Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Further understanding of numpy array and matrix multiplication
Further understanding of numpy array and matrix multiplication
- 不言Original
- 2018-04-04 17:06:211965browse
The following article will share with you a further understanding of the multiplication of numpy arrays and matrices. It has a good reference value and I hope it will be helpful to everyone. Let’s take a look together
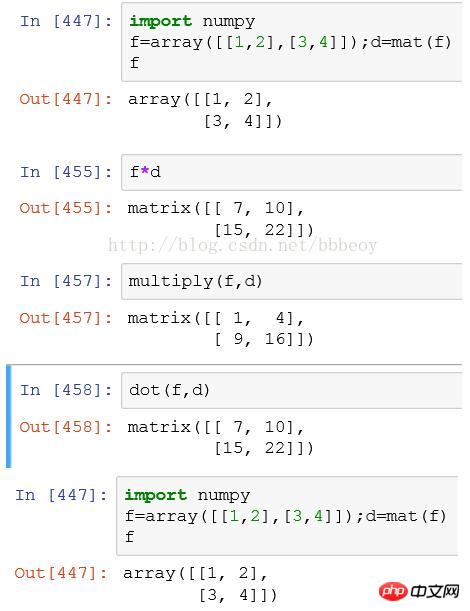
1, When it is an array, the default d*f is the product of the corresponding elements, multiply is also the product of the corresponding elements, dot ( d, f) will be converted into the product of matrices. dot dot multiplication means addition, while multiply only multiplies the corresponding elements and does not add.
2, When it is mat, the default d*f is the product of the matrix, multiply is converted into the product of the corresponding elements, dot (d, f) is the product of the matrix


3. When mixing, generally do not mix.
When mixing, the default is matrix multiplication. multiply is converted into the product of the corresponding elements, dot (d, f) is the product of the matrix
Summary: The default for array multiplication is dot multiplication, and the default for matrix is Matrix multiplication, when mixed together, the default is matrix multiplication. multiply is converted into the product of the corresponding elements, and dot (d, f) will be converted into the product of the matrix. Note that when multiply does not satisfy the corresponding elements, it is performed in the broadcast manner.

Related recommendations:
Convert matrices to lists, etc. in Python’s numpy library Function method_python
Python programming to add a column to the numpy matrix method example
Python method to create a symmetric matrix based on the numpy module
The above is the detailed content of Further understanding of numpy array and matrix multiplication. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

