Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >About the implementation method of data transmission between cloud server ECS
About the implementation method of data transmission between cloud server ECS
- 坏嘻嘻Original
- 2018-09-19 14:01:373629browse
This article introduces the implementation method of data transmission between cloud server ECS, and focuses on its specific steps. The content of this article is very compact, and I hope you will study patiently.
How to implement data transmission between cloud server ECS
Introduction
In today's rapid development of information technology, servers A large amount of file data is exchanged with other stand-alone computers every day, and file transfer is commonplace for everyone. Therefore, its importance is self-evident. There are different file transfer methods. Choosing a file transfer tool that suits you can get twice the result with half the effort at work. Save resources, facilitate transmission, improve work efficiency, encrypt protection, etc. Therefore, many file transfer tools have emerged, such as: NC, FTP, SCP, NFS, SAMBA, RSYNC/SERVERSYNC, etc. Each method has its own characteristics. This article will first briefly introduce the basic principles of file transfer, and then introduce in detail the commonly used file transfer methods on Unix/Linux and Windows platforms, and compare their respective characteristics, so that readers can have a more detailed understanding of file transfer methods. This allows you to choose the appropriate file transfer method according to different needs.
File transfer principle
File transfer is a form of information transfer. It is the transfer of file data between the data source and the data sink. The process is also called file data communication. The operating system extracts the file data into the memory for temporary storage, and then copies it to the destination. Encryption means adding a shell to the file. The file itself is still a whole. Copying just transfers the whole to other places. There is no need to decrypt, only open. Decryption is only required when compressing the package. As a whole data, a large file cannot be transferred from one host to another in an instant. The transfer is a continuous process, but the file is not divided. Therefore, if the transfer process is unexpectedly interrupted, the target path There will be no transferred files. In addition, if multiple files are transferred, then these files are transferred separately in order. If interrupted in the middle, the file being transferred will fail to be transferred. However, the files that have been transferred before will be transferred. Success (if a compressed file package is transferred, no matter how many files are in it, it will be regarded as one file in itself).
Usually the NC, FTP, SCP, NFS, etc. we see are tools that can be used to transfer file data. Below we will introduce in detail the characteristics and usage of the main file transfer tools.
NETCAT
It has the reputation of "Swiss Army Knife" among network tools. It is powerful. As a network tool, its ability to transfer files cannot be underestimated.
Commonly used parameters:
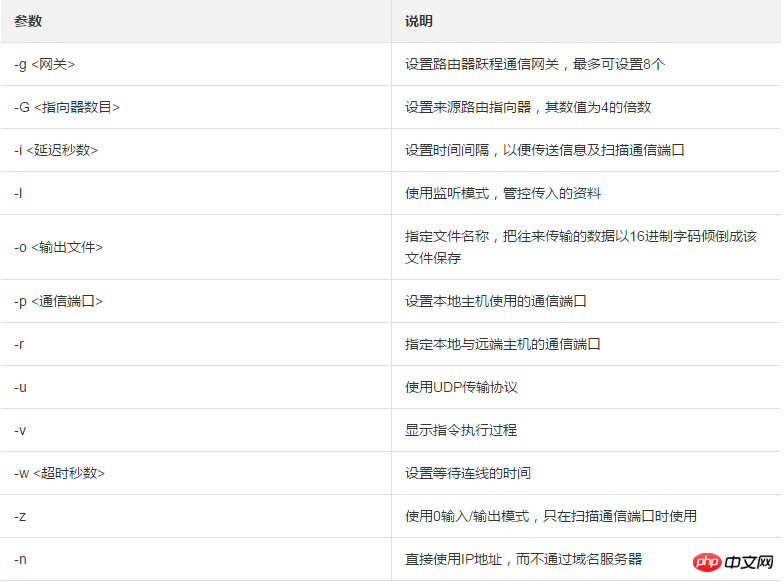
Simple usage examples
1.Port scanning 21 -24 (take IP192.168.2.34 as an example).
nc -v -w 2 192.168.2.34 -z 21-24 nc: connect to 192.168.2.34 port 21 (tcp) failed: Connection refused Connection to 192.168.2.34 22 port [tcp/ssh] succeeded! nc: connect to 192.168.2.34 port 23 (tcp) failed: Connection refused nc: connect to 192.168.2.34 port 24 (tcp) failed: Connection refused
2. Copy the file from 192.168.2.33 to 192.168.2.34.
On 192.168.2.34:
nc -l 1234 > test.txt
On 192.168.2.33:
nc 192.168.2.34 < test.txt
3. Use the nc command to operate memcached.
Storage data:
printf “set key 0 10 6rnresultrn” |nc 192.168.2.34 11211
Get data:
printf “get keyrn” |nc 192.168.2.34 11211
Delete data:
printf “delete keyrn” |nc 192.168.2.34 11211
View status:
printf “statsrn” |nc 192.168.2.34 11211
Simulate top command to view Status:
watch “echo stats” |nc 192.168.2.34 11211
Clear cache:
printf “flush_allrn” |nc 192.168.2.34 11211 #谨慎操作,清空了缓存就没了
SCP (secure copy)
Introduction
## The usage of the #SCP command is very similar to the RCP command format. The difference is that SCP provides more security. SCP will ask you to enter a password or passphrase when verification is required. It is generally recommended to use the SCP command because it is more secure than RCP. The SCP command uses SSH to transmit data and uses the same authentication mode as SSH to provide the same security guarantee. SSH is currently a more reliable protocol that provides security for remote login sessions and other network services. The use of the SSH protocol can effectively prevent Information leakage issues during remote management. SCP is an SSH-based application, so the machine for data transmission must support the SSH service.Features
SCP is similar to RCP, it can retain file attributes on a specific file system, can retain file attributes or needs to be recursive Copy the subdirectory. SCP has better file transfer confidentiality. At the same time, the price paid is that you need to enter a password when transferring files and involve some configuration issues with SSH, which affect its convenience. For users with specific needs, it is a more suitable transfer tool.Common examples
使用 SCP 命令,需要输入密码,如果不想每次都输入,可以通过配置 SSH,这样在两台机器间拷贝文件时不需要每次都输入用户名和密码:
生成 RSA 类型的密钥:
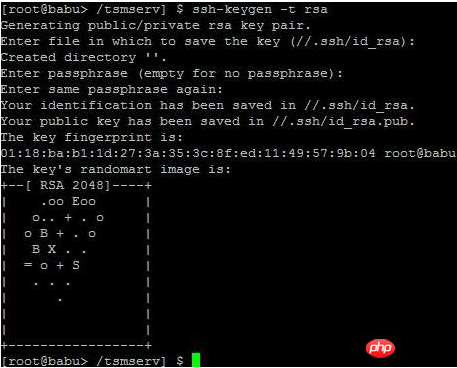
上述命令生成 RSA 类型的密钥。在提示密钥的保存路径和密码时,可以直接回车使用默认路径和空密码。这样,生成的公共密钥保存/.ssh/id_rsa.pub,私有密钥保存在 /.ssh/id_rsa 。然后把这个密钥对中的公共密钥的内容复制到要访问的机器上的 /.ssh/authorized_keys 文件中。这样,下次再访问那台机器时,就不用输入密码了。
scp可以在 2个 linux 主机间复制文件
命令基本格式:
scp [可选参数] file_source file_target
从本地复制到远程(如下四种方式):
scp local_file remote_username@remote_ip:remote_folder scp local_file remote_username@remote_ip:remote_file scp local_file remote_ip:remote_folder scp local_file remote_ip:remote_file
注:第1,2个指定了用户名,命令执行后需要再输入密码,第1个仅指定了远程的目录,文件名字不变,第2个指定了文件名。
第3,4个没有指定用户名,命令执行后需要输入用户名和密码,第3个仅指定了远程的目录,文件名字不变,第4个指定了文件名。
从远程复制到本地:
注:从远程复制到本地,只要将从本地复制到远程的命令的后2个参数 调换顺序 即可
scp root@www.cumt.edu.cn:/home/root/others/music /home/space/music/i.mp3 scp -r www.cumt.edu.cn:/home/root/others/ /home/space/music/ Rsync
Rsync是linux/Unix文件同步和传送工具。用于替代rcp的一个工具,rsync可以通过rsh或ssh使用,也能以daemon模式去运行,在以daemon方式运行时rsync server会开一个873端口,等待客户端去连接。连接时rsync server会检查口令是否相符,若通过口令查核,则可以通过进行文件传输,第一次连通完成时,会把整份文件传输一次,以后则就只需进行增量备份。
安装方式:
注:可以使用每个发行版本自带的安装包管理器安装。
sudo apt-get install rsync #在debian、ubuntu 等在线安装方法; slackpkg install rsync #Slackware 软件包在线安装; yum install rsync #Fedora、Redhat 等系统安装方法;
源码编译安装:
wget http://rsync.samba.org/ftp/rsync/src/rsync-3.0.9.tar.gz tar xf rsync-3.0.9.tar.gz cd rsync-3.0.9 ./configure && make && make install
参数介绍:
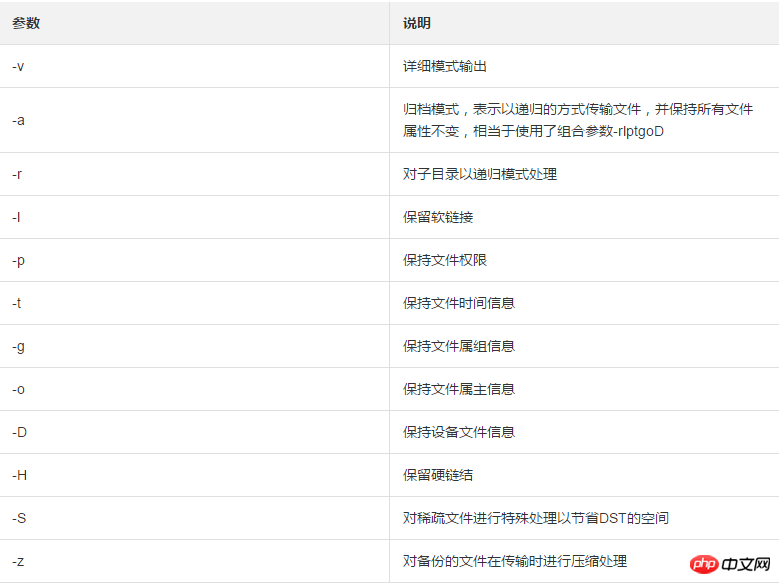
rsync六种不同的工作模式:
1.拷贝本地文件,将/home/coremail目录下的文件拷贝到/cmbak目录下。
rsync -avSH /home/coremail/ /cmbak/
2.拷贝本地机器的内容到远程机器。
rsync -av /home/coremail/ 192.168.11.12:/home/coremail/
3.拷贝远程机器的内容到本地机器。
rsync -av 192.168.11.11:/home/coremail/ /home/coremail/
4.拷贝远程rsync服务器(daemon形式运行rsync)的文件到本地机。
rsync -av root@172.16.78.192::www /databack
5.拷贝本地机器文件到远程rsync服务器(daemon形式运行rsync)中。当DST路径信息包含”::”分隔符时启动该模式。
rsync -av /databack root@172.16.78.192::www
6.显示远程机的文件列表。这类似于rsync传输,不过只要在命令中省略掉本地机信息即可。
rsync -v rsync://192.168.11.11/data
rsync配置文件说明:
cat/etc/rsyncd.conf #内容如下 port = 873 #端口号 uid = nobody #指定当模块传输文件的守护进程UID gid = nobody #指定当模块传输文件的守护进程GID use chroot = no #使用chroot到文件系统中的目录中 max connections = 10 #最大并发连接数 strict modes = yes #指定是否检查口令文件的权限 pid file = /usr/local/rsyncd/rsyncd.pid #指定PID文件 lock file = /usr/local/rsyncd/rsyncd.lock #指定支持max connection的锁文件,默认为/var/run/rsyncd.lock motd file = /usr/local/rsyncd/rsyncd.motd #定义服务器信息的,自己写 rsyncd.motd 文件内容 log file = /usr/local/rsyncd/rsync.log #rsync 服务器的日志 log format = %t %a %m %f %b syslog facility = local3 timeout = 300 [conf] #自定义模块 path = /usr/local/nginx/conf #用来指定要备份的目录 comment = Nginx conf ignore errors #可以忽略一些IO错误 read only = no #设置no,客户端可以上传文件,yes是只读 write only = no #no为客户端可以下载,yes不能下载 hosts allow = 192.168.2.0/24 #可以连接的IP hosts deny = * #禁止连接的IP list = false #客户请求时,使用模块列表 uid = root gid = root auth users = backup #连接用户名,和linux系统用户名无关系 secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.pass #验证密码文件
The above is the detailed content of About the implementation method of data transmission between cloud server ECS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

