Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Nginx scenario practice
Nginx scenario practice
- 不言Original
- 2018-05-07 11:05:511554browse
This article mainly introduces the scenario practice of Nginx, which has certain reference value. Now I share it with everyone. Friends in need can refer to it
1. Nginx as a static resource Web service
1. Dynamic resources and static resources
If the page requested by the client is a static web page, the server will directly respond to the client with the content of the static web page. If the client requests a dynamic web page, the server needs to first replace the dynamic web page with a static web page, and then respond to the converted static web page to the client
Several types of static resources
Browser rendering: HTML, CSS, JAVASCRIPT
Pictures: JPEG, GIF, PNG...
Video : FLV, MPEG...
File: TXT, etc. Any download file
2, CDN (Content Delivery Network) content distribution network
The basic idea is to avoid bottlenecks and links on the Internet that may affect the speed and stability of data transmission as much as possible, so as to make content transmission faster and more stable. By placing node servers throughout the network to form a layer of intelligent virtual network based on the existing Internet, the CDN system can real-time analyze the network traffic and the connection and load status of each node, as well as the distance to the user and response time. and other comprehensive information to redirect the user's request to the service node closest to the user. Its purpose is to enable users to obtain the required content nearby, solve the congestion situation of the Internet network, and improve the response speed of users' access to the website.
3. Configuration syntax
sendfile (file reading)
Configuration syntax: sendfile on|off ;
Default: None
Context: http, server, location, if in location
tcp_nopush (when sendfile is turned on, improve the transmission efficiency of network packets)
Configuration syntax: tcp_nopush on|off;
Default: None
Context: http, server, location
tcp_nodelay (under keepalive connection, improve network packets transmission real-time)
Configuration syntax: tcp_nodely on|off;
Default: None
Context: http, server, location
gzip (compression)
Configuration syntax: gzip on|off;
Default: None
Context: http, server, location, if in location
gizp_comp_level (compression ratio)
Configuration syntax: gzip_comp_level level;
Default: none;
Context: http, server, location
gzip_http_version (gzip http version)
Configuration syntax: gzip_http_version 1.0|1.1;
Default: None
- ##Context: http, server, location
- Configuration syntax: gzip_static on|off|always;
- Default: gzip_static off;
- Context: http, server, location
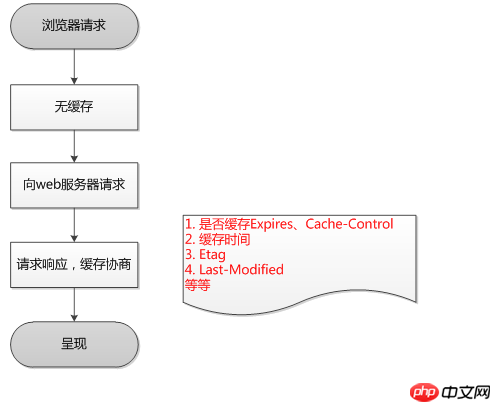
- The browser has no cache:
- Browser request → No cache → Request WEB server → Request response, negotiate → Present
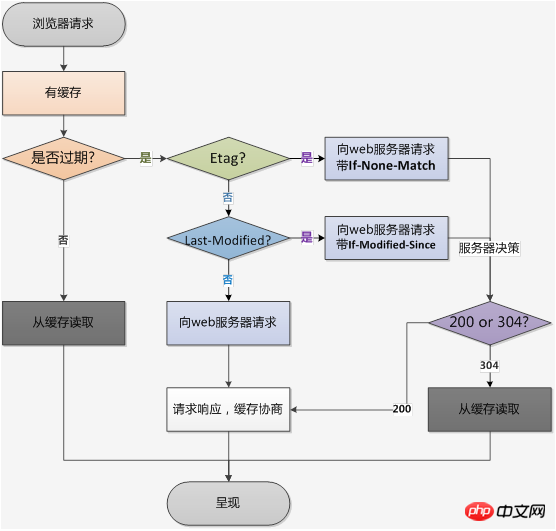
- The client has cache
- Browser request→with cache→verification expiration→present
- Verification expiration mechanism
| Corresponding header information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expires, Cache-Control(max-age) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Etag | ##Last-Modified There is information verification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| param | 意义 |
|---|---|
| down | 当前的server暂时不参与负载均衡 |
| weight=num | 权重,num越大,轮询到的概率越大 |
| backup | 预留的备份服务器 |
| max_fails | 允许请求失败的次数 |
| fail_timeout | 经过max_fails失败后,服务暂停的时间(默认是10s) |
| max_conns | 限制最大的接收的连接数 |
调度算法:
| 算法 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| 轮询 | 按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器 |
| 加权轮询 | weight值越大,分配到的访问几率越高 |
| ip_hash | 每个请求按访问IP的hash结果分配,这样来自同一个IP就固定访问同一个后端服务器 |
| least_conn | 最少连接数,哪个服务器连接数少就分发 |
| url_hash | 按照访问的URL的hash结果来分配请求,是每个URL定向到同一个后端服务器 |
| hash关键字值 | hash自定义的key |
ip_hash:
只需要在upstream中加入 ip_hash; 即可
缺陷:如果走代理,那么remote_addr就不是用户真实的ip
url_hash(1.7.2版本以后可用):
配置语法:hash key [consistent];
默认:无
Context:upstream
key可以是$request_uri,根据url进行hash
四、Nginx作为缓存服务
1、缓存的类型
服务端缓存。例:memcache、reids
代理缓存。例:Nginx缓存服务端的数据
客户端缓存。
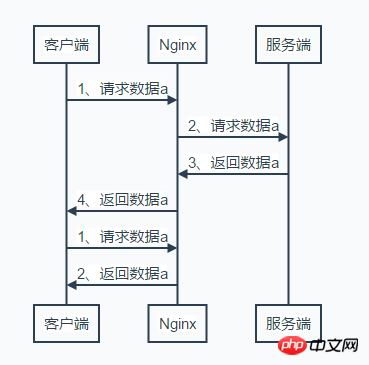
2、常用缓存配置
proxy_cache_path
配置语法proxy_cache_path path [levels=levels] [use_temp_path=on|off] keys_zone=name:size [inactive=time] [max_size] [use_temp_path]...
默认:无
Context:http
proxy_cache
配置语法:proxy_cache zone | off;
默认:proxy_cache off;
Context:http,server,location
proxy_cache_valid(缓存过期周期)
配置语法:proxy_cache_valid [code...] time
默认:无
Context:http、server、location
proxy_cache_key(缓存的维度)
配置语法:proxy_cache_key string;
默认:proxy_cache_key
$scheme$proxy_host$request_uri;Context:http、server、location
常见配置:
proxy_cache_path cache_path levels=1:2 keys_zone=key_name:10m max_size=10g inactive=60m use_temp_path=off;
server {
loaction / {
proxy_pass http://ronaldo;
proxy_cache key_name;
proxy_cache_valid 200 304 12h;
proxy_cache_valid any 10m;
proxy_cache_key $host$uri$is_args$args;
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status";
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
}
}2、清除指定缓存
rm -rf 缓存目录内容
第三方扩展模块:ngx_cache_purge
3、如何让部分页面不缓存
proxy_no_cache
配置语法:proxy_no_cache string ...;
默认:无
Context:http,server,location
简单示例
if ($request_uri ~ ^/(url_3|login|register|password\/reset)) {
set $cookie_nocache 1;
}
location / {
proxy_no_cache $cookie_nocache;
}4、大文件分片请求
slice
语法配置:slice size;
默认:slice 0;
Context:http、server,location
优势:每个子请求收到的数据都会形成一个独立的文件,一个请求断了,其他请求不受影响。
缺点:当文件很大或者slice很小的时候,可能会导致文件描述符耗尽等待情况。
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Nginx scenario practice. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!