In Scala, all values have a type, including numbers and functions. The following figure demonstrates a subset of the type hierarchy.
![[Scala Tour] 3-Unified Type - TOUR OF SCALA SiFou](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/153/291/1631c91b131cc86403e9e57292daefc1-0.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40)
Scala Type Hierarchy
Any Type is the parent type of all types, also known as the top level type. It defines some common methods such as equals, hashCode and toString. Any has two direct subclasses: AnyVal and AnyRef.
AnyVal represents the value type. There are 9 predefined value types, which are not nullable: Double, Float, Long, Int, Short, Byte, Char, Unit, and Boolean. Unit is a value type without any meaning. Unit Only one instance can be declared like this: (). All functions must return some value, so Unit is a useful return type.
AnyRef represents a reference type. All non-value types are defined as reference types. Every user-defined type in Scala is a subtype of AnyRef. If Scala is used within a Java runtime environment, then AnyRef corresponds to Java.lang.object.
Here is an example that demonstrates that strings, integers, characters, booleans, and functions are objects like other objects:
val list: List[Any] = List( "a string", 732, // an integer 'c', // a character true, // a boolean value () => "an anonymous function returning a string" ) list.foreach(element => println(element))
It defines the type List[ Any] variable list. The list is initialized with elements of various types, but they are all instances of scala.Any, so you can add them all to the list.
The following is the output of the program:
a string 732 c true <function></function>
Type conversion
Value types can be converted in the following ways:
![[Scala Tour] 3-Unified Type - TOUR OF SCALA SiFou](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/153/291/880d649cfe1993f6e5c152158f099783-1.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40)
For example:
val x: Long = 987654321 val y: Float = x // 9.8765434E8 (note that some precision is lost in this case) val face: Char = '☺' val number: Int = face // 9786
The conversion is one-way. The last statement below will not compile:
val x: Long = 987654321 val y: Float = x // 9.8765434E8 val z: Long = y // Does not conform
You can also convert a reference type to a subtype. This will be covered in a later article.
Nothing and Null
Nothing are subtypes of all types, also known as bottom types. Type Nothing has no value. Common uses are to signal non-termination, such as throwing an exception, program exit, or infinite loop (i.e., it is an expression that does not evaluate to a value, or a method that does not return a normal value).
Null is a subtype of all reference types (that is, any subtype of AnyRef). It has a single value identified by the keyword null. Null is primarily used for interoperability with other JVM languages and should almost never be used in Scala code. We'll cover alternatives to null in a later article.
The above is the detailed content of [Scala Tour] 3-Unified Type - TOUR OF SCALA SiFou. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 如何在 Windows 11 中更改网络类型为专用或公共Aug 24, 2023 pm 12:37 PM
如何在 Windows 11 中更改网络类型为专用或公共Aug 24, 2023 pm 12:37 PM设置无线网络很常见,但选择或更改网络类型可能会令人困惑,尤其是在您不知道后果的情况下。如果您正在寻找有关如何在Windows11中将网络类型从公共更改为私有或反之亦然的建议,请继续阅读以获取一些有用的信息。Windows11中有哪些不同的网络配置文件?Windows11附带了许多网络配置文件,这些配置文件本质上是可用于配置各种网络连接的设置集。如果您在家中或办公室有多个连接,这将非常有用,因此您不必每次连接到新网络时都进行所有设置。专用和公用网络配置文件是Windows11中的两种常见类型,但通
 用Python实现动态数组:从入门到精通Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:04 PM
用Python实现动态数组:从入门到精通Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:04 PMPart1聊聊Python序列类型的本质在本博客中,我们来聊聊探讨Python的各种“序列”类,内置的三大常用数据结构——列表类(list)、元组类(tuple)和字符串类(str)的本质。不知道你发现没有,这些类都有一个很明显的共性,都可以用来保存多个数据元素,最主要的功能是:每个类都支持下标(索引)访问该序列的元素,比如使用语法Seq[i]。其实上面每个类都是使用数组这种简单的数据结构表示。但是熟悉Python的读者可能知道这3种数据结构又有一些不同:比如元组和字符串是不能修改的,列表可以
 视频矩阵账号怎么做?它的矩阵账号都有哪些类型呢?Mar 21, 2024 pm 04:57 PM
视频矩阵账号怎么做?它的矩阵账号都有哪些类型呢?Mar 21, 2024 pm 04:57 PM随着短视频平台的盛行,视频矩阵账号营销已成为一种新兴营销方式。通过在不同平台上创建和管理多个账号,企业和个人能够实现品牌推广、粉丝增长和产品销售等目标。本文将为您探讨如何有效运用视频矩阵账号,并介绍不同类型的视频矩阵账号。一、视频矩阵账号怎么做?要想做好视频矩阵账号,需要遵循以下几个步骤:首先要明确你的视频矩阵账号的目标是什么,是为了品牌传播、粉丝增长还是产品销售。明确目标有助于制定相应的策略。2.选择平台:根据你的目标受众,选择合适的短视频平台。目前主流的短视频平台有抖音、快手、火山小视频等。
 Golang 与 Scala 在语言特性的差异Jun 02, 2024 pm 01:17 PM
Golang 与 Scala 在语言特性的差异Jun 02, 2024 pm 01:17 PMGo和Scala在语言特性上的差异在于:类型系统:Go采用静态类型系统,而Scala采用混合类型系统。并发性:Go基于轻量级goroutine,而Scala使用基于Akka的actor模型。泛型:Go提供实验性的泛型特性,而Scala具有成熟的泛型系统。函数式编程:Scala受函数式编程影响,支持模式匹配和高阶函数,而Go仅支持部分函数式编程概念。生态系统:Go生态系统庞大,而Scala相对较小。
 Python中类型提示的最佳实践Apr 23, 2023 am 09:28 AM
Python中类型提示的最佳实践Apr 23, 2023 am 09:28 AM使用动态语言一时爽,代码重构火葬场。相信你一定听过这句话,和单元测试一样,虽然写代码的时候花费你少量的时间,但是从长远来看,这是非常值得的。本文分享如何更好的理解和使用Python的类型提示。1、类型提示仅在语法层面有效类型提示(自PEP3107开始引入)用于向变量、参数、函数参数以及它们的返回值、类属性和方法添加类型。Python的变量类型是动态的,可以在运行时修改,为代码添加类型提示,仅在语法层面支持,对代码的运行没有任何影响,Python解释器在运行代码的时候会忽略类型提示。因此类型提
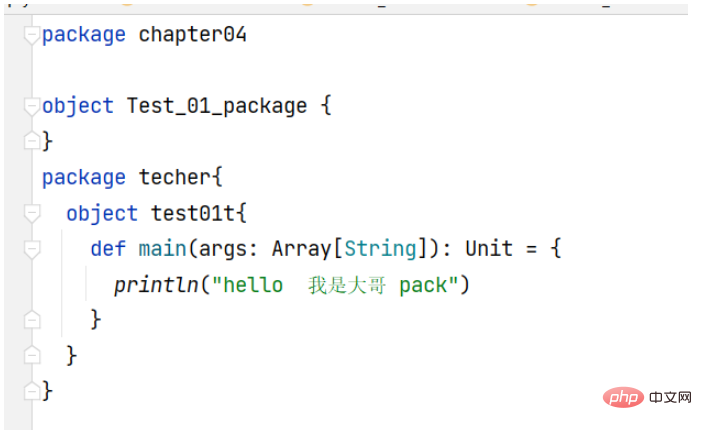 Java和Scala如何实现面向对象编程May 07, 2023 pm 01:46 PM
Java和Scala如何实现面向对象编程May 07, 2023 pm 01:46 PMScala包:基础语法:package包名.类名Scala包的三大作用:区分相同名字的类当类很多时,可以很好的管理类控制访问范围包名的命名规范:一般是小写字母+小圆点com.公司名.项目名.业务模块名写包的好处:在maven中可以将自己写的包通过maven导入到项目中在Scala中独有的包的写法和文件夹不对应可以独立存在下图是我在类下边建的包,和正常的包一样使用包是可以嵌套的内层调用外层不需要导包atguigu包在techer下外层调用内层对象需要导包如下代码:packagechapter04o
 主要的自媒体平台有哪些?自媒体平台的类型有哪些呢?Mar 21, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
主要的自媒体平台有哪些?自媒体平台的类型有哪些呢?Mar 21, 2024 pm 06:36 PM随着互联网的快速发展,自媒体已经成为了信息传播的重要渠道。自媒体平台为个人和企业提供了一个展示自己、传播信息的舞台。目前,市场上主要的自媒体平台有微信公众号、今日头条、一点资讯、企鹅媒体平台等。这些平台各有特色,为广大自媒体从业者提供了丰富的创作空间。接下来,我们将对这些平台进行详细介绍,并探讨自媒体平台的类型。一、主要的自媒体平台有哪些?微信公众号是腾讯推出的自媒体平台,为个人和企业用户提供信息发布和传播服务。它分为服务号和订阅号两种类型,服务号主要为企业提供服务,而订阅号则侧重于资讯传播。由
 C++ 函数的类型和特性Apr 11, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
C++ 函数的类型和特性Apr 11, 2024 pm 03:30 PMC++函数有以下类型:简单函数、const函数、静态函数、虚函数;特性包括:inline函数、默认参数、引用返回、重载函数。例如,calculateArea函数使用π计算给定半径圆的面积,并将其作为输出返回。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft







