Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Detailed example of how nginx handles requests
Detailed example of how nginx handles requests
- 无忌哥哥Original
- 2018-07-12 13:51:571692browse
1. First, the two server blocks are configured as follows
server {
listen 80;
server_name hanmk.com;
location / {
root /tmp/data/;
autoindex on;
}
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name demo.com ;
location / { # tomcat首页
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
location /jenkins { #tomcat部署jenkins
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; #获取真实ip
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_send_timeout 90;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 4 32k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;#获取代理者的真实ip
proxy_redirect off;
}
location /ApprPhD { #nodeJs服务器
proxy_pass http://192.168.XXX.XXX:3030;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; #获取真实ip
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_send_timeout 90;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 4 32k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;#获取代理者的真实ip
proxy_redirect off;
}
}Description:
In the first server, the service points to the static file under the server/tmp/data/ path;
In the second server, the service is pointed to three routing virtual machines (one route points to the tomcat homepage deployed locally on the virtual machine, one points to jenkins deployed under tomcat, and one points to the application deployed on another virtual machine. )
The listening ports configured in both servers are 80 (also to better view the test results)
server_name specifies the (virtual host) server name, and generally configures the domain name (example. org, www.example.org, can be defined using a precise name, wildcard name or regular expression; when you access a request link on the external network, nginx will match whether it is forwarded to server1 or server2 based on the host name you filled in)
Also in order to better view the test results, I filled in the domain name in server_name instead of filling in the real ip or localhost of the virtual machine (because the ip addresses are all virtual machine ips. If you fill in the ip address, you cannot see nginx How to forward the request) (In addition, if there is only one server, there is no need to fill in the server_name, because it will eventually be forwarded to the server under the server. I tried it, and as long as the port is correct, the forwarding can be successful. The internal principle is still there. Not sure...)
Fill in hanmk.com for server_name in server1
Fill in demo.com for server_name in server2
After completing the above configuration, you need to reload the configuration file nginx .conf
2. Configure the client’s hosts file
In the first step, hanmk.com and demo.com were configured in server_name respectively, but because the domain name service was not activated, directly Using these two domain names to send requests on the client will fail, so in order to use these two fake domain names to send requests normally, you must first configure it on the client host. The steps are as follows:
Open the hosts file and add the following two lines (because the mapped IP addresses are the same, you can also add the two domain names on one line, separated by spaces)

3. Test
(1) Use http://hanmk.com/ to send a request, and access the static files under the path of virtual machine/tmp/data/

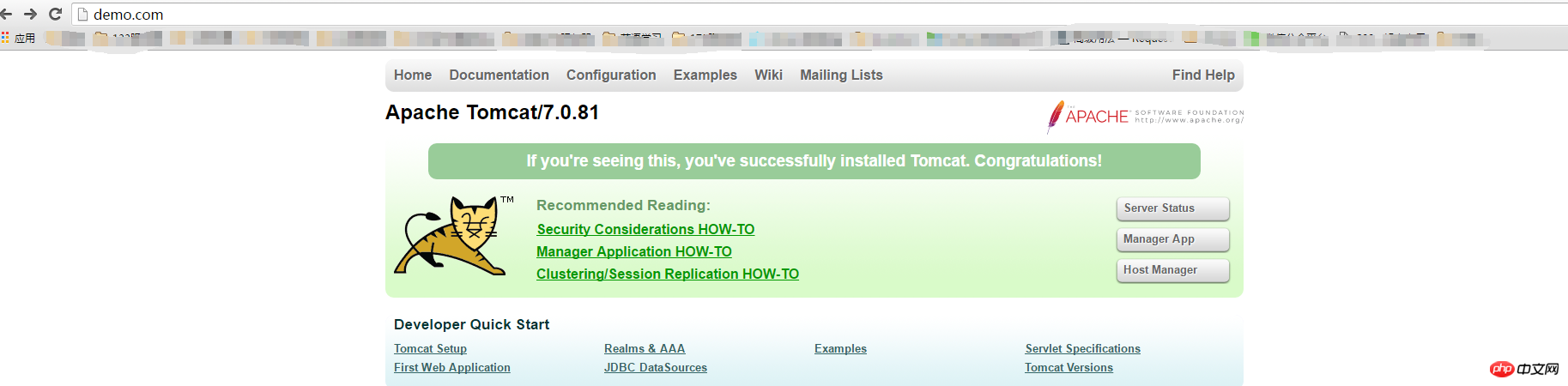
(2) Visit http://demo.com/, http://demo.com/jenkins, http://demo.com/ApprPhD/index respectively, the results are as follows

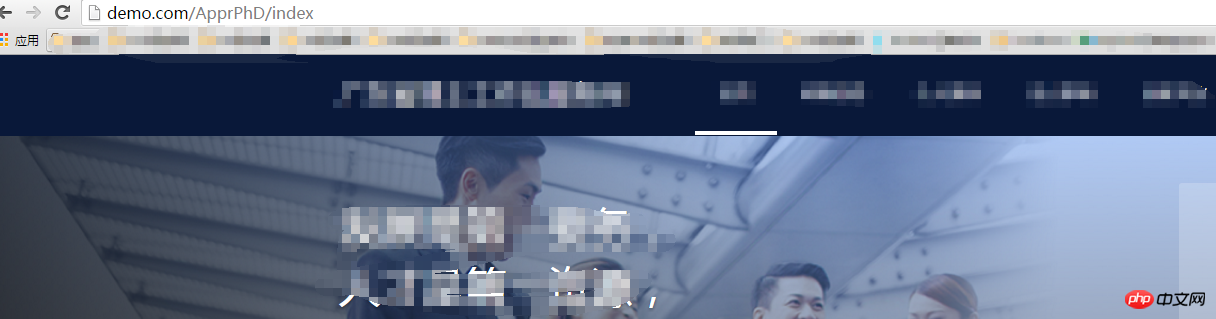

Description nginx matches the corresponding server based on the domain name of the access link, and then based on the location Path, route to the corresponding service
The above is the detailed content of Detailed example of how nginx handles requests. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

