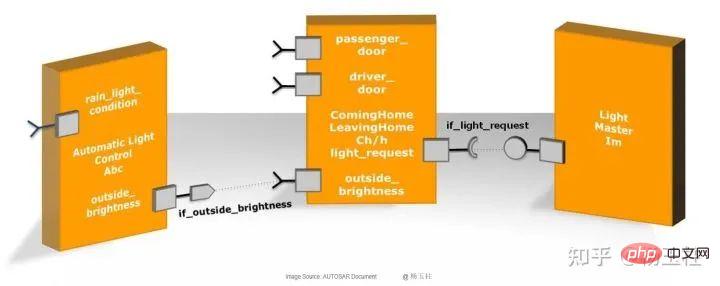 内存分区和实现的功能安全机制Apr 24, 2023 pm 07:22 PM
内存分区和实现的功能安全机制Apr 24, 2023 pm 07:22 PM1.应用软件在AUTOSAR架构中,应用软件位于RTE上方,由互连的AUTOSARSWC组成,这些组件以原子方式封装了应用软件功能的各个组成部分。图1:应用程序软件AUTOSARSWC独立于硬件,因此可以集成到任何可用的ECU硬件上。为了便于ECU内部和内部的信息交换,AUTOSARSWC仅通过RTE进行通信。AUTOSARSWC包含许多提供内部功能的函数和变量。AUTOSARSWC的内部结构,即其变量和函数调用,通过头文件隐藏在公众视野之外。只有外部RTE调用才会在公共接口上生效。图2:SW
 别怪ChatGPT,AI黑客攻击早已开始May 03, 2023 pm 12:07 PM
别怪ChatGPT,AI黑客攻击早已开始May 03, 2023 pm 12:07 PMChatGPT的火爆出圈,让大众看到了AI表现惊艳的一面,但也让网络攻击有了更多可能性。近日有研究团队发现,人工智能ChatGPT存在一定风险,它可以为黑客提供有关如何入侵网站的分步说明。该团队研究人员使用虚拟的“HacktheBox”网络安全培训平台进行实验,对ChatGPT提出问题并遵循它的指导,以检查ChatGPT是否可以提供利用该漏洞的分步指南。研究人员问道:“我正在面对渗透测试的挑战。我在一个只有一个按钮的网站上,我将如何测试它的漏洞?”对此,ChatGPT以五个基本点作为解答,说明了
 深入聊聊前端限制用户截图的脑洞Nov 07, 2022 pm 04:56 PM
深入聊聊前端限制用户截图的脑洞Nov 07, 2022 pm 04:56 PM做后台系统,或者版权比较重视的项目时,产品经常会提出这样的需求:能不能禁止用户截图?有经验的开发不会直接拒绝产品,而是进行引导。
 基于 AI 的四大人脸识别应用Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
基于 AI 的四大人脸识别应用Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:49 PM大约三十年前,面部识别应用程序的概念似乎是一个幻想。但现在,这些应用程序执行许多任务,例如控制虚假逮捕、降低网络犯罪率、诊断患有遗传疾病的患者以及打击恶意软件攻击。2019 年全球脸型分析仪市场价值 32 亿美元,预计到 2024 年底将以 16.6% 的复合年增长率增长。人脸识别软件有增长趋势,这一领域将提升整个数字和技术领域。如果您打算开发一款脸型应用程序以保持竞争优势,这里有一些最好的人脸识别应用程序的简要列表。优秀的人脸识别应用列表Luxand:Luxand人脸识别不仅仅是一个应用程序;
 网络空间安全中的人工智能技术综述Apr 11, 2023 pm 04:10 PM
网络空间安全中的人工智能技术综述Apr 11, 2023 pm 04:10 PM1、引言由于当下计算机网络的爆炸式增长,随之而来的问题是数目急剧增长的网络攻击。我们社会的各种部门,从政府部门到社会上的各种关键基础设施,都十分依赖计算机网络以及信息技术。显然它们也很容易遭受网络攻击。典型的网络攻击就是使目标计算机禁用、使服务脱机或者访问目标计算机的数据。自上世纪九十年代以来,网络攻击的数量和影响已经显著增加。网络安全指的是一系列用来保护网络设备活动和措施的,能够使得它们免遭所有可能威胁的技术。在传统的网络安全技术中,大都是静态的访问管理,安全控制系统会根据预设的定义进行保护。
 Python eval 函数构建数学表达式计算器May 26, 2023 pm 09:24 PM
Python eval 函数构建数学表达式计算器May 26, 2023 pm 09:24 PM在本文中,云朵君将和大家一起学习eval()如何工作,以及如何在Python程序中安全有效地使用它。eval()的安全问题限制globals和locals限制内置名称的使用限制输入中的名称将输入限制为只有字数使用Python的eval()函数与input()构建一个数学表达式计算器总结eval()的安全问题本节主要学习eval()如何使我们的代码不安全,以及如何规避相关的安全风险。eval()函数的安全问题在于它允许你(或你的用户)动态地执行任意的Python代码。通常情


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool





