PHP5 will stop updating at the end of December, 60% of users will face security risks
- 不言forward
- 2018-10-17 11:43:207531browse
Network technology application research company W3Techs recently stated that based on the PHP version used by all websites, from January 1, 2019, nearly 62% of websites will be subject to malicious attacks because they cannot obtain security updates.
According to W3Techs’ survey, starting from the 15th of this month, the proportion of PHP used in the website sample it studied was as high as 78.9%, and the proportion of websites using PHP 5 reached 61.8%. Among subversions, the proportion of websites using PHP version 5.6 is 41.5%, with version 5 having the highest proportion.
According to the supported versions and schedule (below) listed on the PHP official website, PHP
5.6 was released in 2014, major support closed on January 19, 2017, and security support will end on December 31, 2018. That is, two and a half months later, using PHP 5.6
Versions of the website will no longer receive updates for security vulnerabilities or errors unless the user pays for the operating system vendor's update service. If hackers find and exploit older versions of PHP
Vulnerabilities in the Internet could put millions of websites and users at risk.
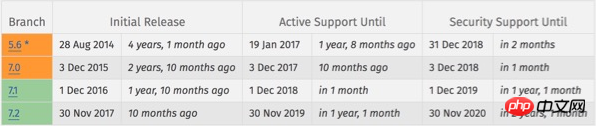
In fact, the major and security update periods of PHP 5.6 have ended long ago, but due to the large number of websites used, the PHP maintenance organization once extended them respectively Its support hours.
Some people describe this situation as a PHP time bomb. The newer PHP 7.0 will no longer provide security support at EOL (End of Life) on December 1st this year. Even version 7.1 will reach end of life on December 1st. Security support ends after one year.
Among the three major website content management system (CMS) projects, only
Drupal announced that starting from March 6 next year, Drupal will support the minimum requirement of PHP 7 for web pages, and it is recommended to use version 7.1. Joomla recommends 5.6
or higher, with support starting at 5.3.10. Wordpress recommends using PHP 7.2 or higher, with a minimum of 5.2.4 supported.
according to ZDNet reports that Sean Murphy, director of security component development at WordFence, said that the main target of PHP vulnerability exploitation is not PHP itself, but PHP libraries and CMS systems, but other security experts believe that when the deadline comes, hackers will actively exploit the vulnerabilities in PHP 5.6.
Related articles
See more- How to get started with learning php? The clearest PHP learning roadmap in history!
- New Year's Day welfare giveaway! Crack Baidu cloud download, 10MB/S is not a dream!
- Teach you 'How to watch the PHP Chinese course video and quietly become a master?'
- A comprehensive inventory of the most internationally influential hacking incidents in 2016!
- WeChat mini program practical video course is online! Learn quickly! Otherwise it will be too late!

