This article mainly introduces the practical examples of uploading and accessing user avatars in Django projects. Now I share them with you and give them a reference. Let’s take a look together
1 Save the file locally on the server
upload.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{% csrf_token %}
<p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username"></p>
<p>头像<input type="file" name="avatar"></p>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^upload',views.upload) ]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
def upload(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
name = request.POST.get('username')
avatar = request.FILES.get('avatar')
with open(avatar.name,'wb') as f:
for line in avatar:
f.write(line)
return HttpResponse('ok')
return render(request,'upload.html')
Summary
In this way, we have made a basic small example of file upload. There are a few points to note here:
1. The form requires Add csrf_token verification
2. The type value of the input box of the file is file
3. To obtain the file in the view function, use the request.FILES.get() method
4. Through obj.name Get the name of the file
2 Upload the file to the database
models.py
from django.db import models class User(models.Model): username = models.CharField(max_length=16) avatar = models.FileField(upload_to='avatar')
views.py
def upload(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
name = request.POST.get('username')
avatar = request.FILES.get('avatar')
models.User.objects.create(username=name,avatar=avatar)
return HttpResponse('ok')
return render(request,'upload.html')
Summary
The function of uploading files to the database has been implemented above. There are a few points to note:
1. The so-called uploading to the database does not mean placing the image itself or the binary code in the database. It actually uploads the file to the server locally. The database only stores the path of a file, so that when the user wants to call the file, he can go to the location specified by the server through the path.
2. When creating the ORM, the avatar field must have an upload_to='' attribute, specify Where to put the uploaded files
3. When adding to the database, the file field attribute assignment is the same as the ordinary field in form, such as: models.User.objects.create(username=name,avatar=avatar)
4. If there are duplicate file names uploaded by two users, the system will automatically rename the file, with the following effect:

##Append

MEDIA_ROOT=os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"blog","media") #blog是项目名,media是约定成俗的文件夹名 MEDIA_URL="/media/" # 跟STATIC_URL类似,指定用户可以通过这个路径找到文件2. Configure in urls.py
from django.views.static import serve
from upload import settings #upload是站点名
url(r'^media/(?P<path>.*)$', serve, {'document_root': settings.MEDIA_ROOT}),
After configuring, you can pass http://127.0.0.1:8001/media/milk.png accessed the picture 3 Use AJAX to submit the file
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<form>
{% csrf_token %}
<p>用户名:<input id="name-input" type="text"></p>
<p>头像<input id="avatar-input" type="file"></p>
<input id="submit-btn" type="button" value="提交">
</form>
<script src="/static/js/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
$('#submit-btn').on('click',function () {
formdata = new FormData();
formdata.append('username',$('#name-input').val());
formdata.append("avatar",$("#avatar")[0].files[0]);
formdata.append("csrfmiddlewaretoken",$("[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val());
$.ajax({
processData:false,contentType:false,url:'/upload', type:'post', data:formdata,success:function (arg)
{
if (arg.state == 1){ alert('成功!') }
else { alert('失败!') } } }) });
</script>
</body>
</html>
views.pyfrom django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from app01 import models
def upload(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
name = request.POST.get('username')
avatar = request.FILES.get('avatar')
try:
models.User.objects.create(username=name,avatar=avatar)
data = {'state':1}
except:
data = {'state':0}
return JsonResponse(data)
return render(request,'upload.html')
Summary2. When Ajax uploads, the value of the data parameter is no longer an ordinary 'dictionary' type value, but a FormData object
- Create the object formdata = new FormData();
- Add the value formdata.append('username',$( '#name-input').val());
- formdata.append("csrfmiddlewaretoken",$("[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val());
- processData:false
- contentType:false
4 There is a preview function when uploading image files
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<form>
<!----用一个label标签将上传文件输入框跟图片绑定一起,
点击图片的时候就相当于点击了上传文件的按钮---->
<label><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="/static/img/default.png" class="lazy" id="avatar-img" style="max-width:90%" height="80px" alt="Django project practical user avatar upload and access" >
<p>头像<input id="avatar-input" hidden type="file"></p>
</label>
<input id="submit-btn" type="button" value="提交">
</form>
<script src="/static/js/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 上传文件按钮(label里的图片)点击事件
$('#avatar-input').on('change',function () {
// 获取用户最后一次选择的图片
var choose_file=$(this)[0].files[0];
// 创建一个新的FileReader对象,用来读取文件信息
var reader=new FileReader();
// 读取用户上传的图片的路径
reader.readAsDataURL(choose_file);
// 读取完毕之后,将图片的src属性修改成用户上传的图片的本地路径
reader.onload=function () {
$("#avatar-img").attr("src",reader.result)
}
});
</script>
##5 Summary
For file upload, whether it is direct form submission or Ajax submission, the fundamental problem is to tell the browser that what you want to upload is a file instead of an ordinary string
What about We tell the browser by requesting the ContentType parameter of the weight. We don’t need to specify it when uploading a normal string, because it has a default value,
. And if you want to upload a file, you need to specify it separately. . Summarize the following points
2. For ajax upload, ContentType is specified through processData:false and contentType:false
3. When the form is uploaded, the file data is "wrapped" through the tag.
4. When the ajax is uploaded, the data is added through a FormData instance object. Just pass this object when passing it
5. After the data is passed, it is encapsulated in request.FILES instead of request.POST
Related recommendations:
How Django loads css and js files and static images
Detailed explanation of the use of django controls and parameter passing
The above is the detailed content of Django project practical user avatar upload and access. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 怎么将Django项目迁移到linux系统中Jun 01, 2023 pm 01:07 PM
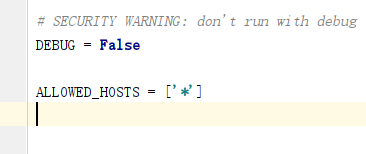
怎么将Django项目迁移到linux系统中Jun 01, 2023 pm 01:07 PMDjango项目配置修改我们需要把原先的Django项目进行修改才能更好地进行项目迁移工作,首先需要修改的是settings.py文件。由于项目上线之后不能让用户看到后台的运行逻辑,所以我们要把DEBUG改成False,把ALLOWED_HOSTS写成‘*’,这样是为了允许从不同主机进行访问。由于linux中如果不加这句可能会出现文件找不到的情况,所以我们要把模板的路径进行拼接。由于做Django项目肯定进行过数据库的同步,所以我们要把migrations
 centos+nginx+uwsgi部署django项目上线的方法May 15, 2023 am 08:13 AM
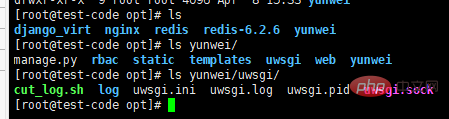
centos+nginx+uwsgi部署django项目上线的方法May 15, 2023 am 08:13 AM我django项目叫yunwei,主要app是rabc和web,整个项目放/opt/下如下:[root@test-codeopt]#lsdjango_virtnginxredisredis-6.2.6yunwei[root@test-codeopt]#lsyunwei/manage.pyrbacstatictemplatesuwsgiwebyunwei[root@test-codeopt]#lsyunwei/uwsgi/cut_log.shloguwsgi.iniuwsgi.loguwsgi.p
 Django框架中的数据库迁移技巧Jun 17, 2023 pm 01:10 PM
Django框架中的数据库迁移技巧Jun 17, 2023 pm 01:10 PMDjango是一个使用Python语言编写的Web开发框架,其提供了许多方便的工具和模块来帮助开发人员快速地搭建网站和应用程序。其中最重要的一个特性就是数据库迁移功能,它可以帮助我们简单地管理数据库模式的变化。在本文中,我们将会介绍一些在Django中使用数据库迁移的技巧,包括如何开始一个新的数据库迁移、如何检测数据库迁移冲突、如何查看历史数据库迁移记录等等
 Django框架中的文件上传技巧Jun 18, 2023 am 08:24 AM
Django框架中的文件上传技巧Jun 18, 2023 am 08:24 AM近年来,Web应用程序逐渐流行,而其中许多应用程序都需要文件上传功能。在Django框架中,实现上传文件功能并不困难,但是在实际开发中,我们还需要处理上传的文件,其他操作包括更改文件名、限制文件大小等问题。本文将分享一些Django框架中的文件上传技巧。一、配置文件上传项在Django项目中,要配置文件上传需要在settings.py文件中进
 如何用nginx+uwsgi部署自己的django项目May 12, 2023 pm 10:10 PM
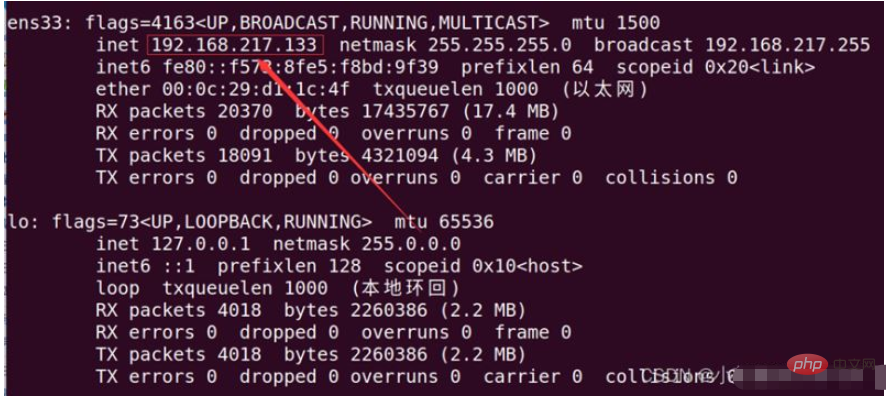
如何用nginx+uwsgi部署自己的django项目May 12, 2023 pm 10:10 PM第一步:换源输入命令换掉Ubuntu的下载源sudonano/etc/apt/sources.list将以下全部替换掉原文件,我这里用的是阿里的源,你也可以换其他的。debhttp://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/bionicmainrestricteddebhttp://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/bionic-updatesmainrestricteddebhttp://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/bionicunive
 使用Django构建RESTful APIJun 17, 2023 pm 09:29 PM
使用Django构建RESTful APIJun 17, 2023 pm 09:29 PMDjango是一个Web框架,可以轻松地构建RESTfulAPI。RESTfulAPI是一种基于Web的架构,可以通过HTTP协议访问。在这篇文章中,我们将介绍如何使用Django来构建RESTfulAPI,包括如何使用DjangoREST框架来简化开发过程。安装Django首先,我们需要在本地安装Django。可以使用pip来安装Django,具体
 使用Python Django框架构建博客网站Jun 17, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
使用Python Django框架构建博客网站Jun 17, 2023 pm 03:37 PM随着互联网的普及,博客在信息传播和交流方面扮演着越来越重要的角色。在此背景下,越来越多的人开始构建自己的博客网站。本文将介绍如何使用PythonDjango框架来构建自己的博客网站。一、PythonDjango框架简介PythonDjango是一个免费的开源Web框架,可用于快速开发Web应用程序。该框架为开发人员提供了强大的工具,可帮助他们构建功能丰
 Django+Bootstrap构建响应式管理后台系统Jun 17, 2023 pm 05:27 PM
Django+Bootstrap构建响应式管理后台系统Jun 17, 2023 pm 05:27 PM随着互联网技术的快速发展和企业业务的不断扩展,越来越多的企业需要建立自己的管理后台系统,以便于更好地管理业务和数据。而现在,使用Django框架和Bootstrap前端库构建响应式管理后台系统的趋势也越来越明显。本文将介绍如何利用Django和Bootstrap构建一个响应式的管理后台系统。Django是一种基于Python语言的Web框架,它提供了丰富的功


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.






