Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >ECMAScript primitive and quoted values - JavaScript ING
ECMAScript primitive and quoted values - JavaScript ING
- 不言Original
- 2018-03-30 12:44:351993browse
This article mainly shares with you some knowledge about ECMAScript original values and reference values. Friends in need can refer to it
1. The concepts of original values and reference values
In ECMAScript, variables can have two types of values, namely original value and reference value.
1.1 Original value
(1) Original value refers to the value of original type, also called basic type, such as Number, Stirng, Boolean, Null, Underfined.
(2) Simple data segments stored in the stack , that is, their values are stored directly in the locations accessed by variables.
(3) NoteIn many languages, strings are regarded as reference types rather than primitive types because the length of the string is variable. ECMAScript breaks this tradition. 1.2 Reference value(1) Reference value refers to the value ofreference type, such as Object, Function, Array, Date, RegExp.
(2) Objects stored in theheap , that is to say, the value stored in the variable is a pointer (point), pointing to the storage The memory location of the object.
2. Stack and Heap2.1 Primitive values are stored in the stackWhen assigning a value to a variable, the ECMAScript interpreter must determine whether the value is a primitive type or a reference type . To do this, the interpreter tries to determine whether the value is one of ECMAScript'sprimitive types, namely Undefined, Null, Boolean, Number, and String. Since these primitive types occupy a fixed space , they can be stored in a smaller memory area - the stack. This storage makes it easy to quickly look up the value of the variable.
2.2 Reference values are stored in the heapIf a value is ofreference type, then its storage space will be allocated from the heap. Since the size of the reference value will change , it cannot be placed on the stack, otherwise it will reduce the speed of variable search. Instead, the value placed in the variable's stack space is the address where the object is stored in the heap. The size of the address is fixed, so storing it on the stack does not have any negative impact on variable performance.
2.3 Illustration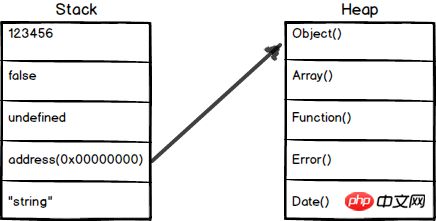
Assigned in copy way, the value is immutable.
4.2 The reference value is assigned in thecopy way of the reference, and the value is variable.
4.3 Example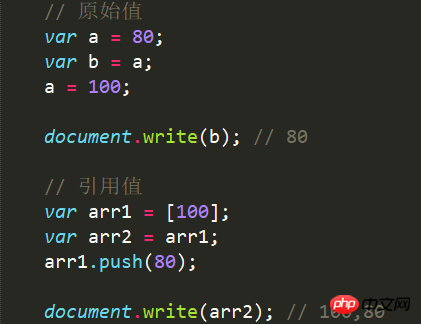
Copy and assign it to a new variable. This value is copy. It is independent of the original value. Changing one value will not affect the other values.
(2) Reference value assignment → When a reference type, such as an object, uses = to assign it to another variable, it is actually theaddress reference of its object that is assigned to the new one. Variables, both variables point to the same address reference, they have the same address. So if you change one of the variables (the object the address reference points to), the other variable (the address reference points to the same object) will also change.
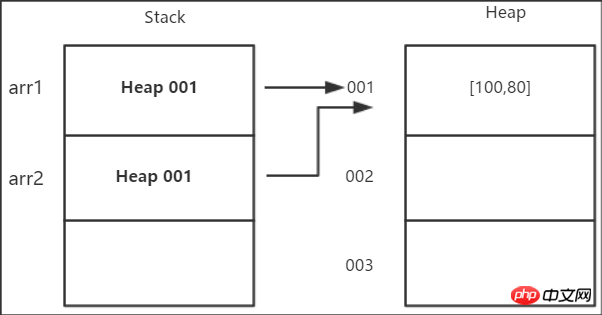
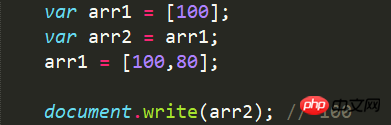
values
5.2 The comparison of reference values is the comparison ofreferences
5.3 Example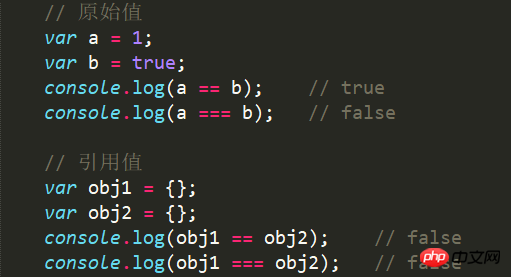
Implicit conversion of data types is automatically performed before value comparison)
- == → Only compare values
- === → Not only compare values, but also compare data types
different values stored in the heap memory Object, so the values (address references) of obj1 and obj2 are different.
read more1. The concept of original value and reference value
In ECMAScript, variables can have two types of values, namely original value and reference value.
1.1 Original value
(1) Original value refers to the value of original type, also called basic type , such as Number, Stirng, Boolean, Null, Underfined.
(2) Simple data segments stored in the stack , that is, their values are stored directly in the locations accessed by variables.
(3) NoteIn many languages, strings are regarded as reference types rather than primitive types because the length of the string is variable. ECMAScript breaks this tradition. 1.2 Reference value(1) Reference value refers to the value ofreference type, such as Object, Function, Array, Date, RegExp.
(2) Objects stored in theheap , that is to say, the value stored in the variable is a pointer (point), pointing to the storage The memory location of the object.
2. Stack and Heap2.1 Primitive values are stored in the stackWhen assigning a value to a variable, the ECMAScript interpreter must determine whether the value is a primitive type or a reference type . To do this, the interpreter tries to determine whether the value is one of ECMAScript'sprimitive types, namely Undefined, Null, Boolean, Number, and String. Since these primitive types occupy a fixed space , they can be stored in a smaller memory area - the stack. This storage makes it easy to quickly look up the value of the variable.
2.2 Reference values are stored in the heapIf a value is ofreference type, then its storage space will be allocated from the heap. Since the size of the reference value will change , it cannot be placed on the stack, otherwise it will reduce the speed of variable search. Instead, the value placed in the variable's stack space is the address where the object is stored in the heap. The size of the address is fixed, so storing it on the stack does not have any negative impact on variable performance.
2.3 Illustration
Assigned in copy way, the value is immutable.
4.2 The reference value is assigned in thecopy way of the reference, and the value is variable.
4.3 Example
Copy and assign it to a new variable. This value is copy. It is independent of the original value. Changing one value will not affect the other values.
(2) Reference value assignment → When a reference type, such as an object, uses = to assign it to another variable, it is actually theaddress reference of its object that is assigned to the new one. Variables, both variables point to the same address reference, they have the same address. So if you change one of the variables (the object the address reference points to), the other variable (the address reference points to the same object) will also change.


values
5.2 The comparison of reference values is the comparison ofreferences
5.3 Example
Implicit conversion of data types is automatically performed before value comparison)
- == → Only compare values
- === → Not only compare values, but also compare data types
different values stored in the heap memory Object, so the values (address references) of obj1 and obj2 are different.
Related recommendations:Detailed explanation of destructuring assignment of ECMAScript6 variables
The difference between JavaScript and ECMAScript
ECMAScript6 Getting Started with Detailed Examples of Class Objects
The above is the detailed content of ECMAScript primitive and quoted values - JavaScript ING. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

