This time I will bring you the vue vue-router vuex operation permissions. What are the precautions for vue vue-router vuex operation permissions? Here are the actual cases, let’s take a look.

https://github.com/linrunzheng/vue- permission-control
Next, let us simulate the process of an ordinary user opening the website and walk through the entire process step by step. First start by opening the local service localhost:8080. We know that after opening, we will enter the login page, so what is the basis for judgment. First is the token. Users who are not logged in will not be able to obtain the token. For characters after logging in, we will save the token to local or seesionStorage. Therefore, you can know whether to log in or not based on whether there is a token currently.In order to access the token and facilitate our operation, it can be combined with vuex to achieve
/* state.js */
export default {
get UserToken() {
return localStorage.getItem('token')
},
set UserToken(value) {
localStorage.setItem('token', value)
}
}
/* mutation.js */
export default {
LOGIN_IN(state, token) {
state.UserToken = token
},
LOGIN_OUT(state) {
state.UserToken = ''
}
}
Interception judgment
No token Enter the page that requires permissions: redirect to the login pageSince our routes are dynamically mounted, including ' ' and 404, when no route is matched, we will also redirect to loginrouter.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (!store.state.UserToken) {
if (
to.matched.length > 0 &&
!to.matched.some(record => record.meta.requiresAuth)
) {
next()
} else {
next({ path: '/login' })
}
}
})Okay, now the user opens localhost:8080, and the default matching path is ''. At this time, we have not mounted the route and have no token, so we come to login. After entering the username and password, there is a token. Trigger *commit('LOGIN_IN')* through the store to set the token. But there is still no route. At present, there is only the login route.
/* 初始路由 */
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/login',
component: Login
}
]
})
/* 准备动态添加的路由 */
export const DynamicRoutes = [
{
path: '',
component: Layout,
name: 'container',
redirect: 'home',
meta: {
requiresAuth: true,
name: '首页'
},
children: [
{
path: 'home',
component: Home,
name: 'home',
meta: {
name: '首页'
}
}
]
},
{
path: '/403',
component: Forbidden
},
{
path: '*',
component: NotFound
}
]We need to go to the background to obtain permissions based on the current user's token. Since there is quite a lot of logic in permissions, a permission module was added to vuex to handle permissions. In order to determine whether there is an existing route list, you need to save a state permissionList in the permission module of vuex for judging. If the permissionList is not null, that is, there is already a route. If it does not exist, we need to work. .
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (!store.state.UserToken) {
...
} else {
/* 现在有token了 */
if (!store.state.permission.permissionList) {
/* 如果没有permissionList,真正的工作开始了 */
store.dispatch('permission/FETCH_PERMISSION').then(() => {
next({ path: to.path })
})
} else {
if (to.path !== '/login') {
next()
} else {
next(from.fullPath)
}
}
}
})Let’s take a look at what store.dispatch('permission/FETCH_PERMISSION') does
actions: {
async FETCH_PERMISSION({ commit, state }) {
/* 获取后台给的权限数组 */
let permissionList = await fetchPermission()
/* 根据后台权限跟我们定义好的权限对比,筛选出对应的路由并加入到path=''的children */
let routes = recursionRouter(permissionList, dynamicRouter)
let MainContainer = DynamicRoutes.find(v => v.path === '')
let children = MainContainer.children
children.push(...routes)
/* 生成左侧导航菜单 */
commit('SET_MENU', children)
setDefaultRoute([MainContainer])
/* 初始路由 */
let initialRoutes = router.options.routes
/* 动态添加路由 */
router.addRoutes(DynamicRoutes)
/* 完整的路由表 */
commit('SET_PERMISSION', [...initialRoutes, ...DynamicRoutes])
}
}First, await fetchPermission() gets the permission array given by the background. The format is roughly as follows
{
"code": 0,
"message": "获取权限成功",
"data": [
{
"name": "订单管理",
"children": [
{
"name": "订单列表"
},
{
"name": "生产管理",
"children": [
{
"name": "生产列表"
}
]
},
{
"name": "退货管理"
}
]
}
]
}Secondly, based on the route array we wrote, compare and filter to get the route we want
/* 这里是我们写好的需要权限判断的路由 */
const dynamicRoutes = [
{
path: '/order',
component: Order,
name: 'order-manage',
meta: {
name: '订单管理'
},
children: [
{
path: 'list',
name: 'order-list',
component: OrderList,
meta: {
name: '订单列表'
}
},
{
path: 'product',
name: 'product-manage',
component: ProductManage,
meta: {
name: '生产管理'
},
children: [
{
path: 'list',
name: 'product-list',
component: ProductionList,
meta: {
name: '生产列表'
}
},
{
path: 'review',
name: 'review-manage',
component: ReviewManage,
meta: {
name: '审核管理'
}
}
]
},
{
path: 'returnGoods',
name: 'return-goods',
component: ReturnGoods,
meta: {
name: '退货管理'
}
}
]
}
]
export default dynamicRoutesFor comparison, I wrote a recursive function, using name and meta .name for comparison, we can get the result we want based on this function
/**
*
* @param {Array} userRouter 后台返回的用户权限json
* @param {Array} allRouter 前端配置好的所有动态路由的集合
* @return {Array} realRoutes 过滤后的路由
*/
export function recursionRouter(userRouter = [], allRouter = []) {
var realRoutes = []
allRouter.forEach((v, i) => {
userRouter.forEach((item, index) => {
if (item.name === v.meta.name) {
if (item.children && item.children.length > 0) {
v.children = recursionRouter(item.children, v.children)
}
realRoutes.push(v)
}
})
})
return realRoutes
}After getting the filtered array, add it to the children with path ''
{
path: '',
component: Layout,
name: 'container',
redirect: 'home',
meta: {
requiresAuth: true,
name: '首页'
},
children: [
{
path: 'home',
component: Home,
name: 'home',
meta: {
name: '首页'
}
},
<!-- 将上面得到的东西加入到这里 -->
...
]
}At this time, path The children of '' are our navigation menu on the left, which are saved to the sidebarMenu of state for later use. After adding to children, DynamicRoutes can be added to the route.
/* 动态添加路由 */
router.addRoutes(DynamicRoutes)
/* 初始路由 */
let initialRoutes = router.options.routes
/* 合并起来,就是完整的路由了 */
commit('SET_PERMISSION', [...initialRoutes, ...DynamicRoutes])After the route is added, that is, the action operation is completed, you can call next({ path: to.path }) in action.then to enter the route. Note here that parameters must be passed in next. The routing information of the entered page, because after next passes the parameter, the current route to be entered will be abolished and the route corresponding to the parameter will be entered. Although it is the same route, this is mainly to ensure that addRoutes takes effect. After entering the routing, we need to start generating the left menu. We have saved it to sidebarMenu before. Now all we need to do is to generate the menu recursively. Although the navigation menu of element is used, for recursive routing, we still need Encapsulate it yourself. The core here is the name of the component. Where there are children in the component, you use yourself again to traverse the routing of the entire tree structure.
<template>
<p>
<template>
<el-submenu>0" :key="v.name">
<template>
<i></i>
<span>{{v.meta.name}}</span>
</template>
<el-menu-item-group>
<my-nav></my-nav>
</el-menu-item-group>
</el-submenu>
<el-menu-item>
<i></i>
<span>{{v.meta.name}}</span>
</el-menu-item>
</template>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'my-nav',
props: {
menuList: {
type: Array,
default: function() {
return []
}
}
},
methods: {
gotoRoute(name) {
this.$router.push({ name })
}
}
}
</script>After refreshing the page, according to our router.beforeEach judgment, there is a token but no permissionList. We will re-trigger the action to obtain the route, so there is no need to worry. But the navigation menu active effect will disappear. However, we have set the key of el-menu-item to the name of the route, so we only need to assign the name of the current route to el-menu default-active in afterEach after refreshing. In the same way, breadcrumb navigation can be achieved by obtaining all matched routes in the afterEach stage.
if (!store.state.permission.permissionList) {
store.dispatch('permission/FETCH_PERMISSION').then(() => {
next({ path: to.path })
})
}
...
router.afterEach((to, from, next) => {
var routerList = to.matched
store.commit('setCrumbList', routerList)
store.commit('permission/SET_CURRENT_MENU', to.name)
})
退出登陆后,需要刷新页面,因为我们是通过addRoutes添加的,router没有deleteRoutes这个api,所以清除token,清除permissionList等信息,刷新页面是最保险的。
最后还有一点,每次请求得带上token, 可以对axios封装一下来处理
var instance = axios.create({
timeout: 30000,
baseURL
})
// 添加请求拦截器
instance.interceptors.request.use(
function(config) {
// 请求头添加token
if (store.state.UserToken) {
config.headers.Authorization = store.state.UserToken
}
return config
},
function(error) {
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
/* axios请求二次封装 */
instance.get = function(url, data, options) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
axios
.get(url, data, options)
.then(
res => {
var response = res.data
if (response.code === 0) {
resolve(response.data)
} else {
Message.warning(response.message)
/* reject(response.message) */
}
},
error => {
if (error.response.status === 401) {
Message.warning({
message: '登陆超时,请重新登录'
})
store.commit('LOGIN_OUT')
window.location.reload()
} else {
Message.error({
message: '系统异常'
})
}
reject(error)
}
)
.catch(e => {
console.log(e)
})
})
}
export default instance
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of vue+vue-router+vuex operation permissions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 探索Windows 11指南:如何访问旧硬盘驱动器上的用户文件夹Sep 27, 2023 am 10:17 AM
探索Windows 11指南:如何访问旧硬盘驱动器上的用户文件夹Sep 27, 2023 am 10:17 AM由于权限,并不总是可以访问某些文件夹,在今天的指南中,我们将向您展示如何在Windows11上的旧硬盘驱动器上访问用户文件夹。此过程很简单,但可能需要一段时间,有时甚至数小时,具体取决于驱动器的大小,因此请格外耐心并严格按照本指南中的说明进行操作。为什么我无法访问旧硬盘上的用户文件夹?用户文件夹的所有权属于另一台电脑,因此您无法对其进行修改。除了所有权之外,您对该文件夹没有任何权限。如何打开旧硬盘上的用户文件?1.取得文件夹的所有权并更改权限找到旧的用户目录,右键单击它,然后选择属性。导航到“安
 linux删除文件需要什么权限Jul 11, 2023 pm 01:26 PM
linux删除文件需要什么权限Jul 11, 2023 pm 01:26 PMlinux删除文件需要所在文件夹的所有权限,分别是读、写、执行。因为定位这个文件过程就需要进入文件夹,即使使用类似rm /xxx/fle的方式,同样系统内部也会进入文件夹,所以要对文件夹有执行权限,然后读取文件夹内容需要读的权限,最后是删除文件,由于文件是上级文件夹的一部分所以需要对文件夹有写的权限。
 iOS 17:如何控制哪些应用程序可以访问您的照片Sep 13, 2023 pm 09:09 PM
iOS 17:如何控制哪些应用程序可以访问您的照片Sep 13, 2023 pm 09:09 PM在iOS17中,Apple可以更好地控制应用程序可以看到的照片内容。继续阅读,了解如何按应用管理应用访问权限。在iOS中,Apple的应用内照片选取器可让您与应用共享特定照片,而照片图库的其余部分则保持私密。应用必须请求访问您的整个照片图库,您可以选择授予应用以下访问权限:受限访问–应用程序只能看到您可以选择的图像,您可以随时在应用程序中或通过转到“设置”>“隐私和安全”>“照片”来查看所选图像。完全访问权限–App可以查看照片
 PHP如何实现角色权限管理系统?Jun 29, 2023 pm 07:57 PM
PHP如何实现角色权限管理系统?Jun 29, 2023 pm 07:57 PMPHP是一种广泛应用的编程语言,被广泛用于创建和开发各种Web应用程序。在许多Web应用中,角色权限管理系统是一个重要的功能,它可以确保不同用户拥有适当的访问权限。本文将介绍如何使用PHP来实现一个简单而实用的角色权限管理系统。角色权限管理系统的基本概念是将用户分为不同的角色,并为每个角色分配相应的权限。这样,用户只能执行他们有权限执行的操作,从而保证系统的
 CentOS搭建web服务器前需注意的权限与访问控制策略Aug 05, 2023 am 11:13 AM
CentOS搭建web服务器前需注意的权限与访问控制策略Aug 05, 2023 am 11:13 AMCentOS搭建web服务器前需注意的权限与访问控制策略在搭建web服务器的过程中,权限与访问控制策略是非常重要的一环。正确设置权限和访问控制策略可以保护服务器的安全性,防止非授权用户访问敏感数据或者对服务器进行不当操作。本文将介绍在CentOS系统下搭建web服务器时需要注意的权限与访问控制策略,并提供相应的代码示例。用户与组的管理首先,我们需要创建一个专
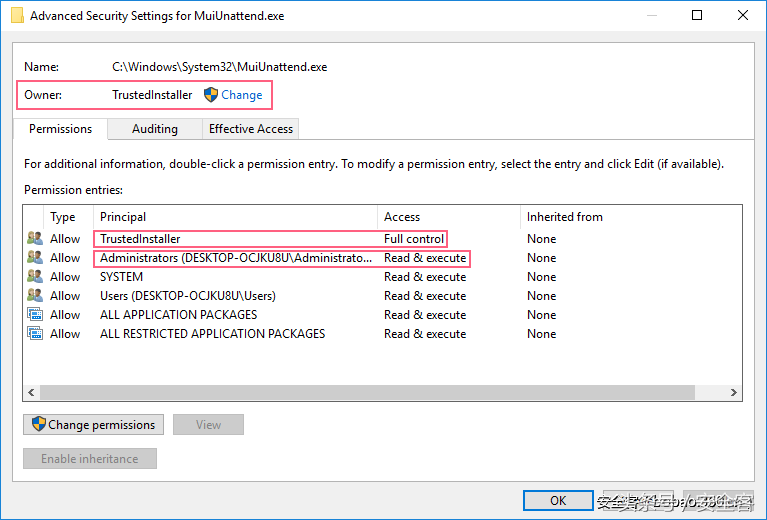 trustedinstaller权限怎么获得「推荐获取TrustedInstaller权限操作步骤」Feb 06, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
trustedinstaller权限怎么获得「推荐获取TrustedInstaller权限操作步骤」Feb 06, 2024 pm 05:48 PM这篇文章将带你了解TI的本质是什么,进一步探索如何在powershell和NtObjectManager模块的帮助下获取TI权限,以便在操作系统中完成任何你想要的操作。如果你曾经管理过Windows系统,那么你应该熟悉trustedInstaller(TI)组的概念。TI组在系统文件和注册表的操作中具有重要的权限。举个例子,你可以查看System32文件夹下文件的属性,在安全选项中,TI组和文件所有者具有删除和修改文件的权限,甚至管理员也无法直接修改安全选项。因此,对于系统文件和注册表的操作,需
 手机档案存取权限是什么Jul 19, 2022 pm 03:50 PM
手机档案存取权限是什么Jul 19, 2022 pm 03:50 PM手机档案存取权限是指允许APK文件读写手机的内存;如果允许APK文件访问手机的内存,那么就可以将应用安装在手机中,如果不允许APK文件访问手机的内存,那么手机就不能安装应用。
 win7修改文件提示更改权限拒绝访问如何解决Jul 04, 2023 pm 07:01 PM
win7修改文件提示更改权限拒绝访问如何解决Jul 04, 2023 pm 07:01 PMwin7修改文件提示更改权限拒绝访问如何解决?一些系统文件在进行修改的时候,常常会提示我们没有权限去进行操作。我们可以去进行文件夹权限的功能关闭,或者获取管理员权限。需要修改此类文件的用户,一起来看看接下来具体的教程分享吧。win7修改文件提示更改权限拒绝访问解决办法 1、首先选中对应文件夹,点击上方工具,选中文件夹选项。 2、进入查看选项卡。 3、取消勾选使用简单文件共享然后确定。 4、然后右键选择对应文件夹,点击属性。 5、进入安全选项卡。 6、选择图示位置,点击高级。 7


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.






