Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Examples of PHP implementing pre-order, in-order and post-order traversal binary tree operations based on non-recursive algorithms
Examples of PHP implementing pre-order, in-order and post-order traversal binary tree operations based on non-recursive algorithms
- jackloveOriginal
- 2018-06-30 18:03:052898browse
This article mainly introduces PHP's implementation of pre-order, in-order and post-order traversal operations on binary trees based on non-recursive algorithms. It analyzes PHP's use of non-recursive algorithms to perform pre-order, in-order and post-order traversal operations on binary trees based on examples. For the principles and specific implementation techniques, friends in need can refer to the following
Examples of this article describe how PHP implements pre-order, in-order and post-order traversal binary tree operations based on non-recursive algorithms. Share it with everyone for your reference, the details are as follows:
Overview:
The principle of binary tree traversal is as follows:
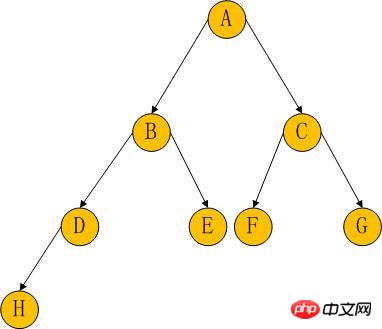
For the binary tree traversal shown in the above figure:
1. Pre-order traversal: First traverse the root node, then traverse the left subtree, and finally traverse the right subtree.
ABDHECFG
2. In-order traversal: First traverse the left subtree, then traverse the root node, and finally traverse the right subtree.
HDBEAFCG
3. Post-order traversal: First traverse the left subtree, then traverse the right subtree, and finally traverse the root node.
HDEBFGCA
Implementation method:
##Pre-order traversal: Use the stack first in last out Features: First visit the root node, then push the right subtree, and then push the left subtree. When taking it out in this way, the left subtree is taken out first, and the right subtree is taken out last.
function preorder($root){
$stack = array();
array_push($stack, $root);
while(!empty($stack)){
$center_node = array_pop($stack);
echo $center_node->value; // 根节点
if($center_node->right != null)
array_push($stack, $center_node->right); // 压入右子树
if($center_node->left != null)
array_push($stack, $center_node->left); // 压入左子树
}
}
In-order: Needs to be traversed from bottom to top, so first push the left subtree onto the stack, and then access the root nodes and nodes one by one Right subtree.
function inorder($root){
$stack = array();
$center_node = $root;
while(!empty($stack) || $center_node != null){
while($center_node != null){
array_push($stack, $center_node);
$center_node = $center_node->left;
}
$center_node = array_pop($stack);
echo $center_node->value;
$center_node = $center_node->right;
}
}
Post-order: Save the root node first, then store the left subtree and right subtree in sequence. Then output.
function tailorder($root){
$stack = array();
$outstack = array();
array_push($$stack, $root);
while($empty($stack)){
$center_node = array_pop($stack);
array_push($outstack, $center_node);
if($center_node->right != null)
array_push($stack, $center_node->right);
if($center_node->left != null)
array_push($stack, $center_node->left);
}
while($empty($outstack)){
$center_node = array_pop($outstack);
echo $center_node->value;
}
}
Articles you may be interested in:
PHP uses two stacks to implement the queue function Explanation of the method
Detailed explanation of PHP serialization and deserialization principles
WeChat code scanning based on Swoole Explanation of the process of implementing the code for the login function
The above is the detailed content of Examples of PHP implementing pre-order, in-order and post-order traversal binary tree operations based on non-recursive algorithms. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

