Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Learning Laravel localization module
Learning Laravel localization module
- 不言Original
- 2018-06-13 16:48:311291browse
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about the localization module of the Laravel learning tutorial. The article introduces it to you in great detail through sample code. It has certain reference learning value for everyone's study or work. Friends who need it Let’s study together.
Preface
This article mainly introduces to you the relevant content about Laravel localization module, and shares it for your reference and study. There is not much to say. Having said that, let’s take a look at the detailed introduction.
This article is based on the analysis and writing of the localized module code of Laravel 5.4 version;
Module composition
The following figure shows the relationship between the various files of the localization module and gives a brief description;
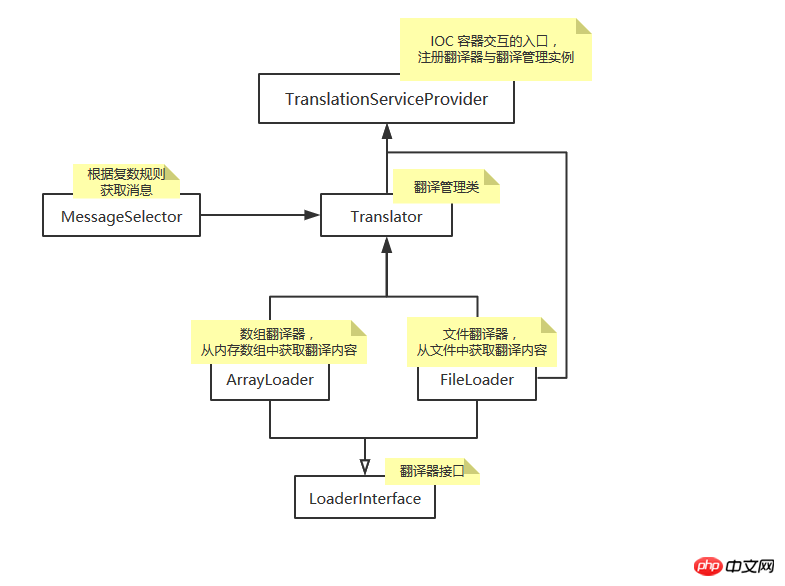
TranslationServiceProvider
The service provider of the localization module is not only the entrance to a module, but also the center of interaction with the IOC container; register the translator instance translation.loader, register the translation management instance translator, and declare the delayed loading service;Translator
Translation management class;MessageSelector
The message filter selects the appropriate message by judging the complex value; for example, the message content is like this: {0} no | [1,19] some | [20,*] a lot, the number we pass is 18, then the last one selected The message is "some";LoaderInterface
Translator interface; declares three methods load, addNamespace, namespaces;FileLoader
Inherits LoaderInterface and obtains localized resource data from files;ArrayLoader
Inherits LoaderInterface and uses arrays to maintain localized resource data in memory;
Configuration instructions
The parameters related to this module in the config configuration directory are only locale and fallback_locale in the app.php file;
locale indicates what the default localization language is, so that translations will be obtained first from the language resource directory (Conversion) content;
If the language represented by the locale does not exist, the fallback_locale alternative language is used;
The author's locale is zh_CN, and the fallback_locale is en;
Function introduction
The global language resource directory is under the resources/lang of the project. Each subdirectory is named after the language, such as en, zh_CN, etc.;
Other subdirectories are named after namespaces, which are supplementary replacements for third-party loading library resource files;
There may also be Json files such as en.json and zh_CN, and projects sometimes start from Json File reading data, these data come from this existing Json file;
Translate global language resources
The author's language resource root directory resources/ There is zh_CN/validation.php under lang, the content is as follows
<?php return [ 'accepted' => ':attribute 必须接受。', 'active_url' => ':attribute 不是一个有效的网址。', 'after' => ':attribute 必须是一个在 :date 之后的日期。', ...... ];
By calling the code
app('translator')->trans('validation.accepted', ['attribute' => '用户名'])
Or the global help function trans
trans('validation.accepted', ['attribute' => '用户名'])
Output "Username must be accepted.";
The calling process is as follows:
Parse the key name: parse the key name into an array (
$namespace = '*', $group = 'validation', $item = 'accepted'); namespace is *, which means it is in the global namespace; group, group, is actually the file name, and one file is a group; item means element;Get the language array : $locale here is null, so what is returned is an array composed of the default and alternate languages, that is, ['zh_CN', 'en']; and perform a for loop to enter the language resource directory to find the required element value. If found , that is, break;
Loading resources: Because the namespace is *, the root directory of the location resource is resources/lang; the language is zh_CN, so the subdirectory is zh_CN; the group name is validation, At this time, all the contents in the resources/lang/zh_CN/validation.php file are loaded into the memory and saved.
$this->loaded[$namespace][$group][$locale] = $ lines;Get resources and replace parameters: from
$this->loaded[$namespace] through theArr::getmethod Get element value in [$group][$locale]: attribute must be accepted. ;At this time, the parameter array is not empty, loop replacement, and get the result "The user name must be accepted.";
Translate languages with namespaces Resources
The author created the vendor/Faker/Provider/zh_CN/Internet.php file under the language resource root directory resource/lang, with the following content:
<?php return [ 'message' => 'hello, Faker/Provider', ...... ];
At the same time, manually register the resource root directory location of the third-party plug-in (that is, with the namespace) in Translator;
app('translator')->addNamespace('Faker/Provider', base_path('vendor/xx/resource/lang'))
Now, get the resource with namespace;
trans('Faker/Provider::Internet.message');
输出 'hello, Faker/Provider';
调用过程如下:
解析键名:将键名进行解析成数组
($namespace = 'Faker/Provider', $group = 'Internet', $item = 'message');获取语言数组: 这里的$locale为null,所以返回的是默认与备用语言组成的数组,也就是['zh_CN', 'en'];并进行for循环,进入语言资源目录中寻找需要的元素值,如果找到,即 break;
加载资源:因为命名空间为Faker/Provider,此时会分两步;第一步读取第三方插件资源库下的信息,这时读取命名空间注册的根目录为base_path('vendor/xx/resource/lang'),就读取base_path('vendor/xx/resource/lang')/zh_CN/Internet.php内容,文件不存在,返回空数组;第二步读取全局语言资源,进行补充,也就是读取
base_path('resource/lang/vendor/Faker/Provider')/zh_CN/Internet.php;最后进行保存$this->loaded[$namespace][$group][$locale] = $lines;获取资源,并替换参数:通过
Arr::get方法从$this->loaded[$namespace][$group][$locale]中获取元素值" hello, Faker/Provider";此时,参数数组为空,直接返回结果 "hello, Faker/Provider";
翻译Json文件中的资源
笔者在语言资源根目录resource/lang下,创建zh_CN.json文件,内容如下:
{
"name": "zh_CN.json",
"place": "../resources/lang/zh_CN.json"
}
现在,获取Json文件中的name值;
trans('*.name')
输出 "zh_CN.json";
调用过程如下:
解析键名:将键名进行解析成数组
($namespace = '*', $group = '*', $item = 'name');获取语言数组: 这里的$locale为null,所以返回的是默认与备用语言组成的数组,也就是['zh_CN', 'en'];并进行for循环,进入语言资源目录中寻找需要的元素值,如果找到,即 break;
加载资源:因为命名空间为*,且组也为*,这时会读取语言根目录下,名字为语言值的Json文件;此时会读取resource/lang/zh_CN.json,将读取的内容,进行保存
$this->loaded[$namespace][$group][$locale] = $lines;获取资源,并替换参数:通过Arr::get方法从
$this->loaded[$namespace][$group][$locale]中获取元素值"zh_CN.json";此时,参数数组为空,直接返回结果 "zh_CN.json";
运行时绑定资源
资源的内容除了放在文件中,用到的时候在读取,也可以在项目运行时,存放;
以resources/lang/zh_CN/validation.php为例,现在想要在运行时,给这个组添加一个新的元素叫 extra,需要指定放在哪个语言下,可以这样写
app('translator')->addLines(array('validation.extra' => '测试添加额外数据'), 'zh_CN');
现在可以获取这个新添加的元素值
trans('validation.extra')
复数资源过滤
笔者通过 运行时绑定资源 添加一条翻译内容:
app('translator')->addLines(array('validation.extra' => '{0}没有|[1,19]一些|[20,*]很多'), 'zh_CN');
如果通过trans('validation.extra') ,获取的就是整条翻译内容,不是我们所期望的;用choice方法:
app('translator')->choice('validation.extra', 0) 得到 没有;
app('translator')->choice('validation.extra', 18) 得到 一些;
app('translator')->choice('validation.extra', 20) 得到 很多;
可以将app('translator')->choice(...)简写成全局帮助函数trans_choice(...);
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网!
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Learning Laravel localization module. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

