 Backend Development
Backend Development Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial Detailed explanation of implementing logistic regression algorithm with TensorFlow
Detailed explanation of implementing logistic regression algorithm with TensorFlowThis article mainly introduces the detailed explanation of using TensorFlow to implement the logistic regression algorithm. It has certain reference value. Now I share it with you. Friends in need can refer to it.
This article will implement the logistic regression algorithm and predict Probability of low birth weight.
# Logistic Regression
# 逻辑回归
#----------------------------------
#
# This function shows how to use TensorFlow to
# solve logistic regression.
# y = sigmoid(Ax + b)
#
# We will use the low birth weight data, specifically:
# y = 0 or 1 = low birth weight
# x = demographic and medical history data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import requests
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
import os.path
import csv
ops.reset_default_graph()
# Create graph
sess = tf.Session()
###
# Obtain and prepare data for modeling
###
# name of data file
birth_weight_file = 'birth_weight.csv'
# download data and create data file if file does not exist in current directory
if not os.path.exists(birth_weight_file):
birthdata_url = 'https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow_cookbook/raw/master/01_Introduction/07_Working_with_Data_Sources/birthweight_data/birthweight.dat'
birth_file = requests.get(birthdata_url)
birth_data = birth_file.text.split('\r\n')
birth_header = birth_data[0].split('\t')
birth_data = [[float(x) for x in y.split('\t') if len(x)>=1] for y in birth_data[1:] if len(y)>=1]
with open(birth_weight_file, "w") as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(birth_header)
writer.writerows(birth_data)
f.close()
# read birth weight data into memory
birth_data = []
with open(birth_weight_file, newline='') as csvfile:
csv_reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
birth_header = next(csv_reader)
for row in csv_reader:
birth_data.append(row)
birth_data = [[float(x) for x in row] for row in birth_data]
# Pull out target variable
y_vals = np.array([x[0] for x in birth_data])
# Pull out predictor variables (not id, not target, and not birthweight)
x_vals = np.array([x[1:8] for x in birth_data])
# set for reproducible results
seed = 99
np.random.seed(seed)
tf.set_random_seed(seed)
# Split data into train/test = 80%/20%
# 分割数据集为测试集和训练集
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.8), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices)))
x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices]
x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices]
y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices]
y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices]
# Normalize by column (min-max norm)
# 将所有特征缩放到0和1区间(min-max缩放),逻辑回归收敛的效果更好
# 归一化特征
def normalize_cols(m):
col_max = m.max(axis=0)
col_min = m.min(axis=0)
return (m-col_min) / (col_max - col_min)
x_vals_train = np.nan_to_num(normalize_cols(x_vals_train))
x_vals_test = np.nan_to_num(normalize_cols(x_vals_test))
###
# Define Tensorflow computational graph¶
###
# Declare batch size
batch_size = 25
# Initialize placeholders
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 7], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
# Create variables for linear regression
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[7,1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
# Declare model operations
model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)
# Declare loss function (Cross Entropy loss)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=model_output, labels=y_target))
# Declare optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
###
# Train model
###
# Initialize variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# Actual Prediction
# 除记录损失函数外,也需要记录分类器在训练集和测试集上的准确度。
# 所以创建一个返回准确度的预测函数
prediction = tf.round(tf.sigmoid(model_output))
predictions_correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, y_target), tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(predictions_correct)
# Training loop
# 开始遍历迭代训练,记录损失值和准确度
loss_vec = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
for i in range(1500):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size)
rand_x = x_vals_train[rand_index]
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals_train[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss)
temp_acc_train = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals_train, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_train])})
train_acc.append(temp_acc_train)
temp_acc_test = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals_test, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_test])})
test_acc.append(temp_acc_test)
if (i+1)%300==0:
print('Loss = ' + str(temp_loss))
###
# Display model performance
###
# 绘制损失和准确度
plt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-')
plt.title('Cross Entropy Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Cross Entropy Loss')
plt.show()
# Plot train and test accuracy
plt.plot(train_acc, 'k-', label='Train Set Accuracy')
plt.plot(test_acc, 'r--', label='Test Set Accuracy')
plt.title('Train and Test Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
Data result:
Loss = 0.845124
Loss = 0.658061
Loss = 0.471852
Loss = 0.643469
Loss = 0.672077

Cross entropy loss graph for 1500 iterations

Accuracy plots of the test set and training set after 1500 iterations
Related recommendations:
Use TensorFlow to implement lasso regression and ridge regression Example of algorithm
Example of implementing Deming regression algorithm using TensorFlow
##
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of implementing logistic regression algorithm with TensorFlow. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 conda怎么安装tensorflowDec 05, 2023 am 11:26 AM
conda怎么安装tensorflowDec 05, 2023 am 11:26 AM安装步骤:1、下载和安装Miniconda,根据操作系统选择适合的Miniconda版本,并按照官方指南进行安装;2、使用“conda create -n tensorflow_env python=3.7”命令创建一个新的Conda环境;3、激活Conda环境;4、使用“conda install tensorflow”命令安装最新版的TensorFlow;5、验证安装即可。
 十个AI算法常用库Java版Jun 13, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
十个AI算法常用库Java版Jun 13, 2023 pm 04:33 PM今年ChatGPT火了半年多,热度丝毫没有降下来。深度学习和NLP也重新回到了大家的视线中。公司里有一些小伙伴都在问我,作为一名Java开发人员,如何入门人工智能,是时候拿出压箱底的私藏的学习AI的Java库来介绍给大家。这些库和框架为机器学习、深度学习、自然语言处理等提供了广泛的工具和算法。根据AI项目的具体需求,可以选择最合适的库或框架,并开始尝试使用不同的算法来构建AI解决方案。1.Deeplearning4j它是一个用于Java和Scala的开源分布式深度学习库。Deeplearning
 使用TensorFlow和Keras创建猫狗图片深度学习分类器May 16, 2023 am 09:34 AM
使用TensorFlow和Keras创建猫狗图片深度学习分类器May 16, 2023 am 09:34 AM在本文中,我们将使用TensorFlow和Keras创建一个图像分类器,可以区分猫和狗的图像。为了做到这一点,我们将使用TensorFlow数据集中的cats_vs_dogs数据集。该数据集由25000张打过标签的猫和狗的图像组成,其中80%的图像用于训练,10%用于验证,10%用于测试。加载数据我们从使用TensorFlowDatasets加载数据集开始。将数据集拆分为训练集、验证集和测试集,分别占数据的80%、10%和10%,并定义一个函数来显示数据集中的一些样本图像。importtenso
 pip安装tensorflow教程Dec 07, 2023 pm 03:50 PM
pip安装tensorflow教程Dec 07, 2023 pm 03:50 PM安装步骤:1、确保已经安装了Python和pip;2、打开命令提示符或终端窗口,输入“pip install tensorflow”命令安装TensorFlow;3、若想安装CPU版本的TensorFlow,可以使用“pip install tensorflow-cpu”命令;4、安装完成后,即可在Python中使用TensorFlow。
 魔兽世界国服重开之际,4大版本选择指南,最后1个更适合休闲玩家Apr 13, 2024 am 09:16 AM
魔兽世界国服重开之际,4大版本选择指南,最后1个更适合休闲玩家Apr 13, 2024 am 09:16 AM魔兽世界目前存在4个版本,国服关闭这一年多,估计很多玩家都不知道各版本发展到哪一步了,下面胖哥就给大家梳理一下各版本的现状。1,正式服10.0版本末期国服关闭前是10.0版本刚刚开始,目前已经处于10.26版本了,后面还有一个10.27版本,巨龙时代资料片就结束了。虽然10.0版本在外服的评价不错,并且为暴雪挽回了一些人气,但是10.0版本的游戏内核是没有任何变化的,依然是大秘境和团本为主,PVP玩家人数少之又少。随着正式服版本的不断更新,玩家们的游戏倾向也从PVE和PVP变成了收集,每月商栈上
 暴雪已备好国服大礼准备魔兽开服,回归玩家突破200万!考迪克被暴打!Apr 12, 2024 pm 03:37 PM
暴雪已备好国服大礼准备魔兽开服,回归玩家突破200万!考迪克被暴打!Apr 12, 2024 pm 03:37 PM今天是暴雪国服停服的第445天。欢迎继续关注当前风靡全球很快又会有国服的大型网络交友聊天室游戏《魔兽世界》的最新消息。国服人气炸裂,首日回归玩家突破200万4月11日晚,魔兽世界官方微博发布了一条重磅消息,仅仅4月10日官宣的那一天(也就是官宣之后的15小时之内),成功登录并且完成预约的暴雪国服玩家数量就达到了200万!同时,在重铸血吼活动留言的玩家数量也达到了95万多,逼近100万。不仅如此,网易还成功帮助玩家修复的账号数量达到9.2万个,成功找回的账号数量则达到了14.7万。这是一个非常夸张
 网易平台开启回归活动,暴雪新CG增加国服版本,重开只剩最后一步Mar 31, 2024 am 10:01 AM
网易平台开启回归活动,暴雪新CG增加国服版本,重开只剩最后一步Mar 31, 2024 am 10:01 AM国服回归的消息已经逐渐从舅舅党爆料过渡到官方明里暗里的小动作了,下面胖哥给大家分享一下最新的消息。第一个消息:KK对战平台开启回归活动最近一段时间一直有玩家在KK对战平台的评论区询问国服回归的进程,而该平台的小编则表示自己很想说,但是领导不让说,之后会给玩家“来波大的”。目前KK对战平台已经开启了国服回归活动,赠送玩家们魔兽世界国服月卡,并且针对国服回归进行了暗示:“春天来了好事将近,你懂得”。很多玩家会疑惑,为什么国服的事情要问KK对战平台?其实原因就是KK对战平台本身就是网易的。国服关闭之前
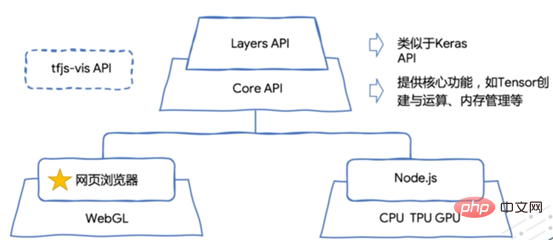 TensorFlow.js 在浏览器上也能搞定机器学习!Apr 13, 2023 pm 03:46 PM
TensorFlow.js 在浏览器上也能搞定机器学习!Apr 13, 2023 pm 03:46 PM在机器学习飞速发展的今天,各种机器学习平台层出不穷,为了满足不同业务场景的需求,可以将机器学习的模型分别部署到 Android、iOS、Web 浏览器,让模型在端侧能够进行推演,从而发挥模型的潜能。其中TensorFlow.js 是 TensorFlow 的 JavaScript 版本,支持 GPU 硬件加速,可以运行在 Node.js 或浏览器环境中。它不但支持完全基于JavaScript 从头开发、训练和部署模型,也可以用来运行已有的 Python 版 TensorFlow 模型,或者基于现


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





