This time I will show you how to use the diff algorithm in vue, and what are the precautions for using the diff algorithm in vue. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
1. When the data changes, how does vue update the node?
You must know that the cost of rendering the real DOM is very high. For example, sometimes we modify a certain data. If we directly render it to the real DOM, it will cause the entire DOM tree to be redrawn and rearranged. Is it possible that we only update the small piece of dom we modified instead of updating the entire dom? The diff algorithm can help us. We first generate avirtual DOM based on the real DOM. When the data of a virtual DOM changes, a new Vnode## will be generated. #, and then compare Vnode with oldVnode. If you find any differences, modify them directly on the real DOM, and then make the value of oldVnode be Vnode . The process of diff is to call the
named patch, compare the old and new nodes, and patch the real DOM while comparing.
Virtual DOM extracts the real DOM data and simulates the tree structure in the form of
object. For example, the dom is like this: <p>
</p><p>123</p>
var Vnode = {
tag: 'p',
children: [
{ tag: 'p', text: '123' }
]
};
(warm reminder:
VNode and oldVNode are both Object, be sure to remember)
When using the diff algorithm to compare old and new nodes, the comparison will only be performed at the same level, and will not be compared across levels.
<p> </p><p>123</p>456
The above code will compare two p on the same layer and p and span on the second layer, but will not compare p and span. A very vivid picture I saw elsewhere:

When the data changes, the set method Will call
Dep.notify to notify all subscriber Watchers, and the subscribers will call patch to patch the real DOM and update the corresponding view.

patch
Let’s take a look
patch How to patch (only the core part of the code is retained) <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">function patch (oldVnode, vnode) {
// some code
if (sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode)
} else {
const oEl = oldVnode.el // 当前oldVnode对应的真实元素节点
let parentEle = api.parentNode(oEl) // 父元素
createEle(vnode) // 根据Vnode生成新元素
if (parentEle !== null) {
api.insertBefore(parentEle, vnode.el, api.nextSibling(oEl)) // 将新元素添加进父元素
api.removeChild(parentEle, oldVnode.el) // 移除以前的旧元素节点
oldVnode = null
}
}
// some code
return vnode
}</pre>patch function receives two parameters
and Vnode represent the new node and the previous one respectively Old node Determine whether the two nodes are worthy of comparison. If they are worthy of comparison, execute
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">function sameVnode (a, b) {
return (
a.key === b.key && // key值
a.tag === b.tag && // 标签名
a.isComment === b.isComment && // 是否为注释节点
// 是否都定义了data,data包含一些具体信息,例如onclick , style
isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b) // 当标签是<input>的时候,type必须相同
)
}</pre> If not worthy of comparison, replace
Vnode If two nodes are the same, then check their child nodes in depth. If the two nodes are different, it means that
has been completely changed, and oldVnode can be directly replaced. Although these two nodes are different, what should I do if their child nodes are the same? Don't forget, diff is compared layer by layer. If the first layer is different, then the second layer will not be compared in depth. (I wonder if this is a disadvantage? The same child node cannot be reused...)
When we determine that the two nodes are worthy of comparison, we The
patchVnode method will be assigned to both nodes. So what does this method do? <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode) {
const el = vnode.el = oldVnode.el
let i, oldCh = oldVnode.children, ch = vnode.children
if (oldVnode === vnode) return
if (oldVnode.text !== null && vnode.text !== null && oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
api.setTextContent(el, vnode.text)
}else {
updateEle(el, vnode, oldVnode)
if (oldCh && ch && oldCh !== ch) {
updateChildren(el, oldCh, ch)
}else if (ch){
createEle(vnode) //create el's children dom
}else if (oldCh){
api.removeChildren(el)
}
}
}</pre>This function does the following:
- Find the corresponding real dom, called
- el
- Vnode
and
oldVnodepoint to the same object, If so, then directly - return
if They all have text nodes and are not equal, then set the text node of
elto the text node ofVnode. If - oldVnode
has child nodes but
Vnodedoes not, delete the child nodesofel 如果
oldVnode没有子节点而Vnode有,则将Vnode的子节点真实化之后添加到el如果两者都有子节点,则执行updateChildren函数比较子节点,这一步很重要
其他几个点都很好理解,我们详细来讲一下updateChildren
updateChildren
代码量很大,不方便一行一行的讲解,所以下面结合一些示例图来描述一下。
updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh) {
let oldStartIdx = 0, newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx
let idxInOld
let elmToMove
let before
while (oldStartIdx oldEndIdx) {
before = newCh[newEndIdx + 1] == null ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].el
addVnodes(parentElm, before, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx)
}else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
}
先说一下这个函数做了什么
将
Vnode的子节点Vch和oldVnode的子节点oldCh提取出来oldCh和vCh各有两个头尾的变量StartIdx和EndIdx,它们的2个变量相互比较,一共有4种比较方式。如果4种比较都没匹配,如果设置了key,就会用key进行比较,在比较的过程中,变量会往中间靠,一旦StartIdx>EndIdx表明oldCh和vCh至少有一个已经遍历完了,就会结束比较。
图解updateChildren
终于来到了这一部分,上面的总结相信很多人也看得一脸懵逼,下面我们好好说道说道。(这都是我自己画的,求推荐好用的画图工具...)
粉红色的部分为oldCh和vCh

我们将它们取出来并分别用s和e指针指向它们的头child和尾child

现在分别对 oldS、oldE、S、E 两两做 sameVnode 比较,有四种比较方式,当其中两个能匹配上那么真实dom中的相应节点会移到Vnode相应的位置,这句话有点绕,打个比方
如果是oldS和E匹配上了,那么真实dom中的第一个节点会移到最后
如果是oldE和S匹配上了,那么真实dom中的最后一个节点会移到最前,匹配上的两个指针向中间移动
如果四种匹配没有一对是成功的,那么遍历
oldChild,S挨个和他们匹配,匹配成功就在真实dom中将成功的节点移到最前面,如果依旧没有成功的,那么将S对应的节点插入到dom中对应的oldS位置,oldS和S指针向中间移动。
再配个图

第一步
oldS = a, oldE = d; S = a, E = b;
oldS 和 S 匹配,则将dom中的a节点放到第一个,已经是第一个了就不管了,此时dom的位置为:a b d
第二步
oldS = b, oldE = d; S = c, E = b;
oldS 和 E 匹配,就将原本的b节点移动到最后,因为 E 是最后一个节点,他们位置要一致,这就是上面说的: 当其中两个能匹配上那么真实dom中的相应节点会移到Vnode相应的位置 ,此时dom的位置为:a d b
第三步
oldS = d, oldE = d; S = c, E = d;
oldE 和 E 匹配,位置不变此时dom的位置为:a d b
第四步
oldS++; oldE--; oldS > oldE;
遍历结束,说明 oldCh 先遍历完。就将剩余的 vCh 节点根据自己的的index插入到真实dom中去,此时dom位置为:a c d b
一次模拟完成。
这个匹配过程的结束有两个条件:
oldS > oldE 表示 oldCh 先遍历完,那么就将多余的 vCh 根据index添加到dom中去(如上图) S > E 表示vCh先遍历完,那么就在真实dom中将区间为 [oldS, oldE] 的多余节点删掉

下面再举一个例子,可以像上面那样自己试着模拟一下

当这些节点 sameVnode 成功后就会紧接着执行 patchVnode 了,可以看一下上面的代码
if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)
}
就这样层层递归下去,直到将oldVnode和Vnode中的所有子节点比对完。也将dom的所有补丁都打好啦。那么现在再回过去看updateChildren的代码会不会容易很多呢?
总结
以上为diff算法的全部过程,放上一张文章开始就发过的总结图,可以试试看着这张图回忆一下diff的过程。

相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of How to use the diff algorithm in vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM
特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM特斯拉是一个典型的AI公司,过去一年训练了75000个神经网络,意味着每8分钟就要出一个新的模型,共有281个模型用到了特斯拉的车上。接下来我们分几个方面来解读特斯拉FSD的算法和模型进展。01 感知 Occupancy Network特斯拉今年在感知方面的一个重点技术是Occupancy Network (占据网络)。研究机器人技术的同学肯定对occupancy grid不会陌生,occupancy表示空间中每个3D体素(voxel)是否被占据,可以是0/1二元表示,也可以是[0, 1]之间的
 基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM
基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟在我之前的博客中,我们已经了解了如何使用因果树来评估政策的异质处理效应。如果你还没有阅读过,我建议你在阅读本文前先读一遍,因为我们在本文中认为你已经了解了此文中的部分与本文相关的内容。为什么是异质处理效应(HTE:heterogenous treatment effects)呢?首先,对异质处理效应的估计允许我们根据它们的预期结果(疾病、公司收入、客户满意度等)选择提供处理(药物、广告、产品等)的用户(患者、用户、客户等)。换句话说,估计HTE有助于我
 Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM
Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟引言模型超参数(或模型设置)的优化可能是训练机器学习算法中最重要的一步,因为它可以找到最小化模型损失函数的最佳参数。这一步对于构建不易过拟合的泛化模型也是必不可少的。优化模型超参数的最著名技术是穷举网格搜索和随机网格搜索。在第一种方法中,搜索空间被定义为跨越每个模型超参数的域的网格。通过在网格的每个点上训练模型来获得最优超参数。尽管网格搜索非常容易实现,但它在计算上变得昂贵,尤其是当要优化的变量数量很大时。另一方面,随机网格搜索是一种更快的优化方法,可以提供更好的
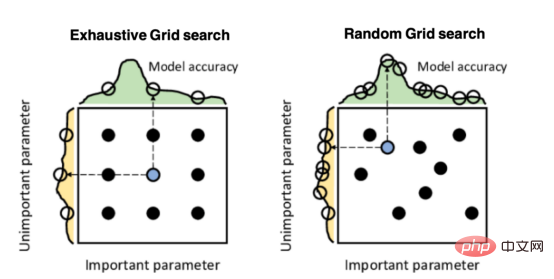
 因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM
因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM导读:因果推断是数据科学的一个重要分支,在互联网和工业界的产品迭代、算法和激励策略的评估中都扮演者重要的角色,结合数据、实验或者统计计量模型来计算新的改变带来的收益,是决策制定的基础。然而,因果推断并不是一件简单的事情。首先,在日常生活中,人们常常把相关和因果混为一谈。相关往往代表着两个变量具有同时增长或者降低的趋势,但是因果意味着我们想要知道对一个变量施加改变的时候会发生什么样的结果,或者说我们期望得到反事实的结果,如果过去做了不一样的动作,未来是否会发生改变?然而难点在于,反事实的数据往往是
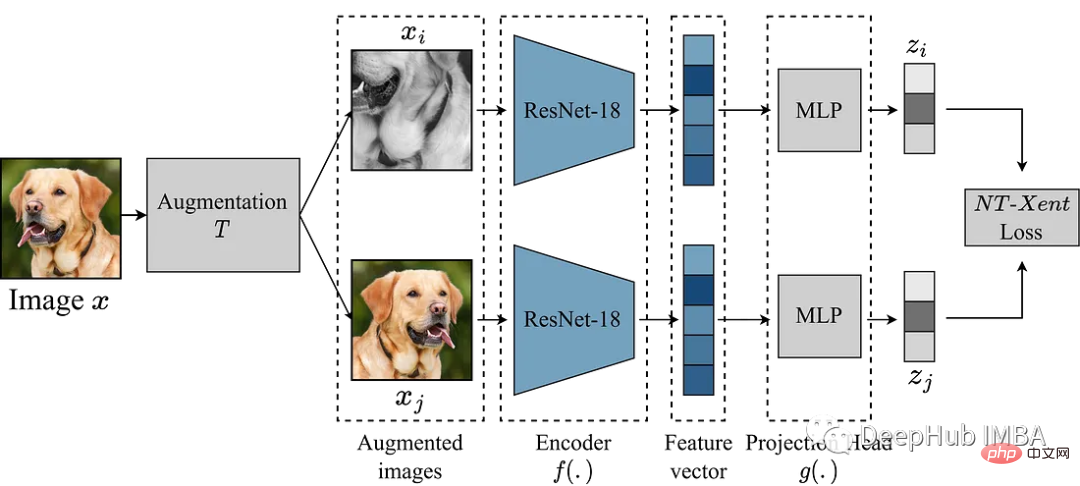 使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PM
使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PMSimCLR(Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Representations)是一种学习图像表示的自监督技术。 与传统的监督学习方法不同,SimCLR 不依赖标记数据来学习有用的表示。 它利用对比学习框架来学习一组有用的特征,这些特征可以从未标记的图像中捕获高级语义信息。SimCLR 已被证明在各种图像分类基准上优于最先进的无监督学习方法。 并且它学习到的表示可以很容易地转移到下游任务,例如对象检测、语义分割和小样本学习,只需在较小的标记
 用vimdiff替代svn diff:比较代码的工具Jan 09, 2024 pm 07:54 PM
用vimdiff替代svn diff:比较代码的工具Jan 09, 2024 pm 07:54 PM在linux下,直接使用svndiff命令查看代码的修改是很吃力的,于是在网上搜索到了一个比较好的解决方案,就是让vimdiff作为svndiff的查看代码工具,尤其对于习惯用vim的人来说真的是很方便。当使用svndiff命令比较某个文件的修改前后时,例如执行以下命令:$svndiff-r4420ngx_http_limit_req_module.c那么实际会向默认的diff程序发送如下命令:-u-Lngx_http_limit_req_module.c(revision4420)-Lngx_
 盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM
盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM一、盒马供应链介绍1、盒马商业模式盒马是一个技术创新的公司,更是一个消费驱动的公司,回归消费者价值:买的到、买的好、买的方便、买的放心、买的开心。盒马包含盒马鲜生、X 会员店、盒马超云、盒马邻里等多种业务模式,其中最核心的商业模式是线上线下一体化,最快 30 分钟到家的 O2O(即盒马鲜生)模式。2、盒马经营品类介绍盒马精选全球品质商品,追求极致新鲜;结合品类特点和消费者购物体验预期,为不同品类选择最为高效的经营模式。盒马生鲜的销售占比达 60%~70%,是最核心的品类,该品类的特点是用户预期时
 人类反超 AI:DeepMind 用 AI 打破矩阵乘法计算速度 50 年记录一周后,数学家再次刷新Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
人类反超 AI:DeepMind 用 AI 打破矩阵乘法计算速度 50 年记录一周后,数学家再次刷新Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:16 PM10 月 5 日,AlphaTensor 横空出世,DeepMind 宣布其解决了数学领域 50 年来一个悬而未决的数学算法问题,即矩阵乘法。AlphaTensor 成为首个用于为矩阵乘法等数学问题发现新颖、高效且可证明正确的算法的 AI 系统。论文《Discovering faster matrix multiplication algorithms with reinforcement learning》也登上了 Nature 封面。然而,AlphaTensor 的记录仅保持了一周,便被人类


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft






