 Java
Java javaTutorial
javaTutorial How to use JDK's built-in jmap and jhat to monitor the running status of Java processes
How to use JDK's built-in jmap and jhat to monitor the running status of Java processesThe content of this article is about how to use JDK’s own jmap and jhat to monitor the running status of Java processes. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
For running Java processes, JDK comes with many tools that allow Java developers to monitor various states of the running process, such as how many object instances are created inside the process, consumption How much memory is required, etc.
This article is written based on JDK1.8.
I wrote the simplest Java class below, which contains an infinite loop that increases the value of a counter every 5 seconds.
package jmap;
class Tool{
private int count = 0;
public void Run() throws InterruptedException{
while(true){
System.out.println("Hello: " + this.count++);
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
}
public class JMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Tool tool = new Tool();
tool.Run();
}
}
Execute this application in Eclipse.
The following describes how to use jmap and jhat to monitor this running process.
1. First get the ID of this Java running process: 15392. I directly used the Task Manager that comes with Windows to obtain the process ID.

2. Use the following command line:
jmap -dump:format=b,file=c:tempheapstatus.bin 15392
jmap is a tool provided by JDK and is located in the bin folder of the JDK installation directory.

Executing the command line will generate a heap dump file: headstatus.bin

3. Now you can use another JDK tool, jhat, to read this dump file and parse it. Use the command line:
jhat c:tempheapstatus.bin








The above is the detailed content of How to use JDK's built-in jmap and jhat to monitor the running status of Java processes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 如何在 Windows 11 上安装 JavaApr 13, 2023 pm 09:22 PM
如何在 Windows 11 上安装 JavaApr 13, 2023 pm 09:22 PM尽管每隔一段时间就会出现大量应用程序,但 Java 仍然是迄今为止最常用和最重要的编程语言之一。许多应用程序依赖于 Windows 操作系统上的 Java,更新它意味着通过为 Java 应用程序提供安全运行的稳定性和安全性来提高性能。您还可以在 Linux 和 macOS 平台上安装 Java。唯一的区别是每个平台的包/文件。现在,有了 Windows 11,是时候下载 Java,在今天的文章中,我们将带您完成在您的设备上安装它的简单步骤。我应该下载哪个版本的 Java?您下载的 Java 版本
 oracle数据库需要jdk吗Jun 05, 2023 pm 05:06 PM
oracle数据库需要jdk吗Jun 05, 2023 pm 05:06 PMoracle数据库需要jdk,其原因是:1、当使用特定的软件或功能时需要包含在JDK中的其他软件或库;2、需要安装Java JDK才能在Oracle数据库中运行Java程序;3、JDK提供了开发和编译Java应用程序的功能;4、满足Oracle对Java函数的要求,以帮助实现和实现特定功能。
 java之JDK动态代理实例分析Apr 30, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
java之JDK动态代理实例分析Apr 30, 2023 pm 01:16 PM1、说明Java中提供了一个动态代理类Proxy,Proxy并不是我们所说的代理对象的类,而是提供了一个创建代理对象的静态方法(newProxyInstance)来获取代理对象。2、实例publicclassHelloWorld{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//获取代理对象ProxyFactoryfactory=newProxyFactory();SellTicketsproxyObject=factory.getProxyObject();proxyO
 深度Linux系统安装JDK教程Feb 15, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
深度Linux系统安装JDK教程Feb 15, 2024 pm 12:36 PM深度Linux系统是一款基于Linux内核的国产操作系统,具有稳定、安全、易用等特点,在深度Linux系统中,安装JDK(JavaDevelopmentKit)是开发Java应用程序的必要步骤,本文将详细介绍如何在深度Linux系统中安装JDK。安装步骤打开深度Linux系统的终端。使用命令行下载JDK安装包,命令如下:```shellsudoapt-getinstallopenjdk-11-jdk```等待下载完成后,系统会自动安装JDK。验证JDK是否安装成功,输入以下命令:```javaj
 linux jdk目录在哪Mar 22, 2023 am 09:52 AM
linux jdk目录在哪Mar 22, 2023 am 09:52 AMlinux jdk目录在bin目录下,具体查找方法是:1、通过“whereis java”命令找到javad的执行目录;2、通过执行文件找到链接文件;3、通过“ls -lrt /etc/alternatives/java”命令找到安装目录即可。
 一起聊聊Java多线程之线程安全问题Apr 21, 2022 pm 06:17 PM
一起聊聊Java多线程之线程安全问题Apr 21, 2022 pm 06:17 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于多线程的相关问题,包括了线程安装、线程加锁与线程不安全的原因、线程安全的标准类等等内容,希望对大家有帮助。
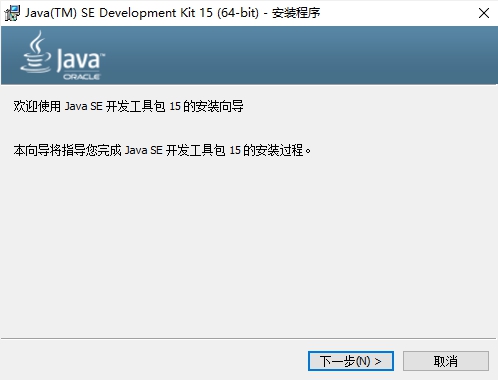 jdk怎么安装-jdk安装教程Mar 04, 2024 pm 05:10 PM
jdk怎么安装-jdk安装教程Mar 04, 2024 pm 05:10 PM近期有很多小伙伴咨询小编jdk怎么安装,接下来就让我们一起学习一下jdk怎么安装的全部内容吧,希望可以帮助到大家。1、首先下载JDK安装文件,进入JDK安装界面,如图所示。2、单击“下一步”按钮,进入JDK自定义安装界面,如图所示。3、建议选择直接安装到默认目录,单击“下一步”按钮即可进行安装,如图所示。也可以单击“更改”按钮,自行选择安装目录。4、安装完毕后,弹出界面,单击“关闭”按钮即可,如图所示。上面就是小编为大家带来的jdk怎么安装的全部教程,希望对大家能够有所帮助哦。
 Linux系统中jdk环境怎么配置May 12, 2023 am 09:31 AM
Linux系统中jdk环境怎么配置May 12, 2023 am 09:31 AM如下操作步骤为linux系统中部署jdk环境1.下载jdk安装包2.新建安装jdk文件夹(/usr/local/java/jdk)cd/usr/localmkdir/usr/local/javalocal目录下新建java目录cd/usr/local/javamkdir/usr/local/java/jdk新建jdk目录cd/usr/local/java/jdk3.上传jdk安装包到linux4.解压jdk安装包解压格式:tarzxvf压缩包名称后面的名称可以只输入一个首字母,然后使用Tab按键


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft





