Home >Web Front-end >HTML Tutorial >Summary about http front-end storage
Summary about http front-end storage
- 不言Original
- 2018-07-26 10:55:541826browse
The content shared with you in this article is a summary of http front-end storage. The content is very detailed. Next, let’s take a look at the specific content. I hope it can help friends in need.
cookie
Why is there cookie
The http protocol is stateless. The so-called stateless means that the server does not know Is this request sent by the same client as the last request? It's like you often go to a supermarket to buy things, and the boss doesn't remember who you are. But if you bring your membership card every time, the boss can identify who you are. The role of the cookie is similar to that of the membership card.
About process
When the server receives an HTTP request, the server can add a Set-Cookie option in the response header. After the browser receives the response, it usually saves the cookie, and then sends the cookie information to the server through the Cookie request header in every subsequent request to the server. In addition, the cookie expiration time, domain, path, validity period, and applicable sites can all be specified as needed.
Of course, the browser can also operate cookies. document.cookie can obtain all cookies of the current page.
Details
domain, path
These two attributes determine whether the cookie will be sent to which URLs
The Domain identifier specifies which hosts can accept cookies. If not specified, it defaults to the host of the current document (excluding subdomain names). If Domain is specified, subdomain names are generally included.
For example, if you set Domain=mozilla.org, the cookie is also included in the subdomain (such as developer.mozilla.org).
Path identification specifies which paths under the host can accept cookies (the URL path must exist in the request URL). Subpaths are also matched using the character %x2F ("/") as a path separator.
For example, domain=qq.com, path=/blog, then the cookie will be sent to:
- ##qq.com/blog
- wx.qq.com/blog ##wx.qq.com/blog/aa
- ....
- expires, max-age
These two attributes determine how long the cookie is stored in the browser
The specific details are :
- Expires Set an expiration date for cookie deletion
- Max-age Set the number of seconds a cookie will expire
- IE browsers (ie6, ie7 and ie8) do not support max-age, all browsers support expires
- If expires and max are set at the same time -age, then browsers that support max-age will ignore the value of expires, and browsers that do not support max-age will ignore max-age and only support expires
- If expires and max- If the age is not set, the cookie will become a session cookie, that is, it will be automatically deleted when the browser is closed.
- secure and httpOnly
Cookies marked as Secure only Should be sent to the server via a request encrypted by the HTTPS protocol. But even if the Secure flag is set, sensitive information should not be transmitted through Cookies, because Cookies are inherently insecure, and the Secure flag cannot provide real security. Starting in Chrome 52 and Firefox 52, insecure sites (http:) cannot use the Secure tag of cookies
To avoid cross-domain scripting (XSS) attacks, the Document.cookie API with HttpOnly cannot be accessed through JavaScript Flag cookies, they should only be sent to the server. If the cookie containing server-side Session information does not want to be called by client-side JavaScript scripts, then the HttpOnly flag should be set for it.
How to set cookie
Server
Just set-cookie on the server
The following picture shows GitHub’s cookie settings
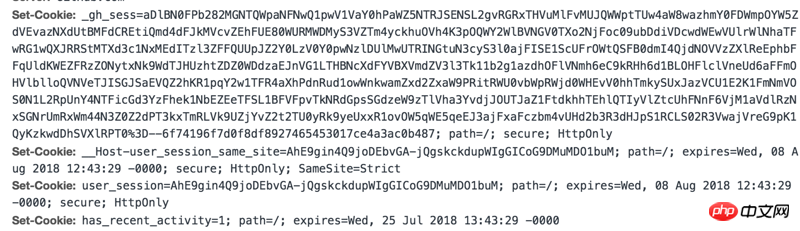 Browser
Browser
You can operate directly in JavaScript:
document.cookie="age=12; expires=Thu, 26 Feb 2116 11:50:25 GMT; domain=github.com; path=/";
How to modify cookie
When modifying a cookie, make sure the name-domain-path is consistent, otherwise The old value is not modified, but a new cookie is added.
How to delete cookies
Make sure the name-domain-path is consistent and set expires to a past time point
sessionStorage
Use
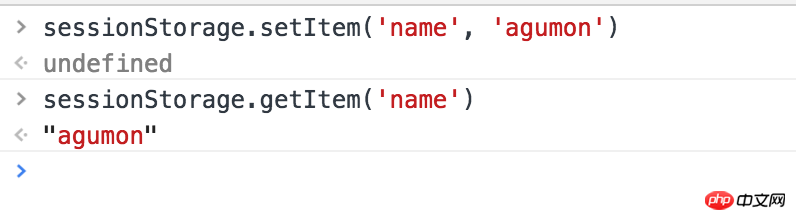
setItem(key, val);
getItem(key)
##Details
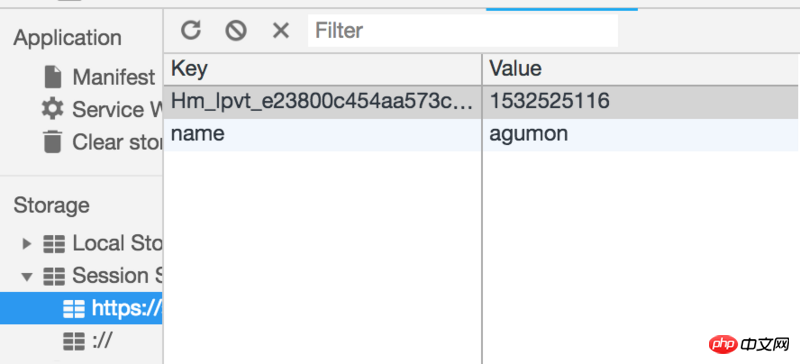
SessionStorage will not be cleared unless the page is refreshed. The rest will clean up sessionStorage (such as opening a new tab, closing the current tab and opening a new tab, not to mention closing the browser)
localStorage
Use
setItem(key, val);
getItem(key)
- Only the current domain where localStorage is set can be used, but the newly opened tab can still be used and the browser is closed and reopened and the user is still there
- If you don't delete it actively, it will be stored forever.
- The size is 4M
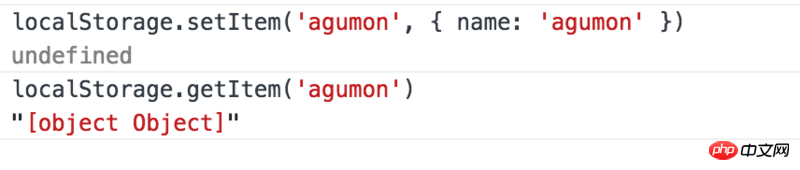
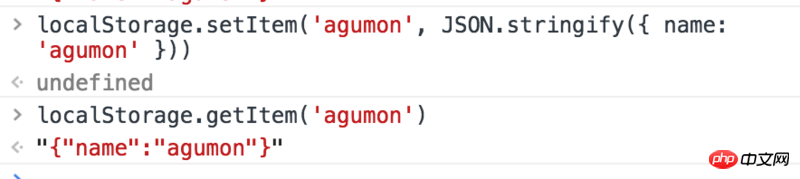
- localStorage can store data in k-v format. The stored value needs to be of string type. The object cannot be stored directly, but the object can be serialized into a string and then stored. If the object is forcibly stored, object.toString will be called, causing tragedy. The correct method should be JSON.stringify
- openDatabase: This method creates a database object using an existing database or a new database.
- transaction: This method allows us to control a transaction and perform commit or rollback based on this situation.
- executeSql: This method is used to execute the actual SQL query.
Analysis of meta information meta tag attributes in HTML (with code)
How to Introduction to the method of dynamically generating html elements and appending attributes to elements (with code)
The above is the detailed content of Summary about http front-end storage. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

