Home >WeChat Applet >Mini Program Development >Detailed explanation of Vue.js two-way binding implementation
Detailed explanation of Vue.js two-way binding implementation
- ringa_leeOriginal
- 2018-05-04 15:41:322569browse
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of Vue.js two-way binding implementation. What are the precautions for Vue.js two-way binding implementation? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script>
<p id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="CurrentTime" placeholder="当前时刻">
<h1>当前时刻{{ CurrentTime }}</h1>
</p>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
CurrentTime: new Date()
},
mounted:function(){
var _this = this;
this.timer = setInterval(function(){
_this.CurrentTime = new Date();
},1000);
},
beforeDestroy:function(){
if(this.timer){
clearInterval(this.timer);
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
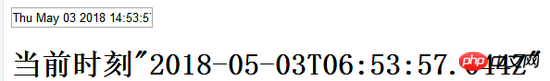
{{ }} is the so-called text interpolation method, the purpose is to display two-way bound data
mounted means el is mounted on the instance The event called
beforeDestory is called before the instance is destroyed
In the above example, a timer is created in the mounted event, every The current time is written into the text box in one second. Due to the two-way binding, the text of the H1 tag will also change and be consistent with the text of the text box. In the beforeDestory event, the timer will be cleared before the Vue instance is destroyed
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
Detailed explanation of the steps to develop mpvue framework with Vue.js
Summary of common knowledge points in vue practical projects
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Vue.js two-way binding implementation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- WeChat Mini Program Simple DEMO layout, logic, and style exercises
- Detailed explanation and examples of WeChat applet wx.request (interface calling method)
- WeChat Mini Program - Detailed explanation of WeChat login, WeChat payment, and template messages
- WeChat applet (application account) simple example application and detailed explanation of the example
- Detailed explanation of WeChat applet for loop

