Home >Java >javaTutorial >JAVA introductory system tutorial (8) Object-oriented (inheritance)
JAVA introductory system tutorial (8) Object-oriented (inheritance)
- php是最好的语言Original
- 2018-08-10 11:06:262057browse
1. The concept of inheritance: Inheritance is a relationship between classes. An "is a" relationship
Parent class--->Base class Subclass--->Derived class
Note: Inheritance in JAVA is single inheritance2. Advantages of inheritance: The subclass has all the properties and methods of the parent class (private modification is invalid) to achieve code reuse
##3 . Grammar rules: class subclass extends parent class
Example:
package example;
public class Animal {
public int age;
public String name;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("动物不吃东西就会饿");
}
}
package example;
public class Dog extends Animal{
}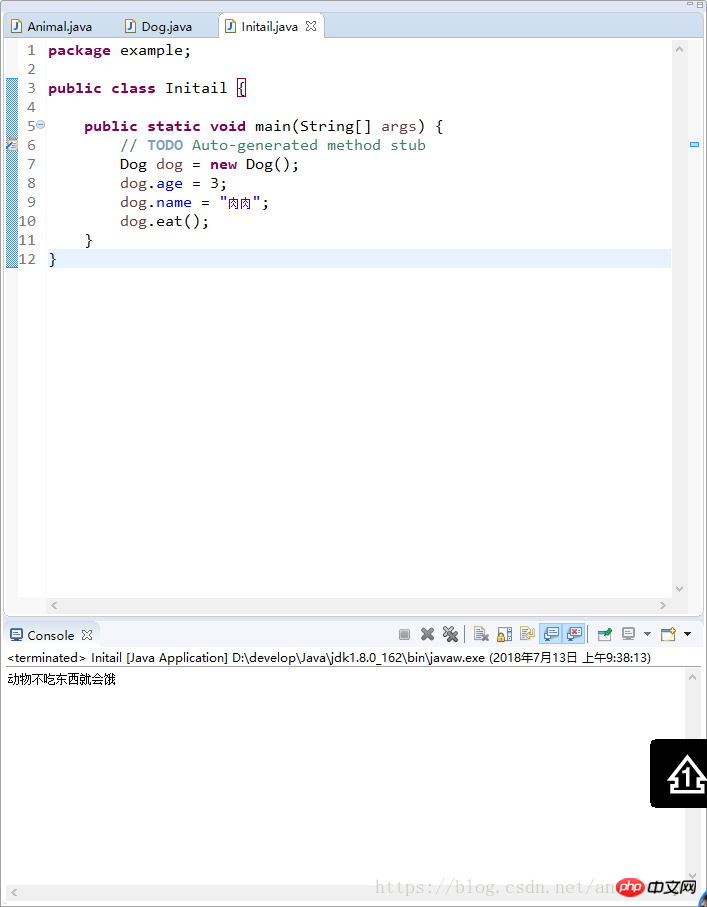
4. Rewriting of methods: If the subclass is not satisfied with the method inherited from the parent class, it can override the method inherited by the parent class. When calling the method, the method of the subclass will be called to a limited extent
package example;
public class Dog extends Animal{
public void eat() {
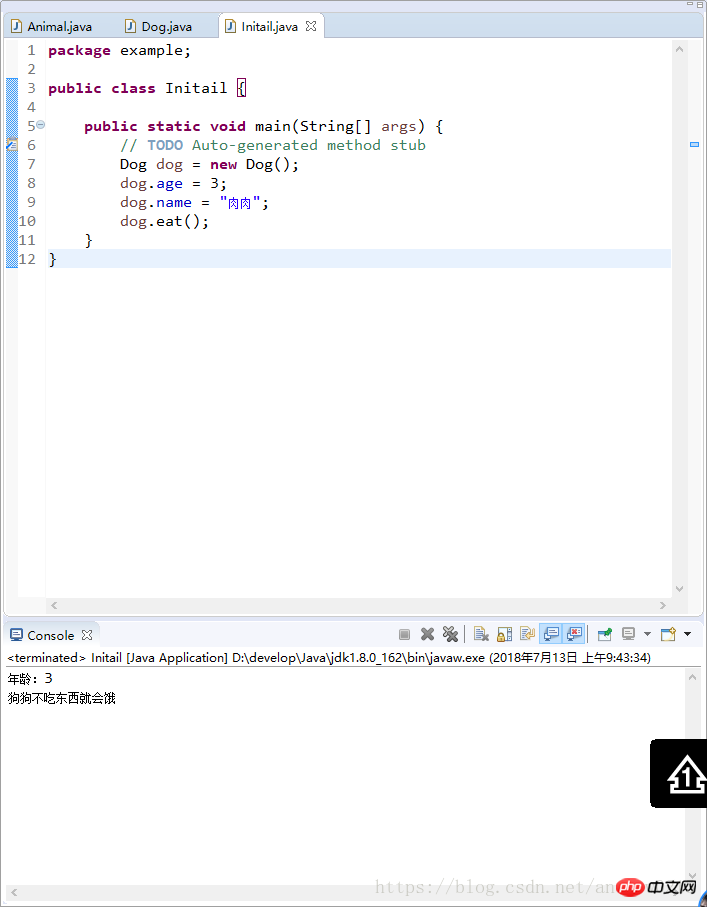
System.out.println("年龄:"+age+"\n狗狗不吃东西就会饿");
}
}
5. Initialization sequence in inheritance
package example;
public class Animal {
public int age;
public String name;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("年龄:"+age+"\n动物不吃东西就会饿");
}
public Animal() {
System.out.println("这是执行了Animal类");
}
}
package example;
public class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog() {
System.out.println("这是执行了Dog类");
}
}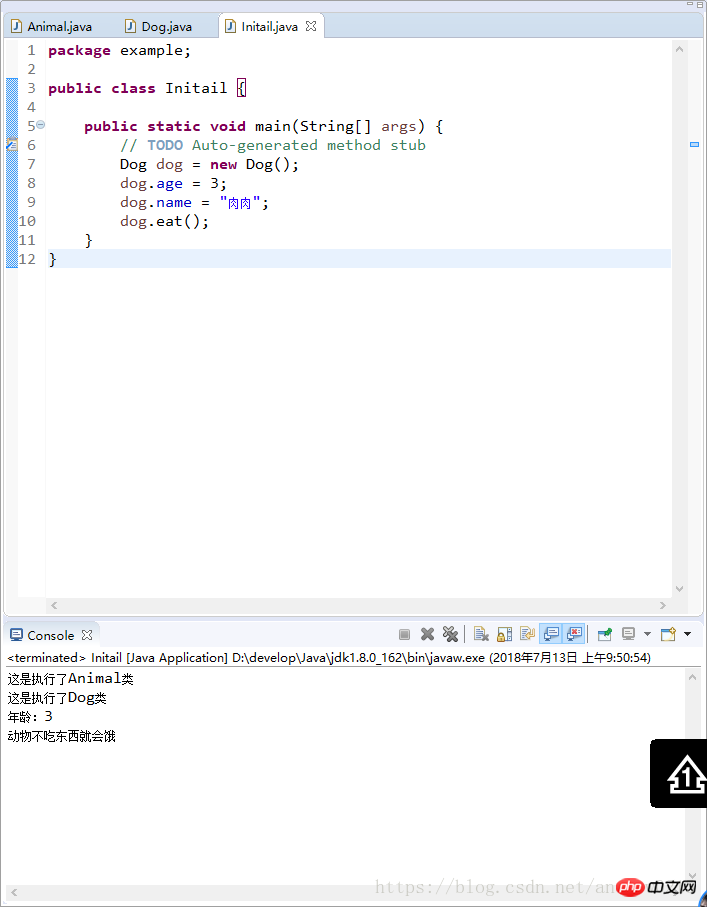 Another example:We first assign a value to age in the Animal class, and then assign it in the Animal method age is assigned again
Another example:We first assign a value to age in the Animal class, and then assign it in the Animal method age is assigned againpackage example;
public class Animal {
public int age = 10;
public String name;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("年龄:"+age+"\n动物不吃东西就会饿");
}
public Animal() {
System.out.println("这是执行了Animal类");
age = 20;
}
}Next let’s look at the output result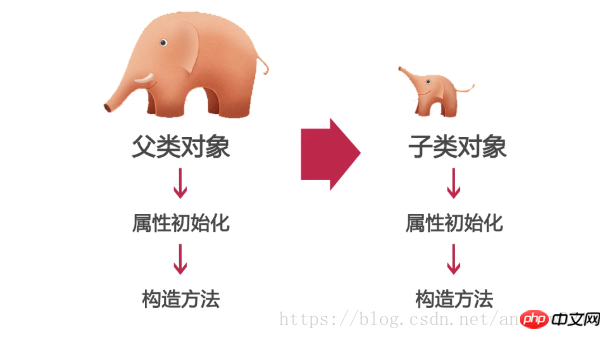

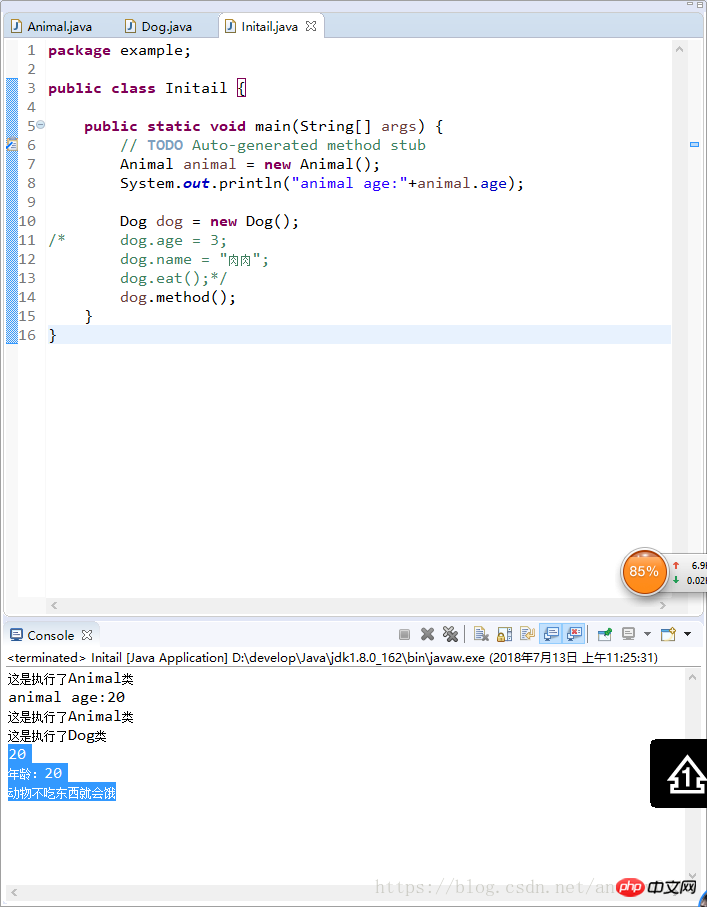
7. The use of super keyword: used inside the object, it can represent the parent class object
1) Access the attributes of the parent class: super.age
2) Access the method of the parent class: super.eat()
Example :
package example;
public class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog() {
System.out.println("这是执行了Dog类");
}
public void method() {
System.out.println(super.age);
super.eat();
}
}
3) Application of super
Construction of subclasses The constructor of its parent class must be called during the method process.
public class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog() {
super(); //这里是显示的 写与不写是一样的 但写的话必须放在第一行
System.out.println("这是执行了Dog类");
}
public void method() {
System.out.println(super.age);
super.eat();
}
}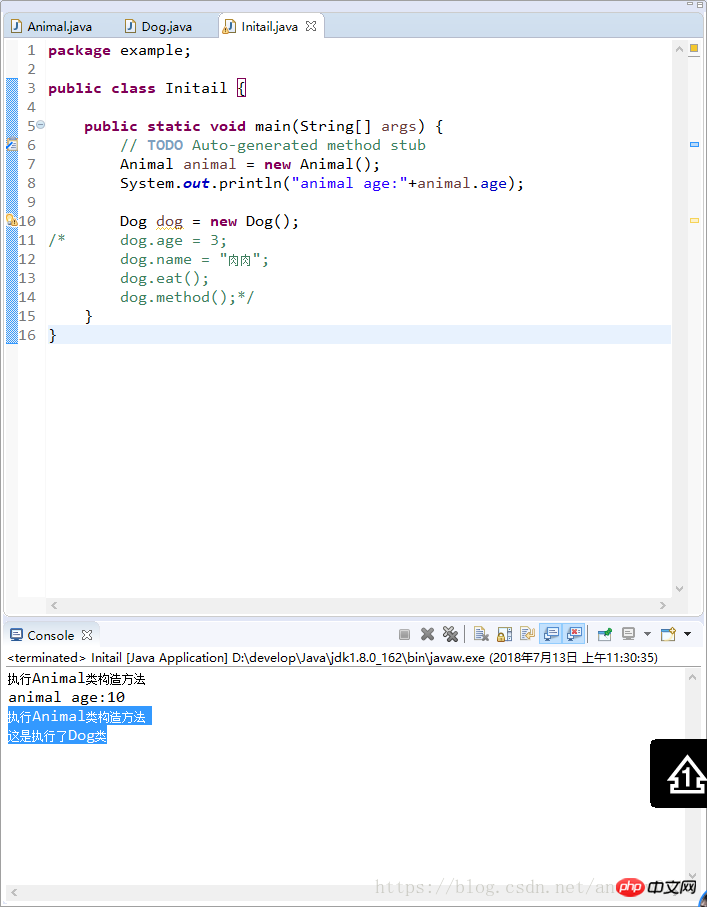
If the constructor of the subclass does not display the constructor of the parent class, the system will call the parent class's no-argument constructor by default
If the constructor is called explicitly, it must be in the first line of Zi Erlei's constructor.
If the constructor of the subclass does not explicitly call the constructor of the parent class, and the parent class does not have a parameterless constructor, a compilation error will occur
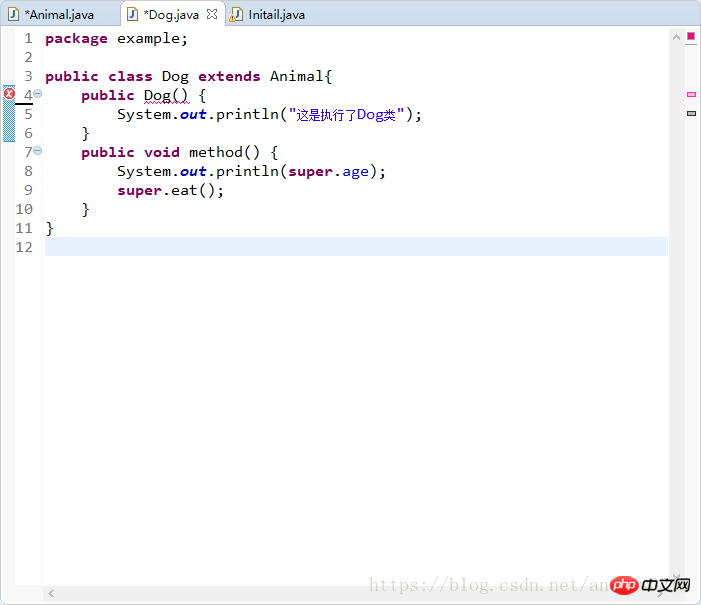
public class Animal {
public int age = 10;
public String name;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("年龄:"+age+"\n动物不吃东西就会饿");
}
/* public Animal() {
System.out.println("执行Animal类构造方法");
}*/
public Animal(int age) {
this.age = age ;
}
}
8. Object class: It is the parent class of all classes. If a class does not use the extends keyword to clearly indicate that it inherits another class, then this class inherits the Object class by default.
Methods in the Object class are suitable for all subclasses.
1) toString() method
The hash code of the object returned when defining a toString() method in the Object class (Object address string)
###可以通过重写toString()方法表示出对象的属性。
2)equals()方法
比较的是对象的引用是否指向同一块内存地址。
一般情况下比较两个对象时比较他的值是否一致,所以要进行重写。
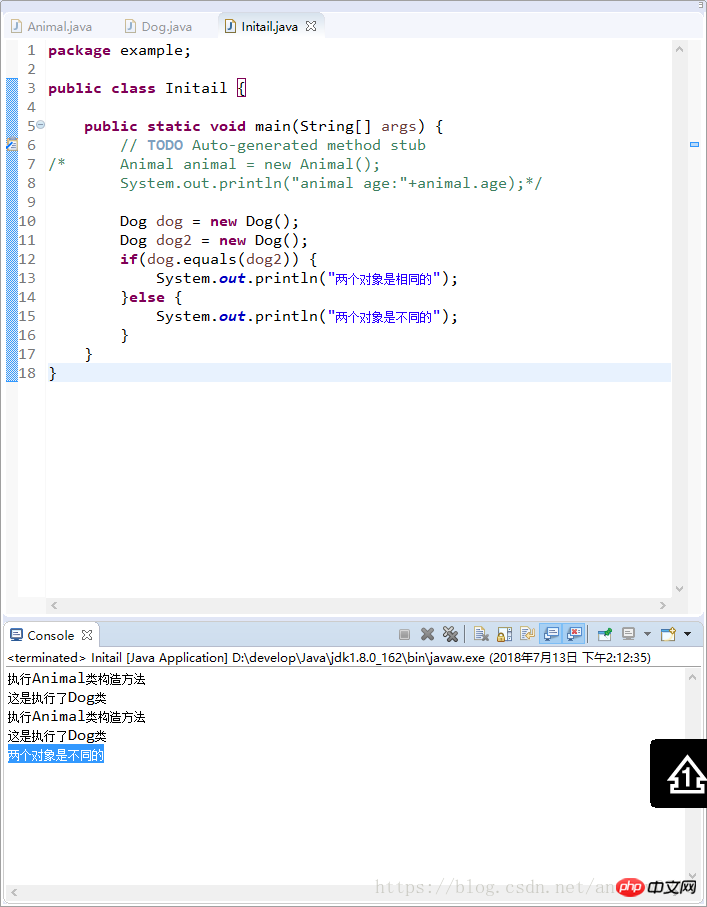
此时若同时给age赋相同值
由此可见还是输出false 在这我们建立equals方法
创建equals方法: Source --> Generate hashCode() and equals()...

@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) //判断两个对象的类型是否相同
return false;
Dog other = (Dog) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
return true;
}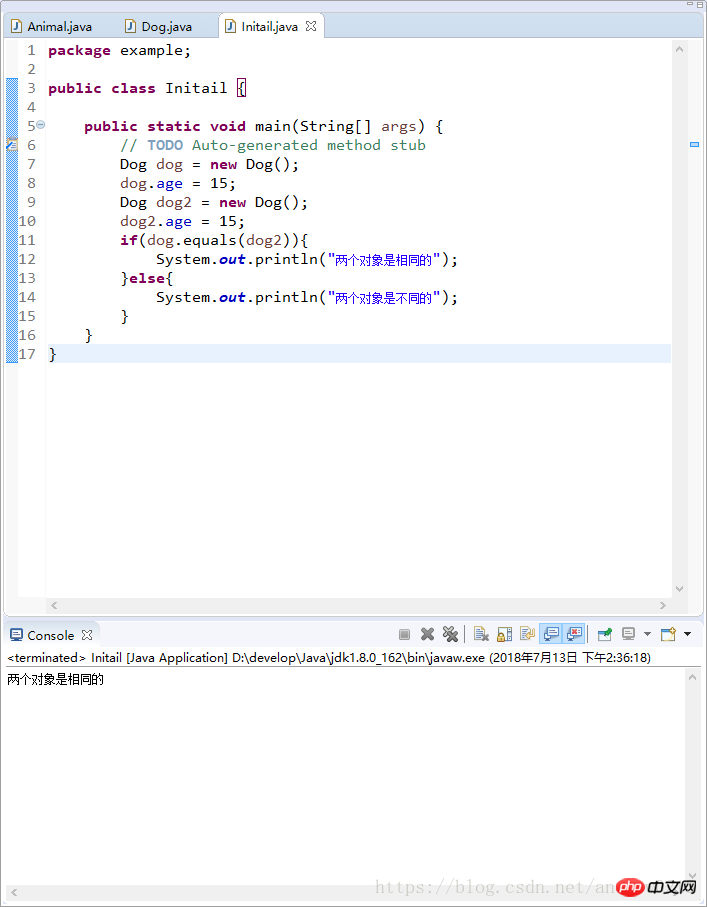
此时结果就为true了
####END####
相关文章:
The above is the detailed content of JAVA introductory system tutorial (8) Object-oriented (inheritance). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

