This time I will show you how to use the diff algorithm in vue, and what are the precautions for using the diff algorithm in vue. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Virtual dom
The diff algorithm must first clarify the concept that the object of diff is the virtual dom, and updating the real dom is the result of the diff algorithmVnode base class
constructor (
。。。
) {
this.tag = tag
this.data = data
this.children = children
this.text = text
this.elm = elm
this.ns = undefined
this.context = context
this.fnContext = undefined
this.fnOptions = undefined
this.fnScopeId = undefined
this.key = data && data.key
this.componentOptions = componentOptions
this.componentInstance = undefined
this.parent = undefined
this.raw = false
this.isStatic = false
this.isRootInsert = true
this.isComment = false
this.isCloned = false
this.isOnce = false
this.asyncFactory = asyncFactory
this.asyncMeta = undefined
this.isAsyncPlaceholder = false
}This part of the code is mainly to better understand the meaning of the specific diff attributes in the diff algorithm, and of course to better understand the vnode instanceOverall process
The core function is the patch function
- isUndef judgment (whether it is undefined or null)
- // empty mount (likely as component), create new root elementcreateElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) Here you can find that creating nodes is not inserted one by one, but put into a queue for unified batch processing
- Core function sameVnode
function sameVnode (a, b) {
return (
a.key === b.key && (
(
a.tag === b.tag &&
a.isComment === b.isComment &&
isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b)
) || (
isTrue(a.isAsyncPlaceholder) &&
a.asyncFactory === b.asyncFactory &&
isUndef(b.asyncFactory.error)
)
)
)
}Here is an outer comparison function that directly compares the key, tag (label), and data of two nodes ( Note that data here refers to VNodeData), and the type is directly compared for input.
export interface VNodeData {
key?: string | number;
slot?: string;
scopedSlots?: { [key: string]: ScopedSlot };
ref?: string;
tag?: string;
staticClass?: string;
class?: any;
staticStyle?: { [key: string]: any };
style?: object[] | object;
props?: { [key: string]: any };
attrs?: { [key: string]: any };
domProps?: { [key: string]: any };
hook?: { [key: string]: Function };
on?: { [key: string]: Function | Function[] };
nativeOn?: { [key: string]: Function | Function[] };
transition?: object;
show?: boolean;
inlineTemplate?: {
render: Function;
staticRenderFns: Function[];
};
directives?: VNodeDirective[];
keepAlive?: boolean;
}This will confirm whether the two nodes have further comparison value, otherwise they will be replaced directlyThe replacement process is mainly a createElm function and the other is to destroy the oldVNode
// destroy old node
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, [oldVnode], 0, 0)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
}Insert To simplify the process, it is to determine the type of the node and call createComponent respectively (it will determine whether there are children and then call it recursively) createCommentcreateTextNodeAfter creation After using the insert function, you need to use the hydrate function to map the virtual dom and the real dom
function insert (parent, elm, ref) {
if (isDef(parent)) {
if (isDef(ref)) {
if (ref.parentNode === parent) {
nodeOps.insertBefore(parent, elm, ref)
}
} else {
nodeOps.appendChild(parent, elm)
}
}
}
Core function
function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm
if (isTrue(oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder)) {
if (isDef(vnode.asyncFactory.resolved)) {
hydrate(oldVnode.elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true
}
return
}
if (isTrue(vnode.isStatic) &&
isTrue(oldVnode.isStatic) &&
vnode.key === oldVnode.key &&
(isTrue(vnode.isCloned) || isTrue(vnode.isOnce))
) {
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance
return
}
let i
const data = vnode.data
if (isDef(data) && isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.prepatch)) {
i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
const oldCh = oldVnode.children
const ch = vnode.children
if (isDef(data) && isPatchable(vnode)) {
for (i = 0; i <blockquote style="text-align: left;">const el = vnode.el = oldVnode.el This is a very important step. Let vnode.el refer to the current real dom. When el is modified, vnode.el will change synchronously. <p style="text-align: left;"></p>
</blockquote><ol class=" list-paddingleft-2">
<li>Compare whether the two references are consistent<p style="text-align: left;"></p>
</li>
<li>I don’t know what asyncFactory does after that, so I can’t understand this comparison<p style="text-align: left;"></p>
</li>
<li>Static node comparison key, no re-rendering will be done after the same, directly copy componentInstance (once command takes effect here) <p style="text-align: left;"></p>
</li>
<li>If vnode is a text node Or <p style="text-align: left;">Comment <a href="http://www.php.cn/code/8105.html" target="_blank"> node, but when vnode.text != oldVnode.text, you only need to update the text content of vnode.elm </a></p>
</li>
<li>Comparison of children<p style="text-align: left;"> </p>
</li>
</ol>
- If only oldVnode has child nodes, then
- If there is only vnode If there are child nodes, then create these child nodes. If oldVnode is a text node, set the text of vnode.elm to empty
- All are valid updateChildren, this will be detailed later
- If neither oldVnode nor vnode has child nodes, but oldVnode is a text node or comment node, set the text of vnode.elm to an empty string
updateChildren
The focus of this part is still on the entire algorithmFirst four pointers, oldStart, oldEnd, newStart, newEnd, two array, oldVnode, Vnode.function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
let oldStartIdx = 0
let newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm
while (oldStartIdx oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
}A Conditions for the entire loop not to end oldStartIdx - oldStart === newStart, oldStart newStart
- oldEnd === newEnd, oldEnd-- newEnd--
- oldStart === newEnd, oldStart Insert to the end of the queue oldStart newEnd --
- oldEnd === newStart, oldEnd is inserted into the beginning of the queue oldEnd-- newStart
剩下的所有情况都走这个处理简单的说也就两种处理,处理后newStart++
newStart在old中发现一样的那么将这个移动到oldStart前
没有发现一样的那么创建一个放到oldStart之前
循环结束后并没有完成
还有一段判断才算完
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of How to use the diff algorithm in vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM
特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM特斯拉是一个典型的AI公司,过去一年训练了75000个神经网络,意味着每8分钟就要出一个新的模型,共有281个模型用到了特斯拉的车上。接下来我们分几个方面来解读特斯拉FSD的算法和模型进展。01 感知 Occupancy Network特斯拉今年在感知方面的一个重点技术是Occupancy Network (占据网络)。研究机器人技术的同学肯定对occupancy grid不会陌生,occupancy表示空间中每个3D体素(voxel)是否被占据,可以是0/1二元表示,也可以是[0, 1]之间的
 基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM
基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟在我之前的博客中,我们已经了解了如何使用因果树来评估政策的异质处理效应。如果你还没有阅读过,我建议你在阅读本文前先读一遍,因为我们在本文中认为你已经了解了此文中的部分与本文相关的内容。为什么是异质处理效应(HTE:heterogenous treatment effects)呢?首先,对异质处理效应的估计允许我们根据它们的预期结果(疾病、公司收入、客户满意度等)选择提供处理(药物、广告、产品等)的用户(患者、用户、客户等)。换句话说,估计HTE有助于我
 Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM
Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟引言模型超参数(或模型设置)的优化可能是训练机器学习算法中最重要的一步,因为它可以找到最小化模型损失函数的最佳参数。这一步对于构建不易过拟合的泛化模型也是必不可少的。优化模型超参数的最著名技术是穷举网格搜索和随机网格搜索。在第一种方法中,搜索空间被定义为跨越每个模型超参数的域的网格。通过在网格的每个点上训练模型来获得最优超参数。尽管网格搜索非常容易实现,但它在计算上变得昂贵,尤其是当要优化的变量数量很大时。另一方面,随机网格搜索是一种更快的优化方法,可以提供更好的
 因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM
因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM导读:因果推断是数据科学的一个重要分支,在互联网和工业界的产品迭代、算法和激励策略的评估中都扮演者重要的角色,结合数据、实验或者统计计量模型来计算新的改变带来的收益,是决策制定的基础。然而,因果推断并不是一件简单的事情。首先,在日常生活中,人们常常把相关和因果混为一谈。相关往往代表着两个变量具有同时增长或者降低的趋势,但是因果意味着我们想要知道对一个变量施加改变的时候会发生什么样的结果,或者说我们期望得到反事实的结果,如果过去做了不一样的动作,未来是否会发生改变?然而难点在于,反事实的数据往往是
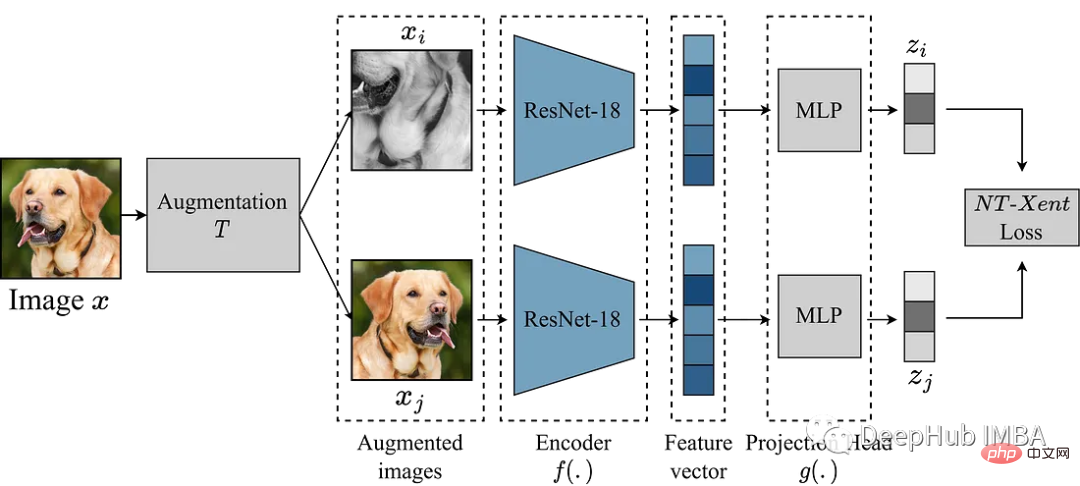 使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PM
使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PMSimCLR(Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Representations)是一种学习图像表示的自监督技术。 与传统的监督学习方法不同,SimCLR 不依赖标记数据来学习有用的表示。 它利用对比学习框架来学习一组有用的特征,这些特征可以从未标记的图像中捕获高级语义信息。SimCLR 已被证明在各种图像分类基准上优于最先进的无监督学习方法。 并且它学习到的表示可以很容易地转移到下游任务,例如对象检测、语义分割和小样本学习,只需在较小的标记
 盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM
盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM一、盒马供应链介绍1、盒马商业模式盒马是一个技术创新的公司,更是一个消费驱动的公司,回归消费者价值:买的到、买的好、买的方便、买的放心、买的开心。盒马包含盒马鲜生、X 会员店、盒马超云、盒马邻里等多种业务模式,其中最核心的商业模式是线上线下一体化,最快 30 分钟到家的 O2O(即盒马鲜生)模式。2、盒马经营品类介绍盒马精选全球品质商品,追求极致新鲜;结合品类特点和消费者购物体验预期,为不同品类选择最为高效的经营模式。盒马生鲜的销售占比达 60%~70%,是最核心的品类,该品类的特点是用户预期时
 用vimdiff替代svn diff:比较代码的工具Jan 09, 2024 pm 07:54 PM
用vimdiff替代svn diff:比较代码的工具Jan 09, 2024 pm 07:54 PM在linux下,直接使用svndiff命令查看代码的修改是很吃力的,于是在网上搜索到了一个比较好的解决方案,就是让vimdiff作为svndiff的查看代码工具,尤其对于习惯用vim的人来说真的是很方便。当使用svndiff命令比较某个文件的修改前后时,例如执行以下命令:$svndiff-r4420ngx_http_limit_req_module.c那么实际会向默认的diff程序发送如下命令:-u-Lngx_http_limit_req_module.c(revision4420)-Lngx_
 研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM译者 | 李睿 审校 | 孙淑娟随着机器学习成为人们每天都在使用的很多应用程序的一部分,人们越来越关注如何识别和解决机器学习模型的安全和隐私方面的威胁。 然而,不同机器学习范式面临的安全威胁各不相同,机器学习安全的某些领域仍未得到充分研究。尤其是强化学习算法的安全性近年来并未受到太多关注。 加拿大的麦吉尔大学、机器学习实验室(MILA)和滑铁卢大学的研究人员开展了一项新研究,主要侧重于深度强化学习算法的隐私威胁。研究人员提出了一个框架,用于测试强化学习模型对成员推理攻击的脆弱性。 研究


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),






