Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Summary of protocols and encapsulation protocols supported by PHP (recommended)
Summary of protocols and encapsulation protocols supported by PHP (recommended)
- 不言Original
- 2018-04-24 15:13:532549browse
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about the protocols and encapsulation protocols supported by PHP. The article introduces it in great detail through sample codes. It has certain reference learning value for everyone to learn or use PHP. Friends who need it can follow Let’s learn together with the editor.
Preface
Today's web program development technology is really a hundred schools of thought contending, ASP.NET, PHP, JSP, Perl, AJAX and so on. No matter how Web technology develops in the future, understanding the basic protocols for communication between Web programs is important because it allows us to understand the inner workings of Web applications.
PHP comes with many built-in URL-style wrapper protocols for file system functions like fopen(), copy(), file_exists(), and filesize(). In addition to these packaging protocols, custom packaging protocols can also be registered through stream_wrapper_register().
Note: The URL syntax used to describe an encapsulated protocol only supports scheme://... syntax. scheme:/ and scheme: syntax are not supported.
php protocol type
file:// — Access local file system
http:// — Access HTTP(s) URLs
ftp:// — Access FTP(s) URLs
php:// — Access various input/output streams (I/O streams)
zlib:// — Compressed streams
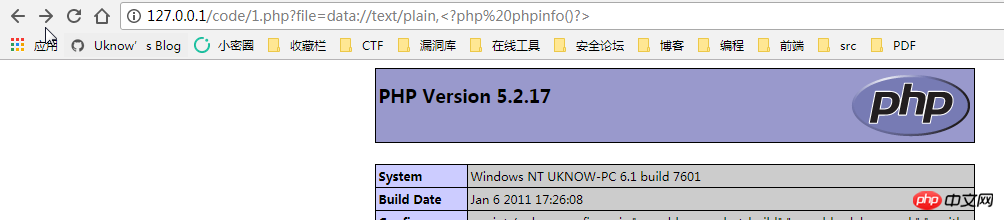
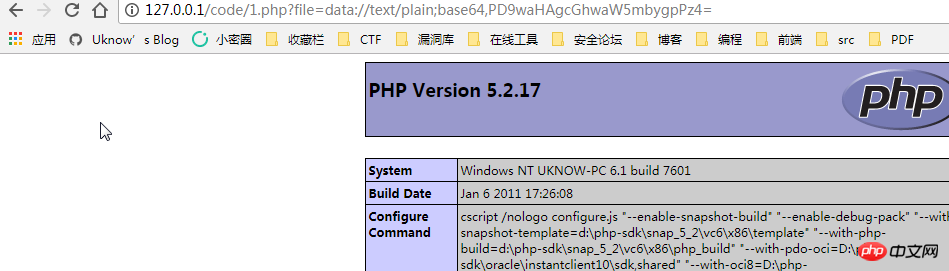
data: // — Data (RFC 2397)
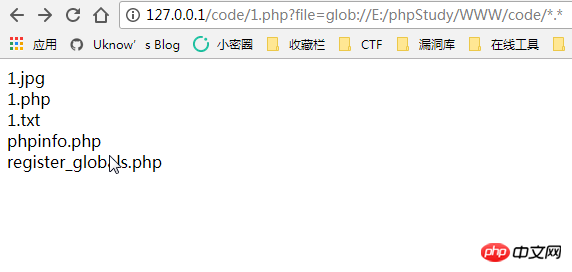
- ##glob:// — Find matching file path pattern
- phar:// — PHP Archive
- ssh2:// — Secure Shell 2
- rar:// — RAR ## ogg:// — Audio streaming
- expect:// — Handling interactive streaming
PHP.ini
- allow_url_fopen: on By default, this option is turned on to activate the fopen encapsulation protocol in the form of a URL, allowing access to URL object files, etc.
- allow_url_include: off is turned off by default. If this option is on, it allows the inclusion of URL object files, etc.
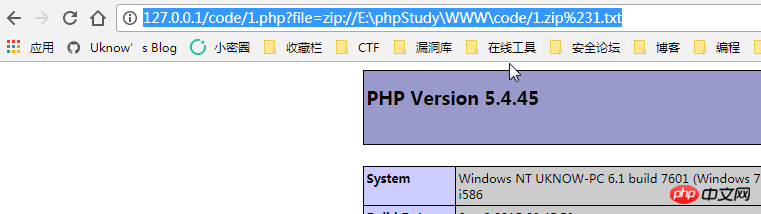
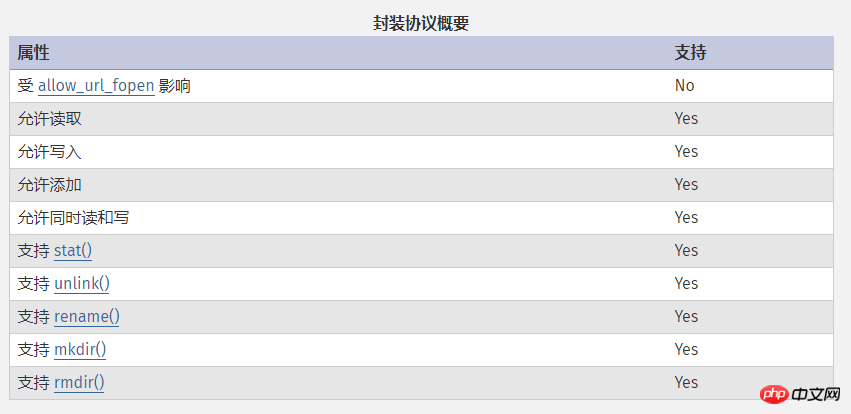
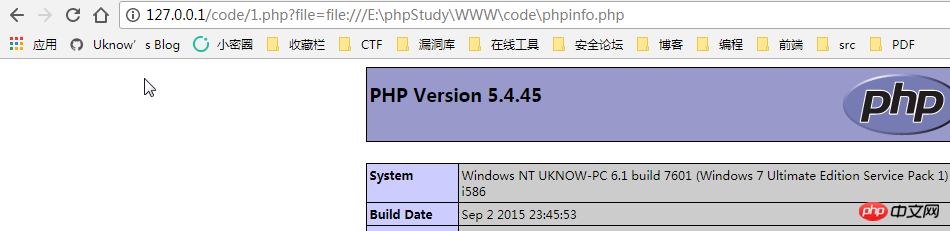
file: //Protocolfile:// — Access the local file system, not affected by allow_url_fopen and allow_url_include
Usagefile:// [absolute path and file name of the file]
http://127.0.0.1/code/1.php?file=file:///E:\phpStudy\WWW\code\phpinfo.php
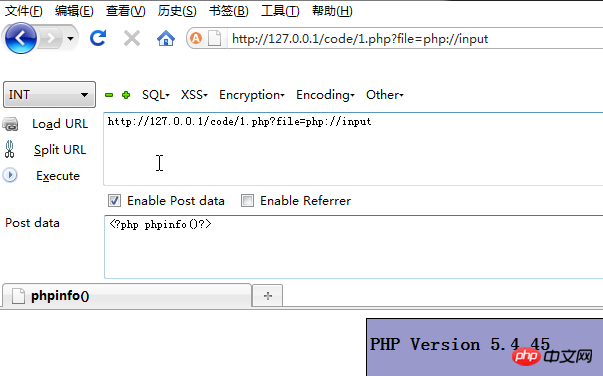
php://protocolphp:// — Access various input/output streams (I/O streams)
There is no need to enable allow_url_fopen, only php://input, php://stdin, php://memory and php://temp need to enable allow_url_include.
php://stdin, php://stdout and php://stderr##php://stdin, php:/ /stdout and php://stderr allow direct access to the corresponding input or output streams of the PHP process.
php://stdin is read-only, php://stdout and php://stderr are write-only.php://stdin
<?php
while($line = fopen('php://stdin','r'))
{//open our file pointer to read from stdin
echo $line."\n";
echo fgets($line);//读取
}
?>
##php: //stdout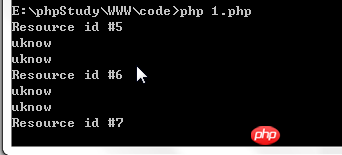
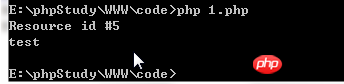
<?php
$fd = fopen('php://stdout', 'w');
if ($fd) {
echo $fd."\n";
fwrite($fd, "test");
fwrite($fd, "\n");
fclose($fd);
}
?>
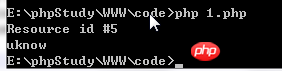
<?php $stderr = fopen( 'php://stderr', 'w' ); echo $stderr."\n"; fwrite($stderr, "uknow" ); fclose($stderr); ?>##php://filter
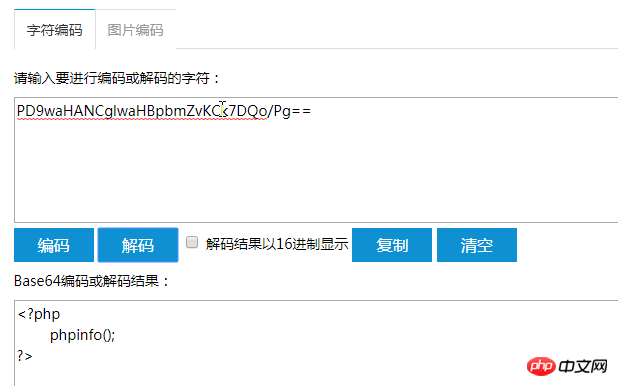
Most commonly used A pseudo-protocol that can generally be used to read arbitrary files. php://filter is a meta-wrapper designed for filtering applications when a data stream is opened. This is useful for all-in-one file functions like readfile(), file(), and file_get_contents(), where there is no opportunity to apply additional filters before the stream contents are read.
parameter| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| This parameter is required. It specifies the data stream you want to filter. | |
| This parameter is optional. One or more filter names can be set, separated by pipe characters. | |
| This parameter is optional. One or more filter names can be set, separated by pipe characters. | |
| Any filter list not prefixed with read= or write= will be applied to read or write= as appropriate. Write chain. |
The above is the detailed content of Summary of protocols and encapsulation protocols supported by PHP (recommended). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!